What is the difference between Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack?


Have you ever been confused between the terms Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack? Well, these terms are frequently used interchangeably. Although they are not the same.

According to a study conducted by the National Institute of Health Research Health Informatics Collaborative by Imperial College Health NHS Trust and Imperial College London, using data from 13,444 patients during 2010-2017, the findings showed that patients with heart attack leading to cardiac arrest were at high risk of developing more complications. People with cardiac arrest were at higher risk and 36 per cent more likely to die within three years of discharge from their respective hospitals.
A heart attack occurs when blood flow to the heart is interrupted. However, when the heart malfunctions and suddenly stops beating, this is referred to as sudden cardiac arrest. A heart attack is considered a "circulation" problem, but sudden cardiac arrest is considered a serious overall health problem.
A heart attack occurs when an artery becomes clogged, preventing oxygen-rich blood from reaching a portion of the heart. If the blocked artery is not rapidly recovered, the portion of the heart that is regularly supplied by that artery begins to perish. The longer a person remains untreated, the greater the risk of serious damage.
Symptoms can be severe and sudden and sometimes can appear gradually. It's also worth noting that you can have minimal symptoms or perhaps none and still have a heart attack. Unlike in cases of sudden cardiac arrest, the heart normally continues to beat during a heart attack and symptoms vary from women to men.
Heart attacks frequently begin with severe chest pain, but they can also be followed by mild pain that comes and goes over several hours. Symptoms of a heart attack might vary, and if you've already had one, your symptoms may be different if you encounter it another time. Chest discomfort is the most prevalent symptom of a heart attack in both sexes.
Other symptoms, including shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and back or jaw pain, are more common in women than in males.
Read more: Signs and symptoms of heart disease.
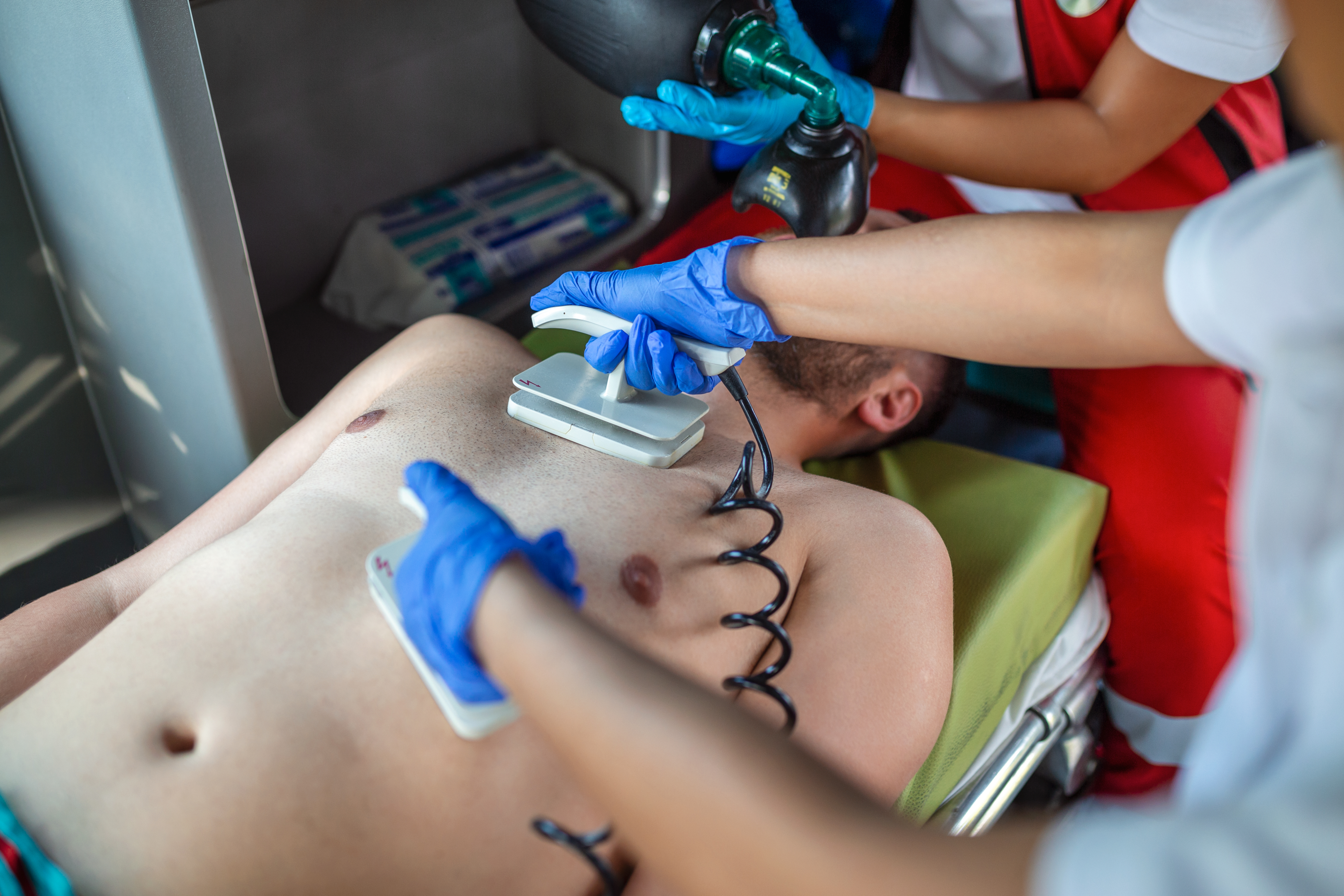
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs unexpectedly, mostly when an electrical problem in the heart generates an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). During this condition, the heart cannot pump blood to the brain, lungs, or other organs if its pumping activity is disturbed. When this occurs, a person will lose consciousness and have a low or no pulse at all. In case of negligence, death happens within minutes.
Causes: Coronary heart disease, which deprives your heart of oxygen, is the most common cause of heart attacks.
Symptoms: Cardiac arrests frequently occur in patients who were unaware they had heart disease. During cardiac arrest, the individual can collapse and lose consciousness. This may also be accompanied by difficulty breathing.
Read more: What is CPR?
When the heart muscle fails to pump as much blood as the body requires, this condition is referred to as heart failure. It is typically a long-term, chronic disorder but can strike unexpectedly.
The heart fails to pump normally in people with heart failure, prompting the hormone and neurological systems to adjust to the lack of blood. The body may boost blood pressure, causing the heart to beat quicker and the body to retain salt and water. Congestive heart failure occurs when this trapped fluid accumulates.
Heart attacks and cardiac arrests have quite diverse causes and risk factors. People who suffer a cardiac arrest may not have known they were in any danger from heart disease. Meanwhile, those who suffered a heart attack may have known that they were at risk.
A heart attack is diagnosed by a physical examination and an ECG, which measures the electrical activity of your heart.
Your doctor might order an echocardiography or a cardiac catheterization to assess the health and vitality of your heart. A blood sample is also commonly collected to look for symptoms of heart muscle injury.
A cardiac arrest means your heart has stopped. This condition is lethal if not treated immediately. If a doctor successfully recovers your heart and revives blood flow, diagnostic procedures will be performed to discover the reason for your cardiac arrest.
An echocardiography, blood tests, and a chest X-ray may be performed to look for further indicators of heart disease.

Treatment choices for heart attacks and cardiac arrests are determined by a variety of circumstances, including:
Based on the severity of your attack, your doctor may recommend several different treatments, ranging from medication and surgery to rehabilitation. Your treatment will be based on reducing pain and preventing further attacks.
CPR or a defibrillator are almost always used to restart the heart after a cardiac arrest. After a cardiac arrest, treatments are similar to those of a heart attack. These include medication, lifestyle changes and sometimes surgery.
Although heart attacks can be fatal, the majority of individuals survive. If you get therapy as soon as possible, you may be able to limit the damage to your heart muscle.
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices boosts your chances of a successful recovery. It is critical to collaborate with a healthcare team at the hospital to develop a recovery strategy that is tailored to your specific needs.
Alongside medical care, an individual should also make an effort to ensure they are cutting down or completely stopping smoking and losing weight if they are overweight. Eating a balanced diet and getting adequate exercise is also important to regain your health.
Treatments and drugs can result in remarkable improvements after a cardiac arrest, but the outlook for an individual is partly reliant on the severity of the incident and their unique condition.
Read more: Eating to beat heart disease.
While people often confuse heart attack and cardiac arrest as the same thing, they are two different conditions that can have severe outcomes.
If you feel you or someone you know is suffering from either illness, seek medical attention immediately.
A doctor and their staff can promptly diagnose your symptoms and start treating you but this treatment may be limited by how quickly you can reach a doctor or healthcare professional.
If you are concerned with your heart health, Welzo offers a Heart Disease Risk Blood Test and an overall Health and Lifestyle Blood Test.










Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.