Esophageal Cancer Diagnosis

The following examinations and techniques are typically used to determine whether a patient has esophageal cancer:
Upright endoscopy
Your doctor will place an endoscope—a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera attached—down your throat and into your esophagus during an upper endoscopy. Then, your doctor can search for abnormalities.
Your doctor may take a tissue sample (biopsy) if abnormal areas are discovered during upper endoscopy for testing. Under a microscope, the tissue is typically examined to determine if esophageal cancer is present.
- imaging tests
If cancer has spread past the esophagus, imaging tests may be used to help identify the location. A treatment plan may be aided by these tests. Computed tomography (CT) scans, positron emission tomography (PET) scans, and MRIs are imaging procedures used to detect esophageal cancer.
An endoscope is inserted into your esophagus and down your throat during endoscopic ultrasound. The endoscope's tiny ultrasound probe is used to take pictures of your esophagus and surrounding structures. If cancer has spread past the esophagus, endoscopic ultrasound may be used to help identify this.
During a barium swallow, you will be asked to drink a liquid that contains barium. Your esophagus' interior is coated with barium, which makes it easier to see on an x-ray. Your upper gastrointestinal (GI) tract is then imaged using an x-ray. Barium swallows may not be as accurate as other tests, so they are less frequently used to diagnose esophageal cancer.
The extent (stage) of the cancer will be determined by your doctor after esophageal cancer has been diagnosed. Staging tests may be used to help determine the stage of the cancer. Imaging tests and endoscopic ultrasound may be among these examinations. It is crucial to know the stage of esophageal cancer because it influences treatment choices. Using a system that describes how far the cancer has spread throughout the body, esophageal cancer is staged. The TNM staging system is the most popular staging method for esophageal cancer:
T denotes the tumor's size and whether it has spread to adjacent tissues.
N is the quantity of lymph nodes that are cancerous.
M stands for metastasis, which is the term for when cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
Esophageal cancer is a condition in which the tissues of the esophagus develop malignant (cancer) cells.
The muscular, hollow tube that carries food and liquids from the throat to the stomach is called the esophagus.
Multiple layers of tissue make up the esophageal wall. Any of these layers may develop esophageal cancer.
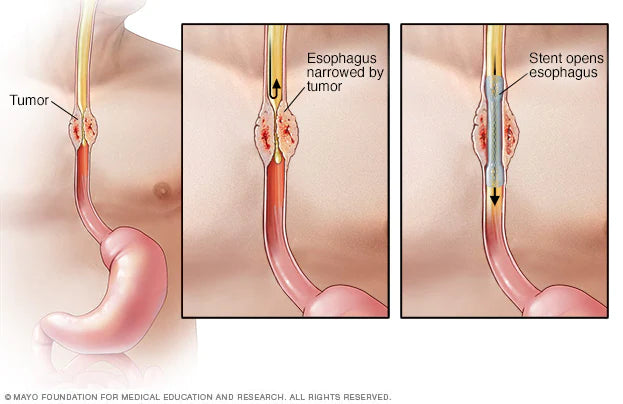
-Swallowing problems (dysphagia)
-Loss of weight
-Burning, pressing, or chest pain
Esophageal cancer is frequently discovered as a result of symptoms a person experiences.










Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.