Amino Acids
Amino Acids for Muscle Growth
For muscle growth, certain amino acids stand out due to their roles in protein synthesis, recovery, and overall muscle health. The most effective amino acids for muscle growth include both essential amino acids (EAAs) that the body cannot produce on its own and must obtain from diet or supplements, and non-essential amino acids that are crucial for specific functions related to muscle development. Here are the amino acids most commonly associated with enhancing muscle growth:
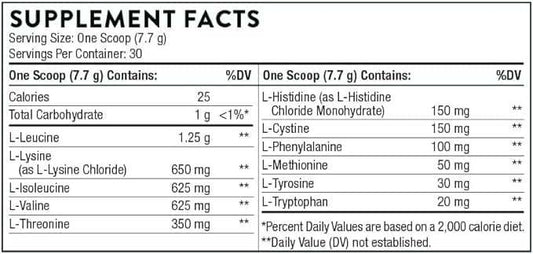
1. Leucine
- Role: Leucine is a critical player in initiating protein synthesis. It's the most potent of the BCAAs in its ability to stimulate the muscle-building process at the cellular level.
- Source: Found in high amounts in BCAA supplements, whey protein, and foods like dairy, meat, and soy products.
2. Isoleucine
- Role: Isoleucine plays a part in muscle metabolism and is important for immune function, hemoglobin production, and energy regulation.
- Source: Available in BCAA supplements and protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, cheese, lentils, nuts, and seeds.
3. Valine
- Role: Valine helps stimulate muscle growth and regeneration and is involved in energy production.
- Source: Included in BCAA supplements and found in foods like dairy, grains, mushrooms, soy products, peanuts, and meat.
4. Arginine
- Role: Arginine is known for its ability to increase nitric oxide levels in the body, which can improve blood flow to muscle tissues, enhancing nutrient delivery and muscle pumps.
- Source: Available in supplement form and naturally found in turkey, pork, chicken, pumpkin seeds, and soybeans.
5. Glutamine
- Role: Glutamine supports immune system function, gut health, and muscle recovery. It can help reduce muscle breakdown and support overall muscle growth.
- Source: Found in beef, eggs, milk, tofu, and various nuts and beans. Also available as a supplement.
6. Methionine
- Role: Methionine plays a role in metabolism and detoxification. It's also important for tissue growth and the absorption of zinc and selenium, minerals vital for muscle health.
- Source: Fish, meat, dairy products, and some nuts and grains.
7. Lysine
- Role: Lysine is important for protein synthesis, hormone and enzyme production, and the absorption of calcium.
- Source: Meat, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
Supplementation for Muscle Growth
While a balanced diet can provide all these essential amino acids, athletes and individuals engaging in heavy resistance training may find it challenging to meet their amino acid requirements through food alone. In such cases, supplementing with a high-quality BCAA or EAA blend can be beneficial. Supplements can offer a convenient and concentrated source of these amino acids, ensuring optimal muscle recovery and growth.
FAQS
What is the best form of amino acids to take?
The best form of amino acids to take can vary based on individual goals, preferences, and dietary restrictions. Amino acids are available in various forms, including powders, capsules, tablets, and ready-to-drink beverages. Here’s a quick overview:
- Powders: Offer flexibility in dosing and are easily absorbed by the body. Ideal for those looking to customize their intake or combine with other supplements.
- Capsules/Tablets: Provide convenience and are best for those who prefer not to taste the supplement or are always on the go.
- Ready-to-Drink (RTD): The ultimate in convenience, though often more expensive per serving compared to powders and capsules.
Ultimately, the best form is one that you can consistently incorporate into your daily routine, aligning with your dietary needs and lifestyle.
What is the most powerful amino acid?
While it's difficult to pinpoint a single amino acid as the most powerful due to their varied and essential roles in the body, Leucine is often highlighted for its critical role in muscle protein synthesis. Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and is particularly effective at activating the body's pathways responsible for muscle building. However, it's important to note that all amino acids play crucial roles in health and bodily functions, making it essential to maintain a balanced intake.
What are the top 10 essential amino acids?
Humans require nine essential amino acids, not ten, which must be obtained through diet as the body cannot synthesize them. These include:
- Histidine: Important for immune response, digestion, sexual function, and neurotransmitter regulation.
- Isoleucine: Involved in muscle metabolism, immune function, hemoglobin production, and energy regulation.
- Leucine: Crucial for protein synthesis and muscle repair.
- Lysine: Important for protein synthesis, hormone and enzyme production, and calcium absorption.
- Methionine: Vital for metabolism and detoxification; it's a precursor to other amino acids like cysteine and taurine.
- Phenylalanine: Precursor to neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
- Threonine: Important for protein balance, immune function, and gut health.
- Tryptophan: Precursor to serotonin, essential for mood, sleep, and appetite regulation.
- Valine: Stimulates muscle growth and regeneration; involved in energy production.
Which is better BCAA or EAA?
Choosing between Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) and Essential Amino Acids (EAAs) depends on your specific fitness goals, dietary intake, and nutritional needs:
-
BCAAs, consisting of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are particularly beneficial for muscle protein synthesis and recovery. They're often recommended for athletes and those looking to improve exercise performance and reduce muscle soreness.
-
EAAs include all nine essential amino acids, covering the BCAAs plus the other six essential amino acids. They provide a comprehensive approach to support not just muscle recovery and growth but overall bodily functions.
Amino Acids
Amino Acids for Muscle Growth
For muscle growth, certain amino acids stand out due to their roles in protein synthesis, recovery, and overall muscle health. The most effective amino acids for muscle growth include both essential amino acids (EAAs) that the body cannot produce on its own and must obtain from diet or supplements, and non-essential amino acids that are crucial for specific functions related to muscle development. Here are the amino acids most commonly associated with enhancing muscle growth:
1. Leucine
- Role: Leucine is a critical player in initiating protein synthesis. It's the most potent of the BCAAs in its ability to stimulate the muscle-building process at the cellular level.
- Source: Found in high amounts in BCAA supplements, whey protein, and foods like dairy, meat, and soy products.
2. Isoleucine
- Role: Isoleucine plays a part in muscle metabolism and is important for immune function, hemoglobin production, and energy regulation.
- Source: Available in BCAA supplements and protein-rich foods such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, cheese, lentils, nuts, and seeds.
3. Valine
- Role: Valine helps stimulate muscle growth and regeneration and is involved in energy production.
- Source: Included in BCAA supplements and found in foods like dairy, grains, mushrooms, soy products, peanuts, and meat.
4. Arginine
- Role: Arginine is known for its ability to increase nitric oxide levels in the body, which can improve blood flow to muscle tissues, enhancing nutrient delivery and muscle pumps.
- Source: Available in supplement form and naturally found in turkey, pork, chicken, pumpkin seeds, and soybeans.
5. Glutamine
- Role: Glutamine supports immune system function, gut health, and muscle recovery. It can help reduce muscle breakdown and support overall muscle growth.
- Source: Found in beef, eggs, milk, tofu, and various nuts and beans. Also available as a supplement.
6. Methionine
- Role: Methionine plays a role in metabolism and detoxification. It's also important for tissue growth and the absorption of zinc and selenium, minerals vital for muscle health.
- Source: Fish, meat, dairy products, and some nuts and grains.
7. Lysine
- Role: Lysine is important for protein synthesis, hormone and enzyme production, and the absorption of calcium.
- Source: Meat, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
Supplementation for Muscle Growth
While a balanced diet can provide all these essential amino acids, athletes and individuals engaging in heavy resistance training may find it challenging to meet their amino acid requirements through food alone. In such cases, supplementing with a high-quality BCAA or EAA blend can be beneficial. Supplements can offer a convenient and concentrated source of these amino acids, ensuring optimal muscle recovery and growth.
FAQS
What is the best form of amino acids to take?
The best form of amino acids to take can vary based on individual goals, preferences, and dietary restrictions. Amino acids are available in various forms, including powders, capsules, tablets, and ready-to-drink beverages. Here’s a quick overview:
- Powders: Offer flexibility in dosing and are easily absorbed by the body. Ideal for those looking to customize their intake or combine with other supplements.
- Capsules/Tablets: Provide convenience and are best for those who prefer not to taste the supplement or are always on the go.
- Ready-to-Drink (RTD): The ultimate in convenience, though often more expensive per serving compared to powders and capsules.
Ultimately, the best form is one that you can consistently incorporate into your daily routine, aligning with your dietary needs and lifestyle.
What is the most powerful amino acid?
While it's difficult to pinpoint a single amino acid as the most powerful due to their varied and essential roles in the body, Leucine is often highlighted for its critical role in muscle protein synthesis. Leucine is one of the three branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) and is particularly effective at activating the body's pathways responsible for muscle building. However, it's important to note that all amino acids play crucial roles in health and bodily functions, making it essential to maintain a balanced intake.
What are the top 10 essential amino acids?
Humans require nine essential amino acids, not ten, which must be obtained through diet as the body cannot synthesize them. These include:
- Histidine: Important for immune response, digestion, sexual function, and neurotransmitter regulation.
- Isoleucine: Involved in muscle metabolism, immune function, hemoglobin production, and energy regulation.
- Leucine: Crucial for protein synthesis and muscle repair.
- Lysine: Important for protein synthesis, hormone and enzyme production, and calcium absorption.
- Methionine: Vital for metabolism and detoxification; it's a precursor to other amino acids like cysteine and taurine.
- Phenylalanine: Precursor to neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
- Threonine: Important for protein balance, immune function, and gut health.
- Tryptophan: Precursor to serotonin, essential for mood, sleep, and appetite regulation.
- Valine: Stimulates muscle growth and regeneration; involved in energy production.
Which is better BCAA or EAA?
Choosing between Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) and Essential Amino Acids (EAAs) depends on your specific fitness goals, dietary intake, and nutritional needs:
-
BCAAs, consisting of leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are particularly beneficial for muscle protein synthesis and recovery. They're often recommended for athletes and those looking to improve exercise performance and reduce muscle soreness.
-
EAAs include all nine essential amino acids, covering the BCAAs plus the other six essential amino acids. They provide a comprehensive approach to support not just muscle recovery and growth but overall bodily functions.
-
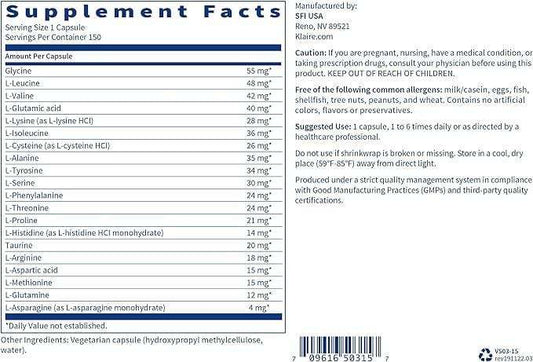
Vendor:Now FoodsSold outVendor:Metabolic MaintenanceVendor:Kirkman LaboratoriesVendor:Doctor's BestVendor:Klaire LabsSold out
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I buy Amino Acids in the UK?
How should I use/ take Amino Acids ?
Can I buy Amino Acids from Superdrug or Amazon?
What is the shelf life of Amino Acids?
Can I buy Amino Acids from Boots?
Disclaimer
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.