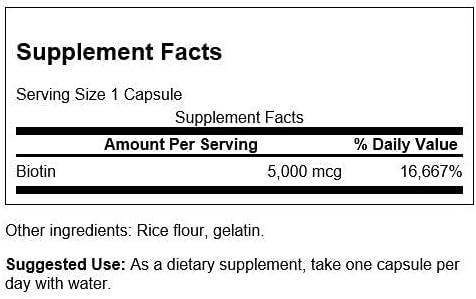
Men's hair loss, also known as male pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition affecting a significant number of men worldwide. It typically begins with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown and can progress to more extensive hair loss over time. This condition is primarily influenced by genetic factors and hormonal changes, particularly the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT affects hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hair strands, eventually leading to the cessation of hair growth in affected areas.
Hair loss can start as early as a man's late teens or early twenties, but it is more commonly observed in middle age. The extent and rate of hair loss can vary widely among individuals, with some experiencing gradual thinning and others noticing more rapid hair loss. While male pattern baldness is the most prevalent form, other factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and certain medications can also contribute to hair loss.
Although hair loss is a natural part of aging for many men, it can have psychological and emotional impacts, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Various treatments are available to manage hair loss, including topical solutions like minoxidil, oral medications such as finasteride, and surgical options like hair transplants. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and stress management, may help slow the progression of hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to individual needs.
Men’s Hair Loss
Men's hair loss, also known as male pattern baldness or androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition affecting a significant number of men worldwide. It typically begins with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown and can progress to more extensive hair loss over time. This condition is primarily influenced by genetic factors and hormonal changes, particularly the presence of dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT affects hair follicles, causing them to shrink and produce thinner, shorter hair strands, eventually leading to the cessation of hair growth in affected areas.
Hair loss can start as early as a man's late teens or early twenties, but it is more commonly observed in middle age. The extent and rate of hair loss can vary widely among individuals, with some experiencing gradual thinning and others noticing more rapid hair loss. While male pattern baldness is the most prevalent form, other factors such as stress, nutritional deficiencies, medical conditions, and certain medications can also contribute to hair loss.
Although hair loss is a natural part of aging for many men, it can have psychological and emotional impacts, affecting self-esteem and confidence. Various treatments are available to manage hair loss, including topical solutions like minoxidil, oral medications such as finasteride, and surgical options like hair transplants. Additionally, lifestyle changes, such as a balanced diet and stress management, may help slow the progression of hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalized advice and treatment options tailored to individual needs.
-
Vendor:Uppercut Deluxe
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I buy Men’s Hair Loss in the UK?
Disclaimer
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.