What are the normal ferritin levels in UK?
.png?v=1673517143175)

Related products
The importance of iron for the body needs no convincing. Its involvement in various vital metabolic processes, such as respiration, growth, and development, as well as oxygen transport via haemoglobin and myoglobin, makes iron important for life. It is, therefore, an essential mineral without which the health of your body could be at risk of many health disorders. Iron is also necessary for maintaining your energy levels and producing certain hormones. Although essential and required in adequate amounts, excess iron may prove to be toxic for your body.
Free iron in the body has poor solubility and also holds the risk of increased cell damage. It can potentially support an existing infection's progress and lead to increased toxicity. The toxic effects of excess free iron in the body are often long-lasting, resulting in permanent organ failure or even death.
Ferritin is the key to preventing the biological damage caused by excess free iron. It is a major storage protein for iron and thereby helps to maintain a balance of iron and its free ions in your body. Ferritin is also known for its role in various metabolic processes and is often a marker for inflammatory disorders. It has also been associated with cardiovascular diseases, nervous health disorders, and cancers.
Chemically, ferritin is a protein that has 24 subunits. Each subunit contains four polypeptides and may be classified as a heavy or light chain subunit. The percentage of heavy and light chain subunits varies for the ferritin present in different organs of the body. For example, heavy chains are present in a higher proportion in the cells present in the brain and the heart, where ferritin plays the role of iron detoxification, whereas light chains are present in a higher proportion in the liver and spleen, where ferritin is primarily for iron storage. A single ferritin can store up to 4500 iron ions.
Role of Ferritin in the body
Iron Storage and availability
Ferritin is primarily known as an iron-storage protein. Iron is found in the form of ferritin in various parts of the body, with higher concentrations in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, as well as some of the immune cells. Apart from storing iron, it also plays a role in iron absorption and the release of iron for various metabolic processes in your body.
Serum Ferritin

Ferritin is present in the serum in lower concentrations. Unlike transferrin, ferritin does not play a role in the transport and uptake of iron.
Antioxidant
Ferritin acts as a major antioxidant in the body by considerably limiting oxidative stress. It protects your body from the toxicity of free iron ions and their reaction with oxygen, thereby preventing cellular and systemic damage.
Inflammatory Marker
Ferritin levels in your body have been used as a marker for the diagnosis of inflammation. Its association with inflammatory processes, liver disease, heart diseases, malignancy, and neurological disorders has made ferritin a useful marker in many health conditions.
Know your Serum Iron levels
A ferritin blood test measures your serum ferritin levels and thereby gives an idea regarding the amount of stored iron in your body. Serum ferritin levels are directly proportional to the amount of iron stored in your body. Stored iron accounts for almost 10-25% of the total iron in your body. A ferritin blood test is often recommended by doctors for persons suffering from anaemia or other iron deficiency disorders to determine their iron levels.
Normal Ferritin Levels (UK)
Normal levels of ferritin for different age groups in the UK population are given below:
-
Normal Ferritin levels for newborns: 25 to 200ng/mL
-
Normal Ferritin levels for children: 7 to 140ng/mL
Normal Ferritin levels for adults
-
Males: 24 to 336ng/mL
-
Females: 24 to 307ng/mL
Range of Abnormal Ferritin levels
-
Low Ferritin Levels: Less than 30ng/mL
-
High Ferritin Levels: More than 400 to 500ng/mL
Ferritin Blood test
A ferritin blood test is often used as an inflammatory marker for many health conditions. It is also useful in the detection of iron deficiency anaemia. It specifically helps to differentiate iron deficiency caused by low iron stores from iron deficiency caused by low intake, absorption, or utilization of iron.
Procedure
A phlebotomist uses a syringe needle to make a tiny puncture in your vein to take your blood sample. Usually, you may not feel more than a mild sting when the needle pricks through your skin into the vein. A small sample of blood is sufficient for a ferritin blood test. Some doctors recommend taking the blood test post a 12-hour fasting period for more accurate results.
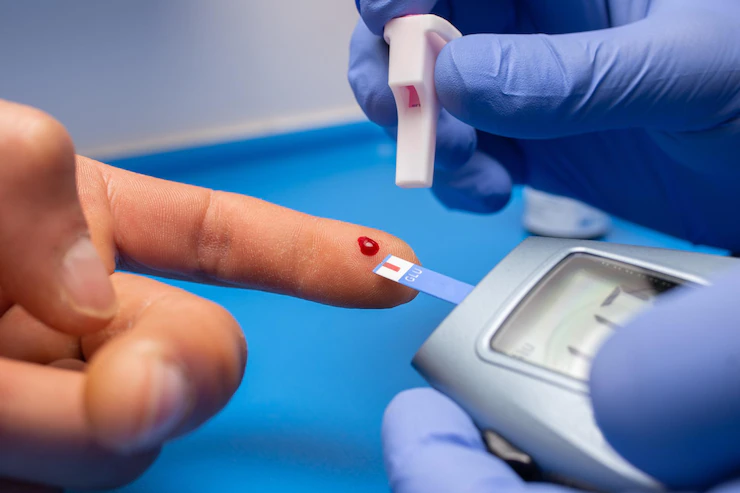
A Ferritin blood test is also available as an at-home test, which may be performed with a small finger prick to draw out the required blood sample.
In addition, your doctor may also advise a full blood count test, HFE gene test and a few other blood tests, along with a ferritin blood test to diagnose your health problem.
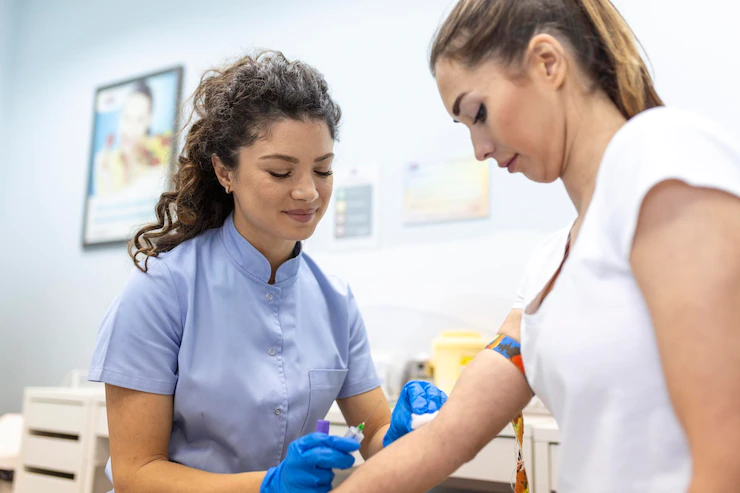
If you are suffering from symptoms of anaemia such as tiredness and weakness, you can take the Welzo Tiredness and Fatigue Blood test, which that uses a combination of markers that help to better diagnose your health problem. Along with ferritin, it includes the following tests:
-
Serum Iron
-
Transferrin Saturation
-
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
-
Vitamin D
-
Thyroid Stimulating hormone (TSH)
-
C Reactive Protein -Highly sensitive test (CRP HS)
Do I need a Ferritin Blood Test?
Symptoms associated with Low Serum Ferritin Level
Your doctor may recommend a ferritin blood test if you are suffering from the following symptoms of low ferritin levels:
-
Tiredness
-
Breathlessness
-
Low energy levels
-
Pale skin
-
Arrhythmia
-
Excessive bleeding
-
Dizziness
Symptoms associated with High Serum Ferritin Level
Your doctor may recommend a ferritin blood test if you are suffering from the following symptoms of high ferritin levels:
-
Joint pain
-
Abdominal pain
-
Abnormal changes in skin tone
-
Tiredness
-
Reduced libido
-
Palpitations
Low Ferritin levels
Low ferritin levels in the body have been associated with the following health conditions:
-
Iron deficiency anaemia
-
Internal Bleeding
-
Chronic infection
-
Excessive menstrual bleeding
-
It may also be caused by certain medications like NSAIDs and antacids.
High Ferritin levels
Elevated Ferritin levels are indicative of the following health conditions:
-
Thalassemia
-
Hemochromatosis
-
Hyperthyroidism
-
Liver disease
-
Alcohol abuse
-
Malignancies
-
Chronic Kidney Disease
Want to learn more about iron deficiency anaemia? Read our article on the symptoms, causes and more.



































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews