How Long Does It Take to Tan?


Related products
What is the Process of Tanning?
The process of tanning is the skin’s natural protective response to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. When your skin is exposed to sunlight, melanocytes—the cells responsible for producing melanin—are triggered into action. Melanin is the pigment that gives your skin its color. The more melanin your skin produces in response to UV exposure, the darker your tan appears. According to Dr. Emma Jones of the Skin Health Institute, “Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen by absorbing harmful UV rays to prevent deeper damage.”
However, the fact that your skin darkens in response to sun exposure is actually a sign of stress. While it may look attractive to some, tanning is a form of mild skin injury. Your skin creates more melanin to shield itself from future harm. That’s why it’s essential to approach tanning with a safety-first mindset, whether you're tanning outdoors or using self-tanning products.
One effective product for achieving an instant, competition-ready glow without prolonged sun exposure is the Pro Tan Instant Competition Color Top Coat Foam With Applicator 207 ml. This foam delivers a deep, bronze finish and is popular among athletes and stage performers who need immediate results.

How Long Does It Take to Tan?
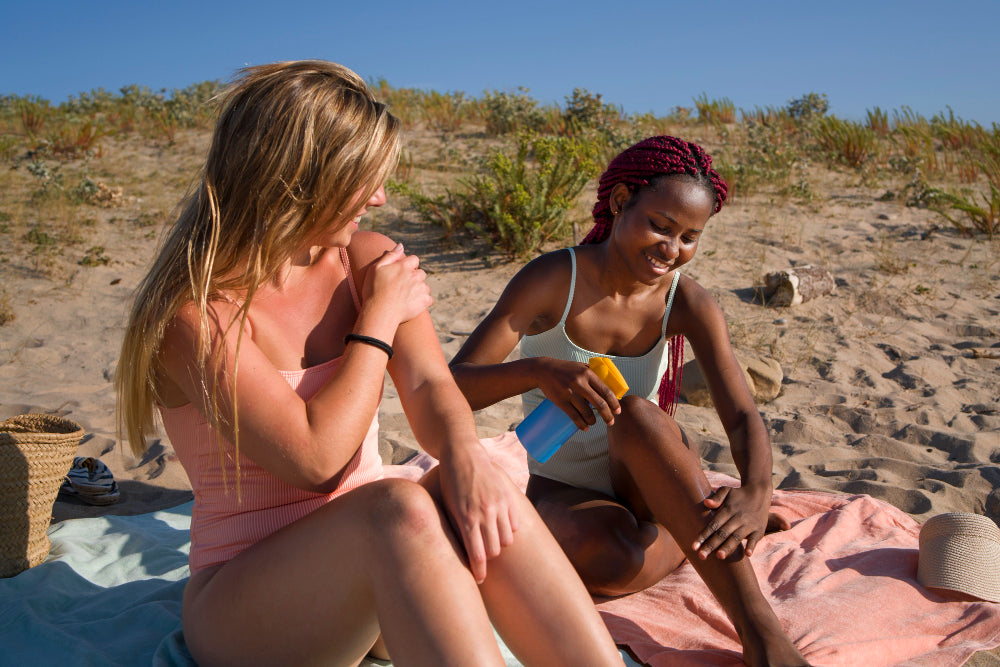
Tanning time can differ significantly depending on various factors, including skin type, geographic location, the time of day, and whether any sun protection is being used. For most individuals, a visible change in skin tone may appear after 1 to 2 hours of sun exposure. However, those with very fair skin might find that they burn before they begin to tan, especially if they spend time in direct sunlight without protection. On the other hand, people with medium to darker complexions may notice a faster tanning effect because they naturally produce more melanin.
If you’re looking for a high-quality sunless tanning solution, Fake Bake Flawless Darker Self-Tanning Liquid Spray 177ml offers a deeper tan while nourishing the skin with botanical ingredients. It dries quickly and leaves an even finish, making it ideal for those looking to tan safely at home.
What Factors Influence the Tanning Time?
Your skin’s ability to tan is influenced by a range of factors, the most important being your skin type, the UV index, and the duration of exposure. Dermatologists use the Fitzpatrick scale to classify skin types from I (very fair, always burns) to VI (very dark, rarely burns). Fair-skinned individuals should tan with extreme caution and start with shorter exposure periods. For darker skin types, the process is more efficient, and the risk of burning is lower, but not entirely absent.
Geographical location and season also determine UV intensity. UV rays are strongest between 10 AM and 4 PM and more intense in tropical climates. According to a report published in the Journal of Investigative Dermatology, high UV levels can enhance melanin production more quickly—but also significantly increase the risk of sunburn, DNA damage, and skin aging.
To highlight your tan while enhancing body contours, try Pro Tan Show Shine Maximum Definition Ultra-Light Competition Posing Oil Spray 118 ml. This lightweight spray adds a radiant finish and is often used in physique competitions.
Safe Tanning Practices to Consider
Despite the popularity of tanning, it’s important to do it safely. Sun exposure helps the body produce vitamin D, but overexposure can lead to sunburn, premature aging, and increased risk of skin cancer. Health experts strongly recommend using broad-spectrum sunscreens with at least SPF 30. The British Association of Dermatologists advises reapplying sunscreen every two hours and after sweating or swimming. Additionally, wear protective clothing and avoid sunbeds, which emit concentrated UV rays that are even more harmful than natural sunlight.
If you're looking to support your skin from the inside out, Orotan Sun Tanning 60 Tablets is a supplement designed to help the body naturally boost melanin production using nutrients like copper, beta-carotene, and vitamin E.
Risk of Excessive Sun Exposure
It’s easy to underestimate the risks of prolonged sun exposure, especially when the weather feels mild. However, even on cloudy days, up to 80% of UV rays still reach the earth’s surface. This means you can still burn or accumulate sun damage without realizing it. Malignant melanoma is one of the fastest-rising cancers in the UK, with more than 16,000 new cases diagnosed every year. Prolonged tanning without protection accelerates the aging process, breaks down collagen, and increases pigmentation irregularities. Early sun protection can reduce these risks significantly.
The SPF collection offers a wide variety of sunscreens designed to defend your skin against both UVA and UVB rays. These products are essential for anyone spending extended periods outdoors, whether tanning or not.
Alternatives to Traditional Sun Tanning
For those who want a tan without UV exposure, self-tanning and sunless bronzing gels offer safe, effective alternatives. They eliminate the risk of burns and reduce the long-term dangers of UV damage. These products are also convenient for achieving an even tan year-round. One standout option is the Pro Tan Two Minute Tan Sunless Bronzer Instant Glow Dark Tanning Gel 237 ml, which delivers instant colour and contains skin-conditioning agents to keep your complexion radiant.
To maintain healthy, radiant skin, be sure to nourish it regularly using high-quality products. The Skin Care collection includes everything from exfoliants to moisturisers that help preserve your glow while keeping your skin barrier intact.
The Importance of Sunscreen for Every Skin Type
Sunscreen isn’t just for fair-skinned individuals—it’s a must for everyone. Melanin may offer some natural UV protection, but it is nowhere near enough to prevent damage. Whether you’re naturally tan or using sunless products, SPF should be a non-negotiable part of your skincare routine. The best sunscreens are broad-spectrum and protect against both UVA (aging) and UVB (burning) rays.
The Sunscreen Skincare collection includes lightweight, non-greasy formulas perfect for layering under makeup or wearing daily as a part of your routine. Choose one that suits your skin type and reapply consistently for maximum protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the safest way to get a tan without sun exposure?
The safest way to achieve a tan without sun exposure is by using self-tanning products such as bronzing sprays, lotions, or gels. These products contain ingredients like DHA (dihydroxyacetone), which react with the outermost layer of the skin to produce a tan-like color. This process doesn't involve UV radiation, so there’s no risk of sunburn or long-term skin damage. For best results, exfoliate your skin beforehand and moisturize afterward to maintain an even tone.
2. Does tanning help clear acne or make it worse?
While some people believe that sun exposure helps dry out acne, the effects are usually temporary and often misleading. UV rays can initially reduce inflammation, but over time, they can lead to increased oil production and clogged pores. Worse still, tanning can darken post-acne scars and make them more noticeable. For acne-prone skin, it’s better to use non-comedogenic self-tanning products and avoid direct sun exposure without SPF.
3. Can you tan while wearing sunscreen?
Yes, you can still tan while wearing sunscreen, but the process is slower. Sunscreens with SPF 30 or higher are designed to block about 97% of UVB rays, not 100%. This means your skin can still produce melanin gradually, which results in a tan over time. The benefit is that you’re protecting your skin from severe burns and long-term damage like hyperpigmentation and premature aging.
4. How do self-tanning tablets like Orotan work?
Self-tanning tablets often contain ingredients such as beta-carotene, copper, and antioxidants that help stimulate melanin production internally. These nutrients support your body’s natural tanning mechanism and may enhance the intensity and longevity of your tan. However, they work best when paired with moderate sun exposure and a balanced skincare routine. They're not a substitute for sunscreen and won’t provide UV protection.
5. What is the difference between UVA and UVB rays?
UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin and are primarily responsible for aging, wrinkles, and long-term damage like collagen breakdown. UVB rays affect the outer layers of the skin and are the main cause of sunburn. Both contribute to skin cancer. That’s why broad-spectrum sunscreens are essential—they protect against both types of radiation and help maintain skin health.
6. Should I exfoliate before applying a self-tanner?
Yes, exfoliating before applying a self-tanner is essential for an even and long-lasting tan. Dead skin cells can cause uneven patches and faster fading if not removed. Use a gentle scrub or exfoliating mitt, focusing on dry areas like knees, elbows, and ankles. After exfoliating, wait about 15–30 minutes before applying your tanning product to ensure your skin is dry and ready.
7. How long does a sunless tan last?
A sunless tan typically lasts between 5 to 10 days, depending on your skin type, the quality of the product, and your post-tan care routine. Moisturizing daily and avoiding harsh exfoliants or long hot showers can extend the life of your tan. Gradual tanning lotions can also be used every few days to maintain color and prevent patchiness.
8. Is it okay to apply fake tan on sensitive skin?
Yes, but with caution. Choose products labeled as hypoallergenic or designed for sensitive skin. Look for formulas free from alcohol, artificial fragrance, and harsh preservatives. Always perform a patch test before full application. If your skin reacts negatively, rinse it off immediately and consult a dermatologist before trying another product.
9. Can tanning cause permanent skin damage?
Yes, both natural and artificial tanning can cause long-term damage. Repeated UV exposure breaks down collagen and elastin, leading to premature aging, sunspots, and increased risk of skin cancer. Even one severe sunburn in youth can double the risk of melanoma later in life. That’s why protective skincare and sun avoidance are crucial components of healthy tanning habits.
10. How can I make my tan last longer?
To prolong your tan, keep your skin hydrated by moisturizing daily and drinking plenty of water. Avoid exfoliating or using products with AHAs or BHAs immediately after tanning. Instead, use gentle, nourishing products. Shower in cool water and pat your skin dry rather than rubbing it. Using a gradual self-tanning lotion every few days can help maintain the color evenly.
11. Can I wear makeup after applying a self-tanner?
Yes, but it’s recommended to wait at least 6 to 8 hours after applying a self-tanner before putting on makeup. This allows the product to fully develop without interference. If you apply makeup too soon, it can affect the final color or cause patchiness. Use clean brushes and avoid oil-based foundations, which may break down the tan faster.
12. What’s the difference between bronzer and self-tanner?
Bronzer is a cosmetic product that temporarily darkens the skin and can be washed off at the end of the day, similar to makeup. Self-tanners, on the other hand, contain active ingredients like DHA that chemically react with your skin’s outer layer to create a tan that lasts several days. Bronzers are great for instant color, while self-tanners offer longer-lasting results.
13. Is tanning safe during pregnancy?
Natural tanning under the sun or on sunbeds is discouraged during pregnancy due to increased sensitivity and the risk of overheating. Hormonal changes can also make your skin more prone to pigmentation (melasma). While most sunless tanners are generally considered safe, always check the ingredients and consult your doctor before use. Avoid aerosol sprays that can be inhaled.
14. How do I prevent self-tanner from staining my hands and feet?
Use a tanning mitt or latex gloves when applying self-tanner. If you apply it with bare hands, wash them thoroughly afterward, especially between the fingers and around the nails. To prevent buildup on dry areas like hands, feet, knees, and elbows, apply a light layer of moisturizer before tanning. Blend well into these areas using a clean brush or sponge.
15. Are tanning beds safer than sun exposure?
No, tanning beds are not safer—in fact, they can be more harmful. They emit concentrated UV radiation that penetrates the skin more deeply, increasing your risk of melanoma and other skin cancers. According to the World Health Organization, tanning beds are classified as carcinogenic. If you want a safer alternative, opt for sunless tanning products that don’t involve UV rays.
Final Thoughts
Getting a tan can be a satisfying aesthetic goal, but it should never come at the expense of your skin’s health. Whether you're basking in natural sunlight or using self-tanners, it’s essential to prioritise protection, hydration, and skin nourishment. Always use sunscreen, choose high-quality tanning products, and give your skin time to rest between exposures. For those who prefer not to risk UV exposure, sunless tanners and bronzers are excellent and safe alternatives that deliver fast, glowing results.
Maintaining your tan is just as important as building it. Stay consistent with moisturisers, avoid harsh exfoliants, and continue using SPF daily to prolong your glow. Most importantly, listen to your skin. If it feels tight, itchy, or inflamed, it’s a sign to rest and repair.
Tanning, when done responsibly, can boost confidence and give a healthy appearance. But safety should always come first. With the right products, smart sun habits, and a commitment to skincare, you can enjoy the sun and keep your skin beautiful for years to come.




















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews