Is creatine a steroid?


Since the early 1900s, millions of doses of creatine have now been consumed. Over a thousand studies have been done on creatine supplementation. Despite being the supplement that has received the most study in the market for sports nutrition, some people have reservations about creatine and falsely believe it to be an anabolic steroid.

The notion that creatine is a steroid is a myth. While creatine is an ergogenic supplement, steroids are anabolic drugs. Anabolic steroids and creatine have different mechanisms of action, despite having similar performance effects.
Anabolic steroids are a synthetic form of the androgenic hormone testosterone, which both males and females naturally generate.
Amino acids such as Glycine, arginine and methionine work together in the body to naturally generate creatine, an endogenous amino group derivative. Only trace amounts of creatine are present in the brain, testes, and other organs. However, they make up 95% of the storage in skeletal muscles and lean muscle mass.
Our bodies create the chemical creatine on their own. However, the body only has 80–130 g of creatine, which is less than half of what we require, and uses two to four grams daily while engaging in normal exercise.
High-intensity training necessitates a higher creatine intake causing a need for creatine supplements.
The liver and kidneys process creatine, which is crucial for carrying and energy storage in our muscle cells.
Read more: Is taking creatine healthy?
Creatine supplements improve performance and muscle mass, which encourages larger training responses. As the muscles contract during exercise, you break a phosphate molecule off of ATP, producing ADP instead.
Creatine supplements raise the level of phosphocreatine in muscle cells, which contributes to creatine phosphate molecules with ADP to create ATP. The PCr system is the fastest and most productive energy-replenishing technology available. Creatine users get quick energy synthesis during intensive anaerobic exercise, increasing muscle power and workout volume, ultimately leading to muscle growth.

For power/strength athletes that sprint sporadically and want to recover more quickly during competitions, creatine supplementation is advised as an ergogenic aid to help improve training adaptation.
In order to maintain appropriate whole-body Creatine reserves, athletes who are undergoing hard training might need to consume 5–10g of Creatine supplements.
Creatine supplements can enhance general health and sports performance, helping people gain weight and build lean muscle mass.
Creatine supplementation is helpful for both short and long-term muscle growth and body weight. Weightlifters were the subjects of a 12-week study that found creatine supplements enhance muscle fibre growth 2-3 times more than training alone.
If you want to gain weight quickly, creatine is a suitable supplement. According to studies, a week of elevated (20 grams/day) creatine supplementation can result in a person gaining 2 to 6 pounds.
The main cause of this is more water inside the muscles, but as time passes, the body weight keeps increasing, and the size of the real muscles will too. To be explicit, weight gain is made up entirely of muscles rather than fat, which is a good adaptation for most athletes.
During challenging workouts, creatine can increase power, strength, and performance. According to one study, including creatine in your exercise regimen can improve your abilities in the following ways:
Strengthening by 8%,
Improve your performance in weightlifting by 14%,
Max one-rep bench press by approximately to 43%
These outcomes result from contrasting training using creatine with training without. Additionally, studies suggest that high-performing athletes can improve their bench-press efficiency by 6% and their cycling sprint performance by 15% only after 28 days of supplementation.
This shows that dietary creatine supplement can increase the body's ability to produce ATP, which has amazing effects.

Increased workload – Using creatine supplements enables a user to perform more work or volume in a single training session, which is crucial for long-term muscle mass development. Simply put, creatine will give you the energy to perform more repetitions throughout your workout, leading to weight gain and more muscle mass.
An increase in anabolic hormones has been observed after consuming creatine, leading to the development of muscle fibres.
Cell hydration is improved because whenever you take creatine supplements, the water content of your muscle cells increases, giving you bigger muscles.
Increased creatine levels slow down protein breakdown, resulting in larger muscles.
New muscles and more muscle growth can develop since myostatin levels are lower.
Creatine supplementation enhances cell signalling, which aids in post-workout muscle recovery and the growth of new, larger muscles.
Your blood's creatinine levels can rise as a result of creatine. People erroneously assume that creatine causes kidney and liver disease or damages kidney function and the liver since it is frequently evaluated to identify renal or liver issues. Fortunately, numerous studies have shown that using creatine for a long time has no negative consequences.
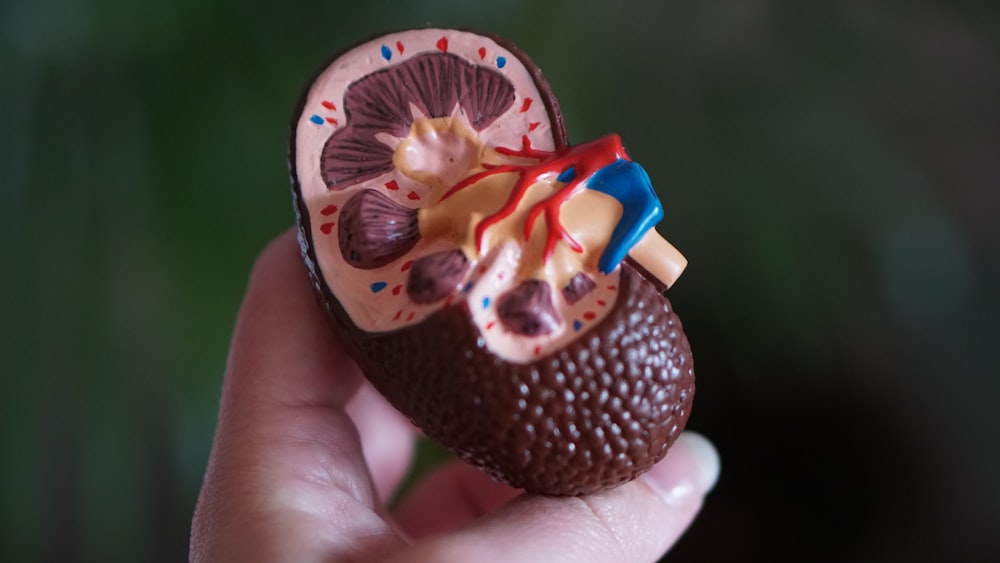
One of the research even had a four-year duration and came to the same conclusion. However, if you have a history of renal disease, you need to be cautious with creatine or sports nutrition in general.
Even if you are in perfect health, you should never exceed the recommended amount of creatine supplementation.
Read more: Can creatine cause hair loss?
Creatine is misunderstood as a steroid. It's an important amino acid that helps people gain weight, more power, strength, and bigger muscles, among other health and fitness advantages. You must be cautious not to use it excessively, just like you would with any other vitamin.
If you're looking to optimise your sports performance, browse our range of products and tests on the Sports Performance Hub.










Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.