Acetyl-L-carnitine is a potent amino acid derivative that improves sports performance, fat metabolism and brain health. It transports fatty acids into mitochondria and converts them into energy through fatty acid oxidation. Its supplementation reduces nerve pain, helps treat depression, reduces the symptoms of Alzheimer's disease, and enhances thinking skills and memory.
It is a valuable supplement for those seeking to improve cognitive function, burn fat, and enhance endurance. The other ingredients in these supplements are magnesium stearate, silicon dioxide, leucine, etc. Explore this collection and select the supplement you desire.
What are the features and uses of Acetyl-L-Carnitine Supplements?
-
These supplements have L-carnitine and acetyl L-carnitine. Both can cross the blood-brain barrier, but acetyl-L-carnitine [ALCAR] is more effective for this job. Both enhance protein synthesis and restore blood glucose levels.
-
It reduces recovery time after a workout and also reduces muscular fatigue.
-
In combination with electrolytes, acetyl-L-carnitine supplements deliver a sustained source of energy during a workout. It keeps the muscles well functioning and properly hydrated.
-
It is helpful for people with low thyroid hormone levels (underactive thyroid). These supplements suit people who regularly engage in workouts.
-
As a part of a balanced diet, it helps in anticonvulsant therapy, reducing the need for anticonvulsant drugs.
-
Acetyl L-carnitine supplementation also enhances sperm motility, as shown by a study published by Reproduction & Fertility in 2020.
-
A randomised controlled clinical trial published in Complementary and Alternative Medicine reported that L-carnitine supplementation reduces the symptoms of mild cognitive impairment.
Why has Welzo selected Acetyl-L-Carnitine Supplements?
Welzo has selected acetyl-L-carnitine supplements for their proven efficacy to enhance nerve functions, energy production, and brain health. These supplements closely align with our mission to provide customers with evidence-based, high-quality supplements for everyday health.
Why buy Acetyl-L-Carnitine Supplements from Welzo?
These supplements are for you if you have low serum carnitine levels. They improve your muscle mass and help in weight loss. They also pair well with protein powders. So, visit our blog titled 7 Best Protein Powders for Weight Loss and Muscle Gain and select a protein supplement based on your needs.
What are the leading products in this collection?
The leading products in this collection that enhance carnitine homeostasis and free L-carnitine levels are;
-
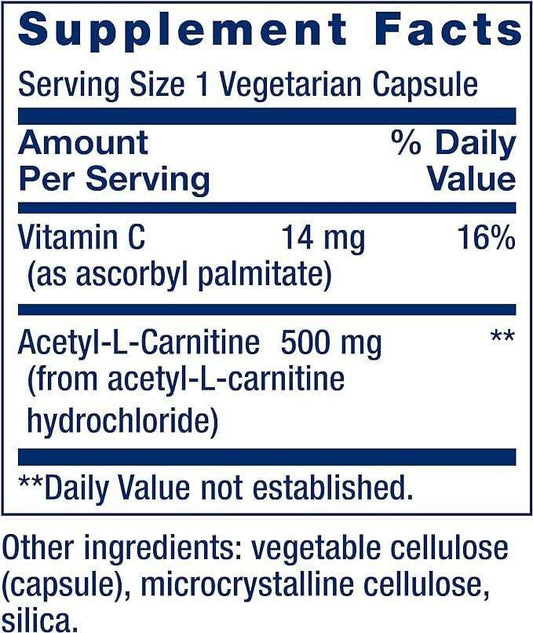
Seeking Health Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500 mg veg caps
-
Life Extension Acetyl-L-Carnitine Arginate vcaps
-
NOW Foods Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500mg
-
Klaire Labs Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500mg Capsules
-
New Beginnings Acetyl-L-Carnitine 500mg Capsules
There are many more. Just keep visiting us to achieve better exercise performance, sperm quality parameters, and many more benefits.
How to use Acetyl-L-Carnitine Dietary Supplements?
Acetyl-L-carnitine supplements should be used as directed on the label. The recommended daily allowance is 500-1500mg daily, up to 2000mg if the doctor advises. They should be used early in the morning, on an empty stomach, for better energy support and optimal absorption. We also suggest checking serum carnitine concentrations before resorting to supplementation.
Reviews and clinical insight on carnitine supplementation
L Carnitine supplements are in good standing with both users and healthcare professionals.
Harry V., a Welzo customer, has reviewed Now Foods acetyl L-carnitine powder as;
'Been taking this Acetyl-L-Carnitine powder daily, feels good for proactive brain energy.'
Another Welzo customer has reviwed Thorne Acetyl-L-Carnitine ( Formerly Carnityl) as;
'Absolutely thrilled with my purchase of Thorne's Acetyl L-Carnitine veggie capsules. They are easy to take and I've noticed a significant boost in my energy levels since I started using them. Highly recommend!'
Dr Muhammad Zeeshan, a Welzo team member, has remarked about our acetyl L-carnitine collection.;
The Acetyl-L-Carnitine supplements by Welzo are excellent. They significantly improve mental clarity and energy levels. The capsule forms are easy to swallow and have no side effects. I highly recommend these products for those looking for a natural boost.'
Quality and certifications of our amino acid supplements
-
Our medical/ nutritional board scientifically tests all ingredients and end-products in this collection and list them as 'expert verified'.
-
We require our suppliers to meet HACCP, ISO, and GMO guidelines.
-
The finished products are tested in the third-party UKAS-accredited labs.
-
These sports supplements are organic-certified, NSF-certified for sports, Informed Choice-certified, and approved by the Vegan Society.
FAQs related to our food supplements
What are the main features and uses of acetyl-L-carnitine Supplements?
Acetyl L-carnitine helps transport fatty acids (such as alpha-lipoic acid) into the mitochondrial matrix, where they are converted into energy. They enhance thinking and memory and reduce depression.
Is it safe to use L-Carnitine during pregnancy?
Yes, using L-carnitine during pregnancy is not just safe, but also useful. It improves the baby's and the mother's health without complications.
Is it fine to use Acetyl L Carnitine supplements daily?
We recommend avoiding using these supplements for a long period of time. Doses up to 2000mg/day are considered safe. People taking acetyl-L-carnitine supplements must combine them with vitamins such as vitamin C.
Can acetyl-L-carnitine help burn fat?
Yes, acetyl-L-carnitine metabolism supports fat burning, helping achieve fat-metabolism and weight-loss targets.
What are the signs of carnitine deficiency?
A chronic deficiency of carnitine causes carnitine deficiency disorders. Its deficiency causes muscular weakness, fatigue, irritability, cognitive decline, poor exercise capacity, heart and liver problems, etc. Research suggests that people opting for a healthy lifestyle must use the acetyl form of carnitine regularly.

























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews