
 Instagram
Instagram
What foods are good for liver repair?

Related products
What’s covered?
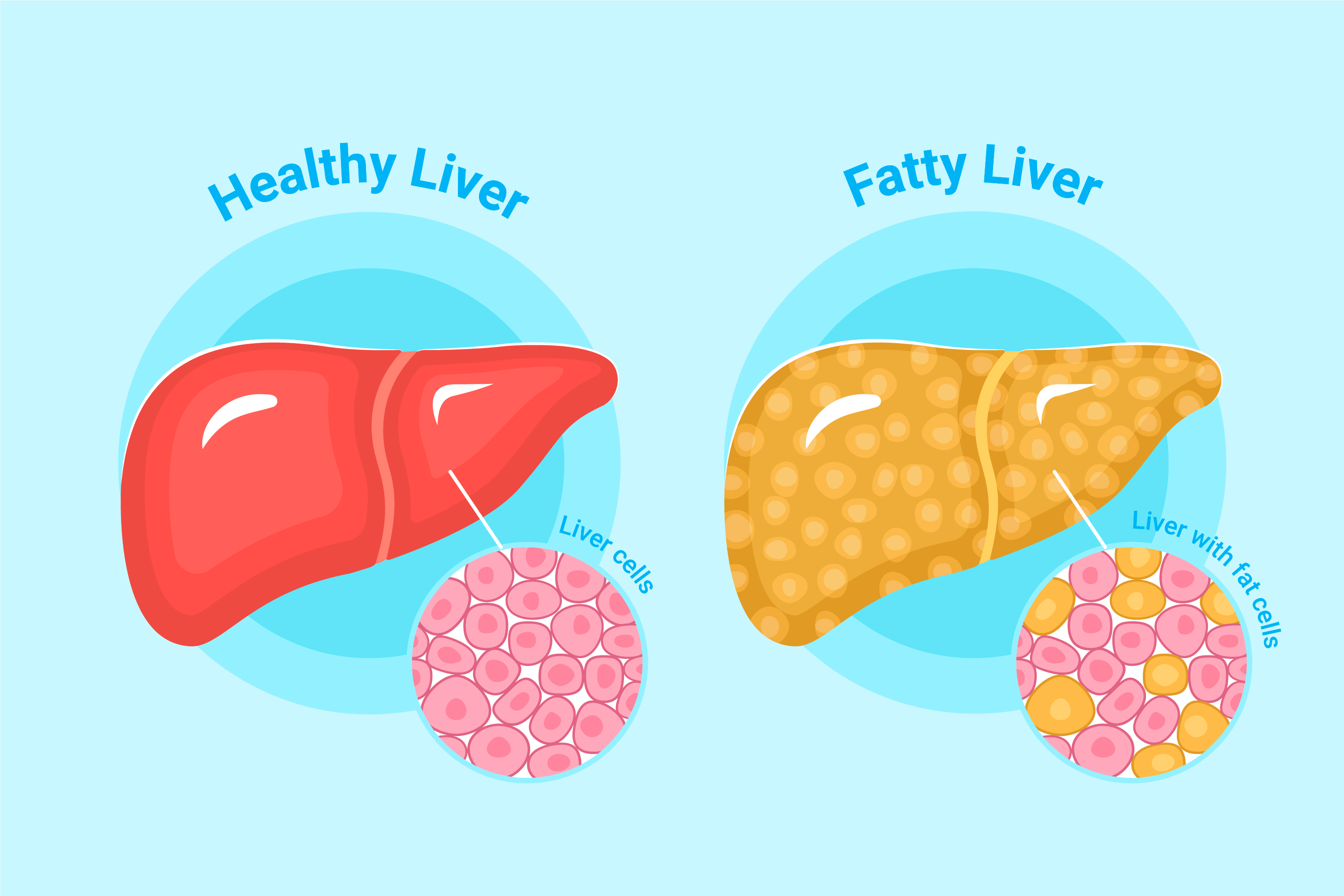
The liver regulates the proteins, carbohydrates, and fats that we eat. Healthy liver function is crucial for overall well-being. An unhealthy liver can lead to metabolic issues and liver disease. One of the most prevalent forms of liver disease is a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It is a disorder where extra fat is deposited in the liver and, if untreated, can result in chronic diseases, liver cancer, and liver failure. NAFLD is more prevalent in adults with obesity and diabetes type 2.
Can a balanced diet help with liver detoxification?
Recent research has shown that oxidative stress and fat build-up play a significant role in the pathophysiology of liver diseases. In the treatment and cure of liver disease, dietary habits can be quite important. Some meals may help promote liver health, even though it may only be possible to control some risk factors.
Dietary Modifications
For liver disease, dietary modifications could include:
- Limit the intake of animal protein. In doing so, you can prevent the accumulation of harmful material that can cause liver inflammation.
- Boost your carbohydrate consumption to be in proportion to your protein intake
- Consume fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, such as fish, poultry, and lentils. Avoid eating raw shellfish.
- Take the vitamins and medications your doctor prescribed for low blood count, nerve issues, or nutritional issues caused by fatty liver.
- Lower salt consumption. Dietary salt may cause liver oedema and fluid retention worse.
The following healthy foods can help your liver heal:
CoffeeCoffee has many health benefits. Your body metabolizes caffeine into paraxanthine. This substance reduces the formation of scar tissues that cause fibrosis. It also helps fight against liver cirrhosis brought on by alcohol, non-alcohol fatty liver disease, and hepatitis C.
Additionally, coffee helps fight inflammation and raises glutathione levels (an antioxidant). Free radicals, which the body naturally produces and can cause cell damage, are neutralized by antioxidants.
Two components of coffee, kahweol, and cafestol; have anti-cancer properties. Although the extent of the benefit is unknown, some medical professionals believe that modest doses of unsweetened coffee may complement the primary therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma, the most prevalent kind of liver cancer.
Cruciferous vegetableCruciferous vegetables like broccoli, brussels sprouts, and mustard greens are among the best foods for your liver. They include substances known as glycosylates, which not only protect liver cells but also help in the synthesis of the glutathione enzyme. The body's primary antioxidant enzyme, glutathione, is the basis for numerous liver detoxification processes.
Green vegetables contain inorganic nitrate. Nitrate improves insulin sensitivity and lowers blood cholesterol levels.
Fatty FishFatty fish, e.g., salmon, tuna, sardines, and trout, contain omega-3 fatty acids. Studies indicate that cirrhosis-damaged livers and non-alcoholic fatty livers have lower concentrations of omega-3 fatty acids than healthy livers. Consuming more omega-3 fatty acids may eventually assist with this illness.
How are omega-3 fatty acids and liver repair related?
Important biological processes are regulated by omega-3 fatty acids such as
- Fatty acid production
- Oxidation of fats
- Breakdown of triacyl glycerides
The omega-3 fatty acid DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) is considered one of the most important and helps heal liver damage. Oily fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, and sardines have the highest concentrations of DHA.
OatmealOatmeal is rich in fibre and a great food for liver detox, but it is not only because of fibre. Additionally, it contains a lot of beta-glucans. Soluble fibres known as beta-glucans are powerful anti-inflammatory agents.
How do soluble fibres prevent fatty liver disease?
Most of the body's cholesterol is low-density lipoprotein (bad cholesterol). Excess LDL speeds up the progression of fatty liver disease, which can result in potentially fatal illnesses like cirrhosis and liver cancer. Therefore, getting rid of extra LDL cholesterol from the body is essential.
This can be managed by increasing the number of soluble fibres in the diet. The gut is unable to absorb soluble fibres. Instead, they attach to cholesterol and remove it from the body, reducing the cholesterol from blood levels. Other best foods high in soluble fibres are:
- Oranges
- Apricot
- Carrots

Antioxidants containing foods
Since the liver is the primary organ for detoxification and regulates metabolic balance, liver disorders are a major global health concern.
Mechanism of action of antioxidantsThe liver processes a variety of substances that result in free radicals (FR). Antioxidants neutralize free radicals and keep the liver's oxidative balance in check. Oxidative stress is a condition that occurs when the liver's antioxidative balance is disturbed. Oxidative stress triggers harmful liver processes that result in chronic liver diseases. Antioxidants must be provided through a healthy diet to reduce oxidative stress.
The list of foods with antioxidants that protect against liver diseases is provided below:- Grapefruits (contains naringin and naringenin as antioxidants)
- Linseeds and sunflower seeds
- Almonds (have vitamin E as an antioxidant)
- Blackberries, raspberries, strawberries
- Beef liver
- Olive oil
- Sweet cherries
- Black beans
- Dark leafy greens
- Milk thistle (a plant that contains silymarin as an antioxidant)
- Green tea (green tea extracts contain Polyphenols or Flavonoids as an antioxidant enzyme)
Foods to avoid for healthy liver
Not all foods, though, are healthy for your liver. Some may be harmful for several reasons. We discuss a few things below that you should avoid or eat sometimes.
Sugary foods: Refined sugar and high-fructose corn syrup are frequently present in sugary foods. It can accumulate fat in the liver, resulting in fatty liver disease.
Alcohol: Alcohol consumption induces inflammation, which, if consumed excessively, can result in scar tissue that interferes with proper liver functioning—too much alcohol results in alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Saturated fatty acids: The mitochondria are adversely affected by saturated fat. By using beta-oxidation, mitochondria break down fatty acids. Affected mitochondria may fail to break down fatty acids, which will cause fatty liver disease. People with NAFLD should limit their saturated fat intake to promote liver health, e.g., red meat and fried foods.
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests assess liver enzymes for signs of liver cell injury. The liver function test measures,
- Alanine transaminase (ALT)
- Aspartate transaminase (AST)
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
- Albumin and total protein
- Bilirubin
- L-lactate dehydrogenase
If you experience unusual symptoms, you should get liver blood tests to diagnose liver problems. We suggest you take a look at our Liver Blood Test kit which will let you have a detailed insight into your liver health with a simple finger prick method.
Conclusion
The above foods have been shown to have beneficial effects on the liver. The following are some of these benefits:
- A decreased risk of cancer and liver disease
- Protection against harmful toxins from higher levels of antioxidant and detoxifying enzymes
Including these foods in your diet is a natural strategy to maintain a healthy weight and healthy liver.



























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews