How long will you test positive for COVID after recovery?
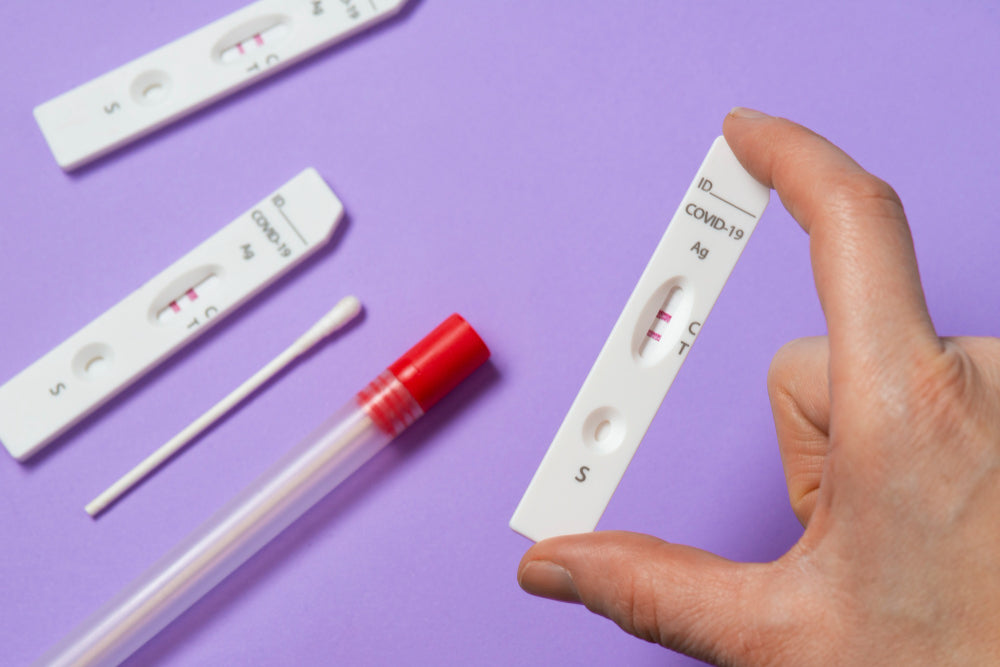


Many patients have tested positive for COVID well before the onset of symptoms. After a usual course of 1-2 weeks, the symptoms begin to resolve, and a negative antigen test is expected after 7-10 days of the onset of symptoms. Most people remain infectious for around 10 days.
However, a positive test is a product of many other factors. Let's discuss how long a person can remain positive and when you can start normal life activities.
The interpretation of test results depends upon the type of test used. Two types of tests are available for COVID.
The nucleic acid amplification (PCR) based tests detect the viral genome. These tests can give positive results for months. It is because even if the virus has died, the viral RNA can still be there in your body, and you can get a false positive test without any disease for an extended period. These tests are also time-consuming, but they provide highly accurate results.
Rapid antigen/ antibody tests detect the viral antigens or antibodies in the sample and are positive for most people for around 10 days. The question mostly deals with rapid antigen tests for the most common purposes. Rapid tests are less sensitive (65-75% depending upon the source), and they need to be combined with clinical signs of the disease.

The rapid antigen tests form the mainstay of the diagnosis and are the only possible option for mass testing.
At Welzo.com, we have both types of tests that can help you diagnose COVID-19. Our PCR Fit to Fly COVID Test for Travel is accepted by all major airlines and is approved for use in USA and EU. The results are also provided online. Click here to avail.
If, however, you are looking for a quick home test, our COVID-19 Antibody Blood Test is best for you. It just needs the blood from a single finger prick and gives accurate and fast results quickly. Click here to get your test kit.
A positive COVID test means isolating yourself to avoid spreading the infection to others. A positive test for COVID is combined with clinical signs of disease for advisory purposes. For example,
If you don't develop symptoms, the World Health Organisation (WHO) recommends that you can end your isolation after 5 days. But, if you develop mild symptoms, you need to isolate as long as the symptoms start to regress and you don't develop a fever in the last 24 hours.
In the case of a mild to severe disease, you need to isolate yourself for at least 10 days from the start of symptoms.
But, the decision to end the isolation and resume routine life activities can sometimes be complicated by various issues, e.g., you may continue to test positive for too long. Some tests can continue to give positive results for weeks and months with variable degrees of symptoms. We will discuss the advisory guidelines in the below section. Let's see how long a positive test is expected.
The time taken for the negative test after contracting the virus depends upon several factors, e.g., the test used, the disease's severity, the degree of viral exposure and the immunity of the individual patients.
PCR tests can detect and amplify a very small viral genome fragment and give specific and sensitive tests for days. Such fragments can stay in our body for months even if the virus has been cleared and the disease is over. So, after weeks and months of disease, a positive PCR test is nothing to worry about, and you can exit your isolation.

The good news is that a positive COVID PCR test doesn't mean you are still contagious and spreading the disease to people around you.
On the other hand, the lateral flow tests which detect the viral proteins are less sensitive and are less likely to be positive after 1-2 weeks of the end of clinical signs. They usually reflect that you are contagious.
For advisory purposes, the comparison of both test types can be useful. In short, if you have a positive PCR test and a negative rapid antigen test, you are not infectious, and the PCR is just detecting the leftover viral remnants that don't pose any risk to the others.
The opposite results (negative PCR and positive antigen test) could be attributed to the poor sensitivity of the antigen test, or they could mean that you are still infected and need to isolate yourself for more days, as the local health authorities recommended.
However, for routine uses, most health agencies regard antigen tests enough to limit viral exposure.
If you continue to get a positive antigen test after weeks, it is still nothing to worry about, as you are not likely to remain contagious for very long from a single infection. You can start your normal activities without any fear of disease spreading.
Read more: Can you still test positive for COVID after 14 days?
Although the immunity provided by natural infection is strong enough to thwart a re-infection within a few weeks or months, some people can develop a long form of COVID or a rebound COVID which can result in a continuation of symptoms for months ahead.

We will explain these conditions in the later lines. In short, a positive antigen test is more important than a positive PCR test because detecting viral protein could mean that the virus is still replicating its core proteins and forming new viral particles.
Most people develop an acute form of the disease and recover quickly. However, it has been found that around 10-35% of patients develop a long-term disease after recovery from the primary infection.
The risk of this condition is also different for different viral variants. For example, a recent study published in the Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy in 2022 noted that the risk of the post-COVID condition with the omicron variant is less than the other variants.
What are the common symptoms of post-COVID conditions?
The symptoms of this so-called post-COVID condition or 'long COVID' range from mild to moderate. These can be either the continuation of symptoms from the previous disease or may develop after recovery from the initial disease. The condition can persist for months and has a markedly negative effect on the person's ability to carry out routine activities.
A variety of symptoms are noted, including
Fever
Anxiety and depression
Loss of taste or smell
Muscular aches
Difficulty in speaking
Chest pain
Persistent cough
Loss of concentration
Sleeping disturbances
Some degree of memory loss
Difficulty in breathing or breath shortness
Hair loss
Fatigue etc.
The condition often needs weeks of hospitalization.

How can you prevent the post-COVID condition?
To avoid the long COVID, continue to practice precautions against COVID. Get proper vaccination according to the recommended schedule and follow the hygiene protocols. The WHO has recommended the following precautions during the post-COVID condition;
Frequently wash your hands with hand wash
Continue to wear a properly fitting mask to your mouth and nose
Open the windows of the house for proper ventilation
Ensure to keep a minimum distance of 1 meter from the nearest person.
Can you have a positive test during the post-COVID condition?
You will not pass out the disease to the people around you, but you can get the virus. That's why you should continue to practice precautions. The antigen test is likely to be negative because the virus is not replicating anymore and has been cleared from the body long ago.
However, you can have a positive PCR test because some fragments of the viral genome can still exist. If you test positive for COVID-19 during this phase, you have probably contracted the rebound COVID.
It is a situation in which the symptoms of COVID reoccur after 2-8 days of the end of the disease and a negative test. You can also have a new positive test. Initially, the blame was placed on Paxlovid, the antiviral drug used during the initial phase of the infection. It was thought that this drug didn't allow the development of proper immunity.
However, later on, it was noted that the rebound is the natural part of the disease process in some people and is independent of the vaccination status or the use of Paxlovid. What should you do in case of a rebound, and if you are supposed to have a positive test?
How can you manage the rebound of COVID?
The rebound COVID can rarely be as serious as the original disease. However, you do need to practice isolation and other measures. The guidelines of the World Health Organisation are accepted throughout the world and include the following;
According to the recent guidelines of the WHO, people with a rebound COVID should go into isolation for additional 5 days. The isolation can be ended after 5 days if the symptoms improve and there is no fever for 24 hours.
According to the advisory, people should continue to wear a face mask for 10 days.
Will you test positive?
Concerning the test, you will be testing positive for the rebound COVID, both the antigen and PCR tests. It is because you have contracted the virus again after recovery, and it will complete a new life cycle before elimination from the body.
You can end isolation with a negative test result at any time. However, you can see that the COVID disease is not the same for everyone. So, the guidelines for ending the isolation will also be different and depend upon the disease severity and the immune status. The currently used standard of 10 days from the symptom onset has up to a 6.6% risk of causing the release of an infectious person, as noted by a report published in 2021.
The currently used guidelines are;
The isolation can be ended after 5 days of the onset of symptoms and if you have no fever in the last 24 hours. The loss of smell and taste can persist for days to weeks and shouldn't be a factor to consider while ending the isolation. Continue to wear a high-quality mask up to day 10.
In case you again notice the symptoms due to a rebound, the isolation should restart. However, if you can't wear the mask for any reason (e.g., for young babies and disabled people), extend your isolation period to 10 days. An isolation period of 10 days is also recommended if you live in a highly congested environment with a high risk of viral transmission.

Around a quarter of patients with this situation will be asymptomatic with a positive test. The same guidelines apply to the above category.
For such people, an isolation period of 10 days is recommended starting from the day of onset of symptoms. Some people with a severe infection require hospitalisation and remain infected for more than 10 days. In such cases, the isolation can be extended for up to 20 days and ended if there is no fever for 24 hours and symptoms have improved.
A positive antigen test should be conducted again after 48 hours to remove the risk of a false positive test. A healthcare professional can ask you to have a negative test before ending the isolation.
People with weak immunity will likely remain infectious for more than 20 days because their immune systems will not develop enough antibodies to clear the infection. The recommendation for such people is to end the isolation after 10 days and a negative test after consulting the local health authorities.
However, the authorities can ask for more days of isolation, depending on the situation. If the patient has a positive PCR test for more than 30 days, viral culturing or genome sequencing can be helpful. The degree of immunosuppression could differ for different people, and the doctor's recommendation should be valued.
Read more: The FFP2 mask provides very effective protection against coronavirus.
The novel coronavirus can be asymptomatic or cause a moderate or severe illness. The antigen tests remain positive for 10 days in most cases. However, the PCR tests can be positive for many months. Some people can get a 'rebound COVID' or 'long COVID' and may continue to get a positive test for days and weeks ahead.
Each situation requires a different approach to end the isolation and resume routine life. Immunosuppression can also complicate the matter. Therefore, stay in touch with infectious disease experts for any issue.

The information provided in this article is just for information and doesn't substitute professional medical advice. At Welzo.com, we provide all sorts of health services ranging from health products and tests to online consultations and doctor appointments. Our page is also a rich source of health-related informative articles.
To explore Welzo's world, click here.










Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.