Common questions about vaginal health
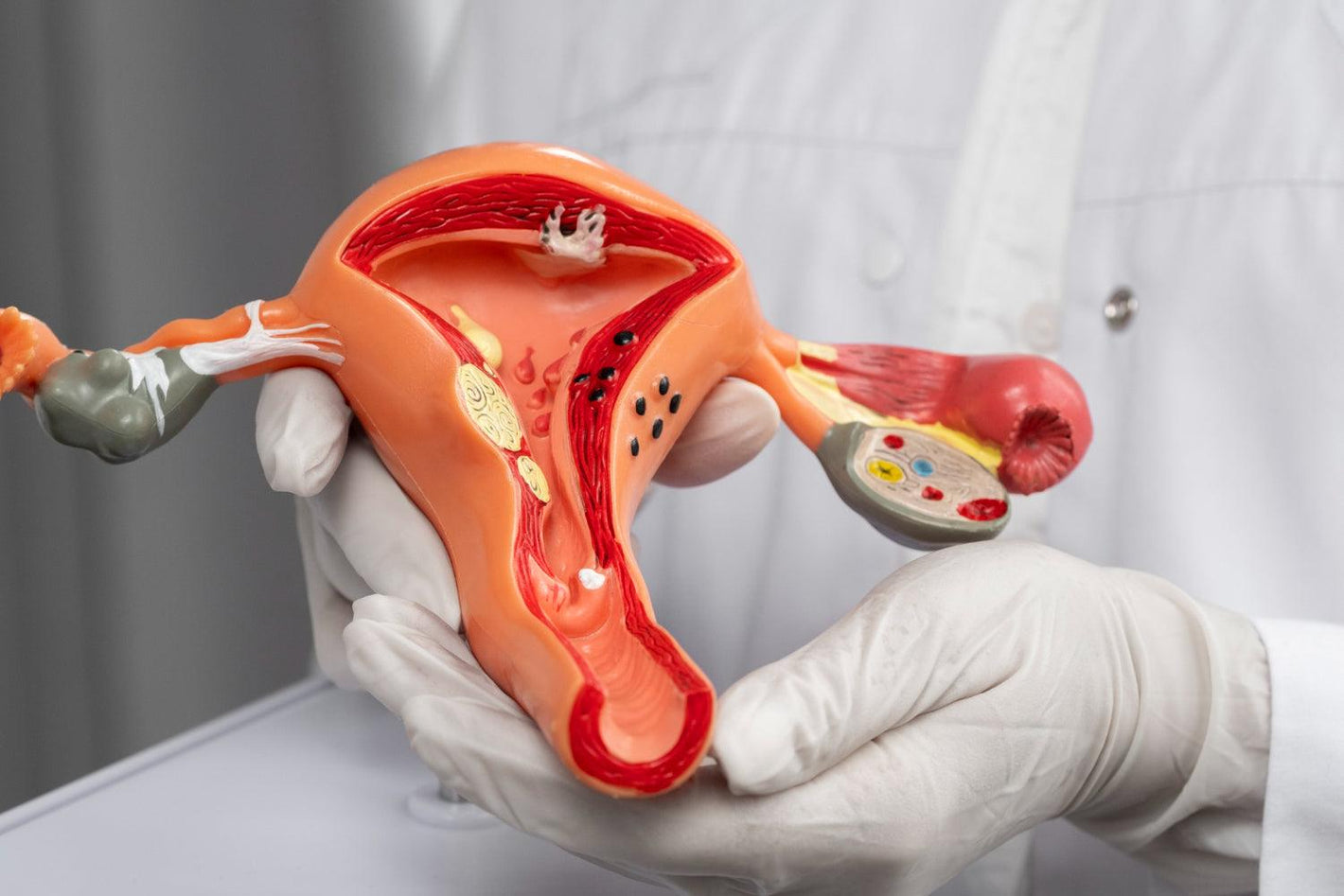

The vagina is the central part of the female reproductive system. It connects the vulva to the body of the uterus. Throughout their fertile years, most women often experience various issues concerning the vagina, e.g., bacterial vaginosis, yeast infections, abnormal vaginal discharges etc.

Given the importance of a healthy vagina, we have summarized some frequently asked questions about vaginal health. Let's go through them.
Vaginal and valvular itching is very common. According to a 2018 study, about 1.2 million women in the UK suffer from this condition. It can be a source of pain, irritation and embarrassment. What causes the vagina to become itchy? It is a complex issue, and several factors can be responsible.
The exact signs and symptoms depend upon the severity and the causative agent.

Your itchy vagina can be due to any one of the following factors.
An allergic reaction is the body's response towards a foreign object called an allergen. Various allergens are present around you, e.g., dust, germs, fungal spores, metallic particles etc. Some ingredients in vaginal products can act as allergens, causing allergic reactions. So, if you have an itchy vagina, look for the potential allergens in the following products you might be using;
Fragrances used in the douches and deodorants
Latex condoms
Scented lotions, creams, soaps etc.
Use of scented detergents to wash undergarments
Menstrual pads
The irritation caused by these agents disappears automatically once you stop using them. However, severe allergic reactions can cause breathing difficulty, painful rashes, swellings etc. and require immediate medical attention.
Many women of reproductive age experience bacterial vaginosis (BV). It can occur whenever the normal microbial environment of the vagina is disturbed, and the harmful bacteria gain the upper hand. According to the NICE clinical knowledge summaries (CKS), its prevalence is 5% in asymptomatic college students and 12% in pregnant women attending the local reproductive clinics.
In another article, we have detailed the information about bacterial vaginosis, its causes and treatment options, etc. click here to read it.

Regardless of the cause, the BV causes;
Noxious odours from the vagina, e.g., a fishy smell after sex
Itching in and around the vaginal opening
Grey or white discharge from the vagina
Burning, pain or itching inside the vagina
If you are experiencing the symptoms of vaginal infections and want to consult health professionals, click here.
Vaginal candidiasis is a fungal infection of the vagina and is experienced by many women during their reproductive life. This infection is rarely serious. However, it causes vaginal irritation, clear-to-white discharge, and burning or itching in the vagina.
The causes of vaginal candidiasis (vaginal thrush) can be many. The treatment options are according to the reason. Click here to read more.
Some skin conditions which are known to irritate the vagina and vulva are;
Skin writing (dermographism)
Folliculitis (inflammation of hair follicles)
Seborrheic dermatitis (mostly occur at the scalp. However, it can also be experienced around the vagina)
Contact dermatitis (allergic reaction due to direct contact with allergens)
Psoriasis in which patches of red and thick skin form
Lichen planus (a condition causing the irritation and swelling of the skin)
Pruritis (dry skin)

At Welzo, we have various treatment options available for you. Click here to view our products and place an order. You may need an online consultation to purchase some products.
STIs are diseases transferred from one person to the other through sexual intercourse. Besides other issues, these diseases can also cause vulvar or vaginal itching. Some common STIs causing itchy vaginas are;
Trichomoniasis
These conditions demand immediate medical attention. As a precaution, you should suspend sexual activities until these issues are treated.
We have an All-in-One STI Test Kit that allows you to diagnose common STIs through a single blood test. Click here to know more and place your order.
The vaginal and valvular itching is not limited to these issues. Some other factors that can also cause vaginal itching include;
Neuropathy (damage to the local nerve)
Vaginal cancer (a rare cause)
Local parasitic infestations
Regardless of the cause, vaginal itching needs proper care and treatment. A completely normal sexual life requires a healthy vagina. So, keep an eye on these issues and consult the doctor in case of any of these issues.
A normal vaginal canal should have a very mild or absolutely no smell. But what if there is an abnormal, repulsive and strong odour?
You may have seen some products in the local pharmacies that claim to mask the natural odours produced by the vagina. These products are, however, not recommended by the medical community as they disrupt the normal microbial balance of the vagina, causing serious infections. But what is the source of normal vaginal odour? Why can it go abnormal? Let's understand.

Some vaginal odours are normal; some are signs of infection or other issues. Let me explain some important vaginal odours and what they tell about your vagina.
This smell reflects the changes in the vaginal micro-environment and the acid-base balance (pH). The changes in pH due to infections (e.g., BV) or other causes disturb the micro-flora of the vagina, causing the population of fermentation bacteria to proliferate. It will cause a sweetish odour from the vagina.
Having this smell for several days requires visiting the nearest reproductive health clinic.
Sometimes, an odour resembling ammonia or bleach can be noted. It could be due to the following reasons;
Bacterial Vaginosis: It often causes a fishy smell from the vagina.
Urination: urine contains urea. So, a chemical smell could be due to the accumulation of urine in the undergarments or around the vulva. However, keep in mind that a strong urea smell from the urine is a sign of dehydration, which means your body doesn't have enough water to remove the excessive urea.
Some cosmetic products may also contain strong-smelling chemicals.
The bacteria, e.g., Lactobacillus, produce a sour and tangy smell (like pickled foods). The same bacteria are responsible for the smell of bread, sourdough, yoghurt, etc. The vaginal environment is slightly acidic (pH 3.8-5.0). The acidic pH controls the growth of dangerous bacteria.

It can signify the development of an infection in the vagina, particularly if a vaginal discharge accompanies it.
A putrid odour resembling those coming from a decaying dead body is not a normal sign. It is a sign that your vagina may have a foreign body (e.g., a forgotten tampon etc.). Removal of the foreign body will eliminate this odour.
Such an odour can also develop due to some infections, e.g., bacterial vaginosis.
A coppery and metallic smell from the vagina is rarely a sign of worry. It could be due to the following;
Bleeding from the vagina due to vigorous sex or vaginal dryness. It will cause some bleeding.
Menstrual bleeding: The blood has iron. So, blood and tissue debris in the vagina during menstruation can cause a metallic smell.
If such a smell lingers for longer, you need to see a doctor. If you have any such smell, click here to consult our sexual health experts.
Many people also experience a smell resembling smoked herbs, e.g., marijuana. It is mainly due to excessive sweating. Activated apocrine glands (found abundantly in your armpits, groin etc.) can cause a foul odour. These glands also secrete pheromones, the chemicals that attract the opposite gender.
This smell resembles the smell of a rotting fish. This smell is produced by the chemical called trimethylamine and is a sign of vaginal infections, e.g.,
Trichomoniasis: it causes a highly pungent and fishy smell from the vagina.
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV): it is due to an imbalance in the bacteria population and causes fishy odours.
Regardless of the cause, any strong and repulsive smell through the vagina can embarrass your relationship. Besides treating the causative agent, you can also use various products to help reduce vaginal odours.
The abnormal and unpleasant odours from the vagina should not be ignored, particularly if they are accompanied by bleeding, cottage cheese-like thick discharge, pain, painful sex, burning, itching etc.
The vagina is the central organ of the reproductive system. It is the most important target of sexual activities. Have you ever imagined the size of your vagina? The size increases as a female matures.
How deep and long is it? Just like there is a variation in the size of the hands, feet and breasts, women also have a vagina of variable depth and dimension. According to various studies, the average depth of the vagina is around 3.5 inches (9.1cm). However, the size is not uniform, and women have vaginas between 3-7 inches (7.5-17.5cm) deep.
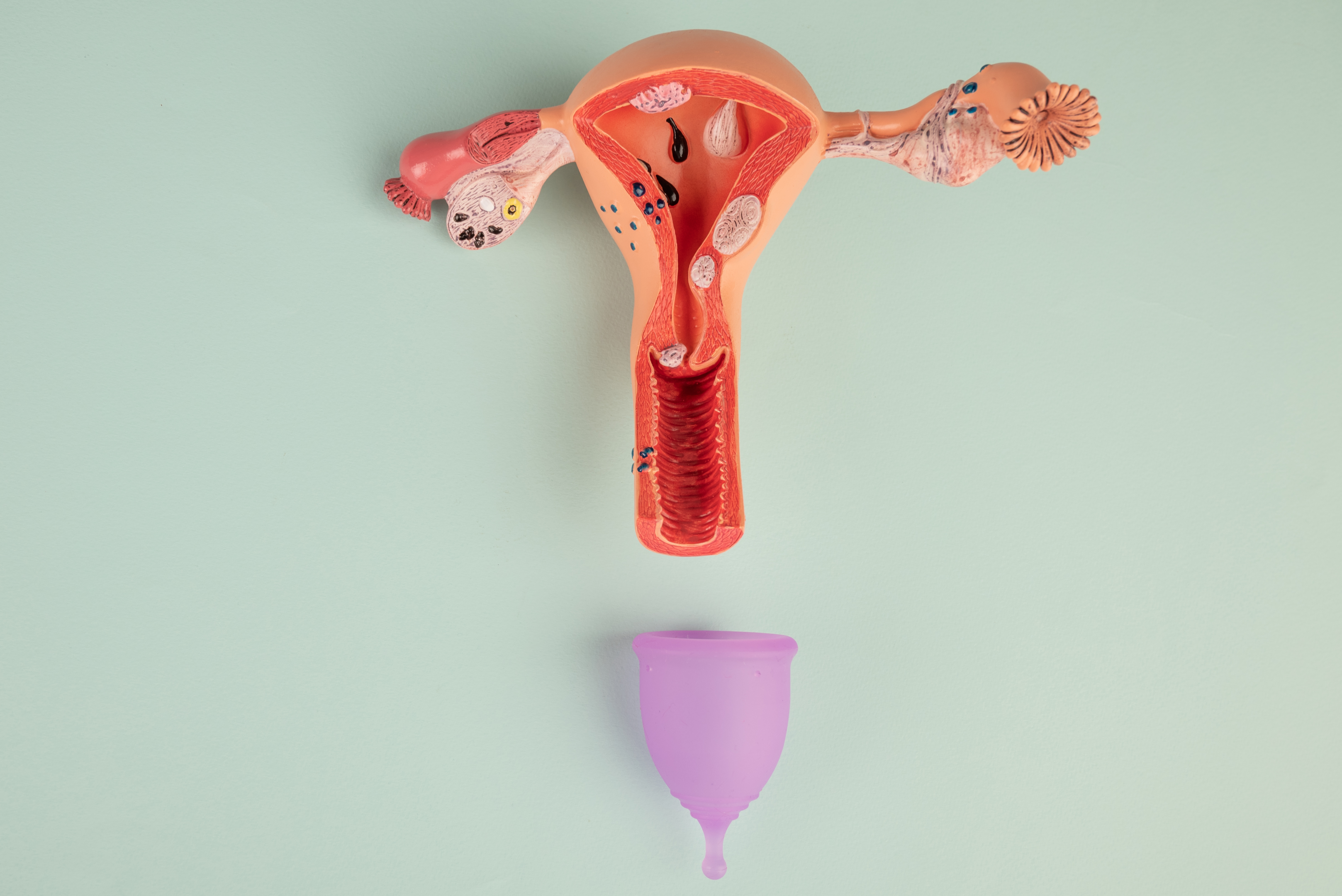
The vagina is between the cervix and the uterus and connects both parts. Towards the outside, there lies the vulva, which is the lip-like part of the female reproductive system. The external lips (labia majora) vary in length between 2-4 inches (7-10cm), and the diameter and length of the clitoris are around 0.5 inches (1-1/5cm). However, the clitoris is enlarged and swollen during sexual arousal.
Like other body organs, the size of reproductive organs also changes with various factors. Some situations influence the depth and length of the vagina. It has a remarkable elasticity and can stretch to adjust to the size of a penis, a finger or a tampon.
When a female is sexually aroused, the blood supply to the vagina is increased, causing it to elongate. At the same time, the cervix also lifts, allowing the finger, penis or sex toy to adjust.
However, don't go too far as the elasticity is not too great and discomfort during sex can still occur.
There is some evidence that the vaginal depth changes with age. A study has found an association between age and the depth of the vagina. The vulva may shrink and become smaller in size with age. It is often attributed to reduced collagen and fat due to falling oestrogen levels.

Similarly, although there is little effect on the length of the vagina, it does become narrower and less elastic with age. Menopause also has a marked impact on the length and overall size of the vagina. A 2006 study published in the American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology found that menopause decreased the total vagina length by 0.17cm.
The average size of the penis is considerably larger than the vaginal depth. The average size of the penis is around 5-6 inches (12-15cm). Despite the variation in length, these two organs accommodate each offer. However, some women may find it discomforting if their partner has a penis larger than their vagina and the penis touches their cervix. To maintain the pleasure of sexual activities, you can use lubrication and communicate any discomfort to your partner.
The lump is an overgrowth formed over any organ or on the body's surface. You are not alone if you ever develop a swelling or bump on the vagina. Vaginal lumps and bumps are very common in women of reproductive age. Very rarely, it could be a sign of cancer, as 1400 new cases of vulvar cancer are reported each year in the UK.
Why do these lumps develop? What complications can they cause, and when do you need to see a doctor? Stay on the lines for answers.
These bumps can reflect an underlying medical condition, although sometimes, they are perfectly normal. The important causes are;
Vaginal cysts: these are in the form of firm bumps on the vaginal wall and are the size of a pea or even smaller. These cysts are rarely painful, but a grown-up cyst can cause pain during sex and must be removed surgically or drained manually.
Vulval cysts: vulva has various glands which produce multiple secretions. These glands include the Skene's, Bartholin's, and oil glands. A cyst can develop when the duct of any of these glands is occluded. However, only the infected cysts can cause pain or discomfort. The treatment and management protocol is the same as for vaginal cysts.
Ingrown hair: the in-growth of pubic hairs can occur due to plucking, shaving and waxing. The result can be a small, occasionally painful and itchy bump. See a doctor if the ingrown hair has become infected or is causing pain and discomfort.
Varicosities: it is the swelling of veins around your vulva. The veins in the affected area (e.g., pelvic floor area) become twisted and enlarged, forming a bump. The swollen veins can create bluishly and raised bumps around the outer and inner lips. These lumps often recede automatically after pregnancy in pregnant women. However, they can reoccur.
Fordyce spots: these are the yellow-to-white bumps that are formed inside the vagina. These are, however, not painful and are harmless. These are the raised and enlarged sebaceous glands that normally develop on hairless skin parts and are rarely noticed in the vagina.
Cancer: vaginal or vulvar cancers are rare. According to Cancer Research UK, only 250 new cases of vaginal cancer are reported annually in the UK (2016-18). However, when they do occur, they can cause lumps and raised sores on the vulva. Thickened patches form on the skin, becoming darker or discoloured from the surrounding skin.
Genital warts: these are caused by the human papillomavirus and are transmitted through anal or vaginal sex. Besides itching and burning, it can cause lumps of various shapes, e.g., cauliflower.
Genital herpes is another viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. In addition to other symptoms, it can cause swollen glands resembling lumps. The signs need immediate medical assistance, although they can clear up naturally.
Vaginal skin tags: these are the small and protruding flaps of the skin. They are often painless unless scratched or become infected. These tags are, however, not contagious or sexually transmitted infections.
Lichen sclerosis is a very uncommon condition and is often experienced by women after menopause. The blisters are among the major signs that may or may not be blood-filled. It is an autoimmune condition and is often characterized by hyper-pigmentation and atrophy of the skin.
Your vaginal lump can be due to any of these causes. However, you need to see a doctor if the swelling is increasing in size, is going more and more painful, the node is secreting discharge, has blood or pus, or the symptoms resemble a sexually transmitted infection.
A cyst is a closed pocket containing pus, air or blood. The cysts can also form in the vagina and can be of various types. These cysts are rarely harmful. However, they can cause pain and discomfort during tampon insertion or sex. Some cysts become too large or infected and cause itching or pain.
Various types of cysts may develop in the vagina. They are often associated with the blockage of the ducts of the glands (as mentioned above) or are caused by injury on the vaginal wall during surgery or childbirth.
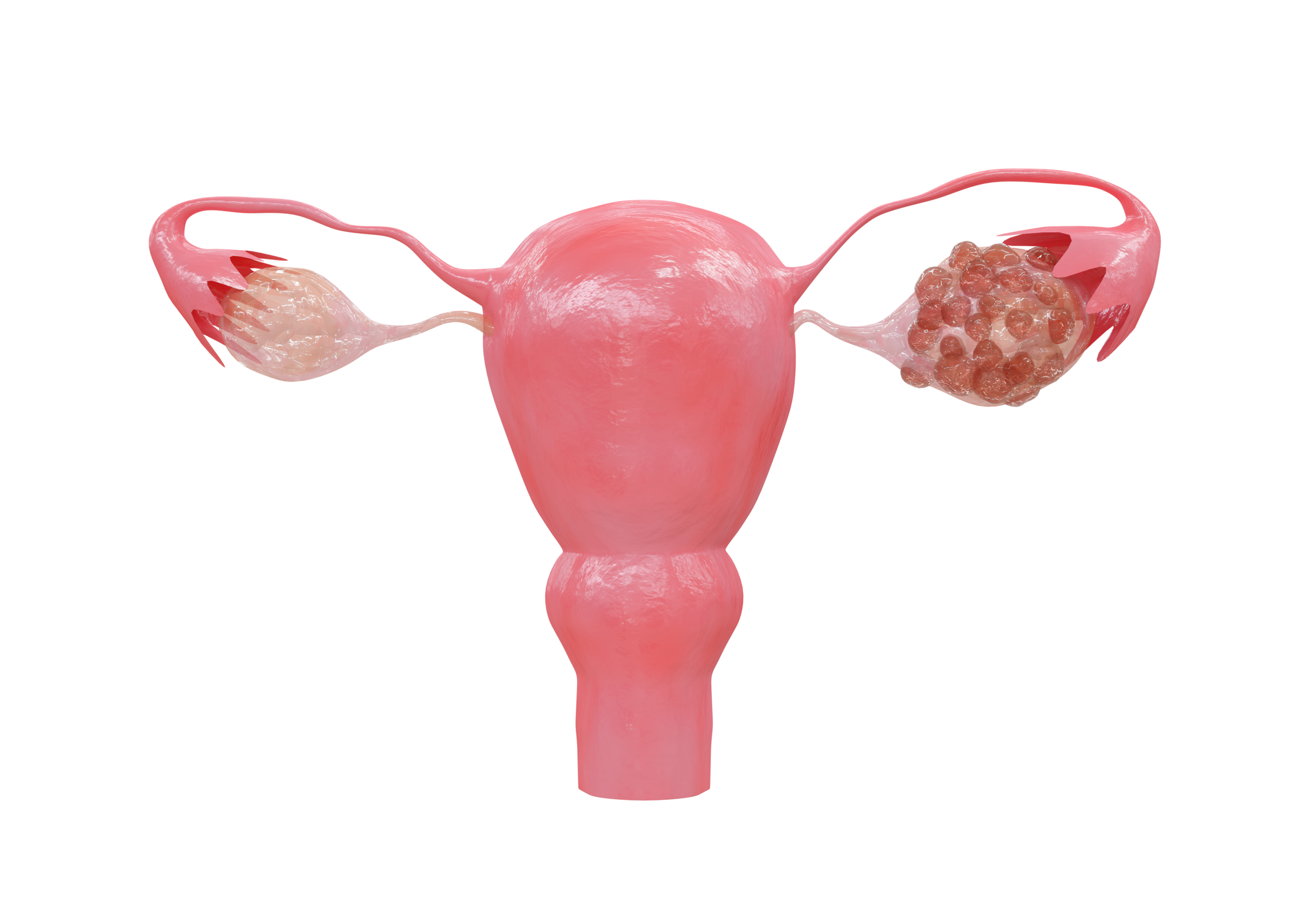
Most of the cysts are harmless. You will find a small painless lump hanging from the vaginal wall. However, the only noticeable sign will be discomfort or pain during sex or while insertion the tampon into the vagina. The cysts are often diagnosed through CT, MRI, ultrasonography, biopsy or pelvic exam.
If you have been diagnosed with a cyst, you need to regularly consult the doctor to monitor the changes in the growth or size. Surgery is often the only option for some cysts that are extremely painful or become too painful. The doctor can also prescribe antibiotics if the cyst becomes infected.
The complications are rare except the irritation and pain during sex in case the cyst becomes too large. The risk of infection is high for large cysts and may need surgical removal. Surgical removal is, however, the last resort.
The prognosis is generally good. Most of the cysts are benign and remain smaller. They also don't reoccur after surgical removal. The larger ones are also treatable and rarely threaten life.
Do you feel pain in your vagina? If so, it could be a sign of infection (acute or chronic), injury or some chronic disease. However, there is also a condition called Vulvodynia, wherein there is persistent pain in the vagina without any clear cause. Although limited data is available on this condition, some researchers claim that this condition affects 8-10% of women globally.
However, most vaginal pains are due to some cause. Let me summarize the major causes of vaginal pain.
Physical injury to the vulva or vagina can be a cause of pain. These injuries can range from Minor cuts during shaving to major physical damage during a stressful childbirth.

A painful and difficult vaginal childbirth can cause a tear in the vagina, perineum or, in rare cases, in the labia and clitoris. Minor cuts may revolve spontaneously. However, major cuts and injuries need stitching by a surgeon.
According to an estimate, 1.2 million women experience the vaginal yeast infection (vaginal candidiasis) in their reproductive years in the United Kingdom. This infection causes cottage cheese-like discharge, burning and itching in the vagina.
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) is a bacterial infection of the vagina which causes similar symptoms along with a fishy odour from the vagina. Some sexually transmitted infections (STIs), e.g., gonorrhoea, Chlamydia, trichomoniasis etc., can also cause vaginal pain.
If vaginal pain persists for a long time, you need to consult the physician.
An injury in the pelvic floor can cause pain in the back, stomach, vagina and adjacent muscles. Pelvic floor injuries can occur for various reasons, but advanced age, childbirth injuries, episiotomy (the surgical procedure to enlarge the vaginal opening for easy birth) and advanced pregnancy are the predisposing factors. The injuries of pelvic floor muscles and bones can also cause other issues e.g., painful stools, faecal incontinence etc.
Cysts develop when the ducts of the glands in the vagina are blocked due to any reason. For example, Bartholin's glands are present near the vaginal opening and help to lubricate it. A blockage of the ducts of these glands will cause Bartholin's cyst. This pimple-like cyst can also cause vaginal pain.
Such a cyst can rupture and get infected. If this happens, you need to consult the doctor.
Spasms, tightness and soreness in the muscles adjacent to the vagina can be caused by various reasons, e.g., pelvic floor injuries, exercise injuries etc. These issues can also occur due to some unknown factors. Vaginal muscles become stiff, causing pain and discomfort during sex.
The skin around the vulva and vagina can become sensitive, causing pain and tenderness. Visible swelling or lump can also form, becoming infected and causing intense pain.
Vaginal pain can be due to several factors and can have various clinical pictures. If you have persistent pain in your vagina, you need to consult the doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis and proper treatment.

The pain is likely to go with the right treatment. Typically, the diagnosis involves physical examination, ultrasonography and medical history and the treatment options available are antibiotics, antifungals, painkillers and home remedies.
The job of a gynaecologist is to make your vagina healthy. The vagina can develop various issues, e.g., yeast infections, cysts, bumps, irritation and itching, noxious odours, etc. Understanding these issues and respective risk factors is essential for proper care and treatment.

At Welzo, we have various sexual health products, e.g., birth control pills, vaginal delivery drugs etc. Click here to view the Welzo world of female reproduction. You can also discuss your issues with our sexual health experts.










Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.