How to Increase Ferritin Levels?
.png?v=1674643717001)

Related products
You may already know that ferritin is concerned with iron levels in the body. Iron and ferritin levels do seem to go hand in hand. But what exactly is ferritin and what makes it such an essential component in the human body? Iron is an important mineral for your body; red blood cells would not survive without iron and it is vital for the smooth functioning of various metabolic reactions in the body, such as oxygen storage, respiration, and DNA synthesis, as well as maintaining your energy levels.
How to Increase Ferritin Levels
Depending on the cause of low ferritin levels in your body, your doctor will prescribe the appropriate treatment for you.

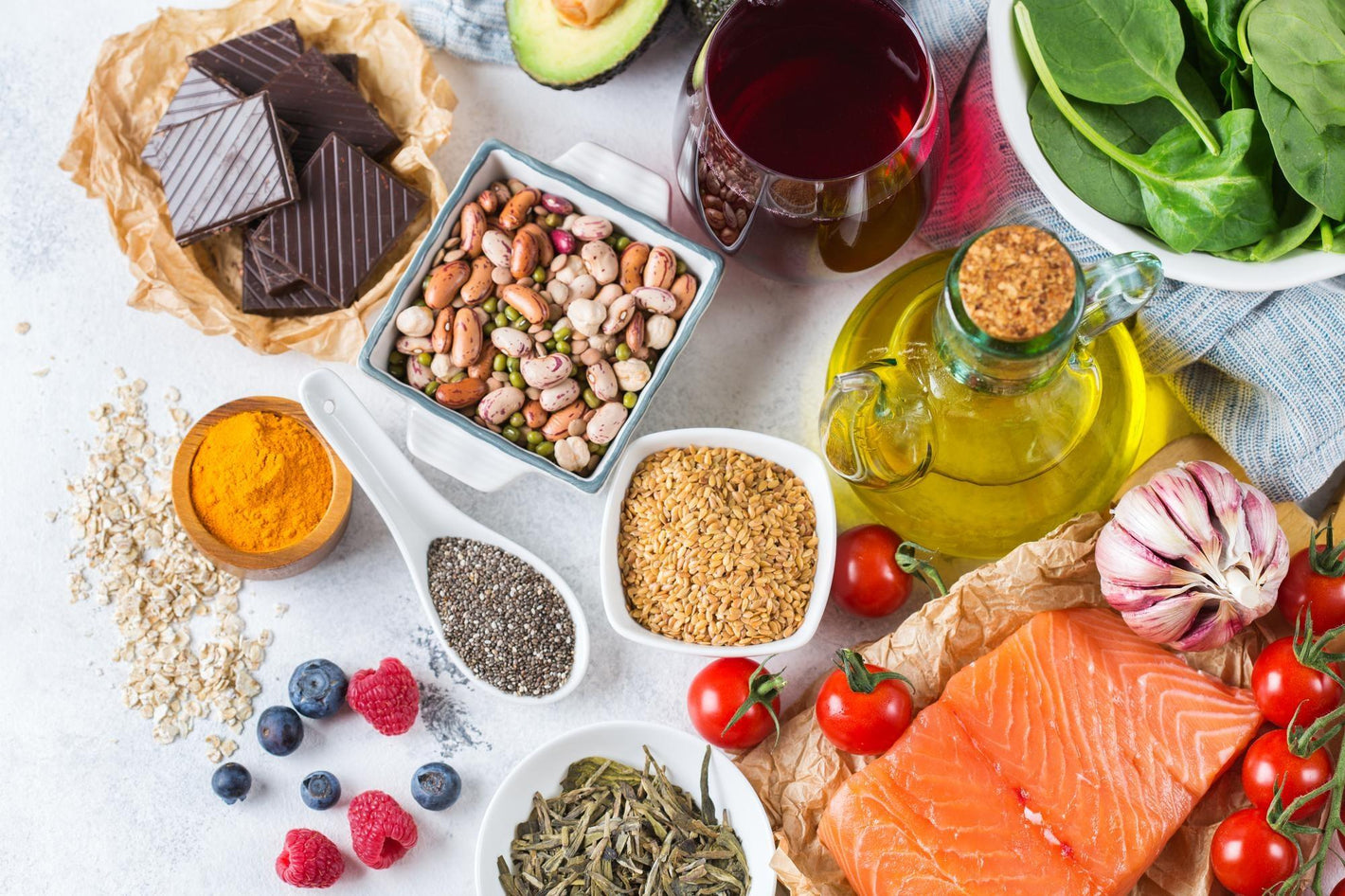
As dietary iron can help curb iron deficiency, you may need to eat food items rich in ferritin.
Ferritin rich foods
Ferritin-rich food includes:
-
Legumes like peas, soybean
-
Leafy vegetables
-
Fruits like dates, prunes, strawberries, and watermelons
-
Dried peaches, apricots, and raisins
-
Eggs
-
Meat liver
-
Fishes like sardines, tuna, mackerel
-
Grains like oats and corn
In some countries, crops are fortified with iron, resulting in iron-fortified grains and fortified cereals that are beneficial for persons having anaemia or ferritin deficiency.
Eating vitamin C-rich food, such as drinking a glass of orange juice every other day in addition to taking iron supplements, is a great idea as it helps to better absorb non-heme iron in the body.
Supplementation
Your doctor may also recommend taking oral iron supplements. You may consider taking the Wellwoman original supplements that contain vitamin B 12, magnesium, and other nutrients along with iron supplementation.
Iron toxicity
But excess free iron in the body could be more toxic rather than useful to the body. Because of its potential to cause organ damage and create a favourable environment for microorganisms to thrive, free irons certainly need to be balanced and maintained at an optimum level.
Read more: Iron-Deficiency Anaemia, Causes, Symptoms and More.
What exactly is Ferritin?
Ferritin is your body's solution to the problem of iron toxicity. It is the primary iron-storing protein in the body. Storing almost 10% of the body's total iron, ferritin maintains a perfect balance of stored and free iron in the body and helps maintain iron absorption and the availability of iron for different cells and tissues in the body.
The structure of Ferritin
Structurally, ferritin found in the human body is a polypeptide containing 24 subunits. It has the capacity to store almost 4500 iron ions within each ferritin molecule, which takes up 24% of its weight.
Ferritin's role in the body
Ferritin is found more abundantly in organs that prevent iron toxicity, including the brain, bone marrow, spleen, liver, and serum. It plays a significant role in iron detoxification and antioxidation and works to limit bacterial iron reactions.
Normal Range of Ferritin levels
-
Ferritin levels for adult males range from 24 to 336ng/L
-
Ferritin levels for adult females range from 24 to 307ng/L
-
Ferritin levels below 30ng/L are considered deficient and require a consultation with your doctor.
Read more: What are the normal ferritin levels in the UK?
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Symptoms of low ferritin levels
-
General tiredness,
-
Fatigue,
-
Dizziness,
-
Pallor,
-
Irregular heartbeat,
-
Palpitations,
-
Breathlessness,
-
Internal bleeding,
-
Excessive menstrual bleeding,
-
Unhealthy nails and hair.
Read more: Is anaemia dangerous?
Diagnosis
Your doctor may recommend a ferritin blood test along with a Full Blood count blood test to assess your health and evaluate if you have low ferritin levels. In addition, they may also advise you to take a serum iron blood test.
Learn more about iron and ferritin on our Health Hub.


























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews