
 Instagram
Instagram
What Happens When You Have PCOS and Go Off Birth Control?


Related products
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex endocrine disorder affecting approximately 10% of women of reproductive age, making it one of the most common hormonal disorders among women in this demographic. The condition is characterised by a variety of symptoms, the severity and combination of which can vary significantly from one individual to another. PCOS is primarily identified by irregular menstrual cycles, hyperandrogenism (excessive levels of androgens), and polycystic ovaries, as visible via ultrasound.
Dr. Emily Thompson, an endocrinologist specialising in PCOS, states, "PCOS is not only about cystic ovaries; the syndrome can manifest with a range of metabolic and cardiovascular health issues, significantly impacting a woman's life." This highlights the multifaceted nature of PCOS, affecting various aspects of health and wellbeing.
Among the treatments for PCOS, hormonal birth control, particularly oral contraceptives, plays a crucial role. These medications are frequently prescribed to normalise menstrual cycles, manage hormonal imbalances, and mitigate the risk of endometrial cancer. This article delves into the significant changes that may occur when individuals with PCOS decide to discontinue the use of hormonal birth control, exploring both the immediate and long-term effects on their health.
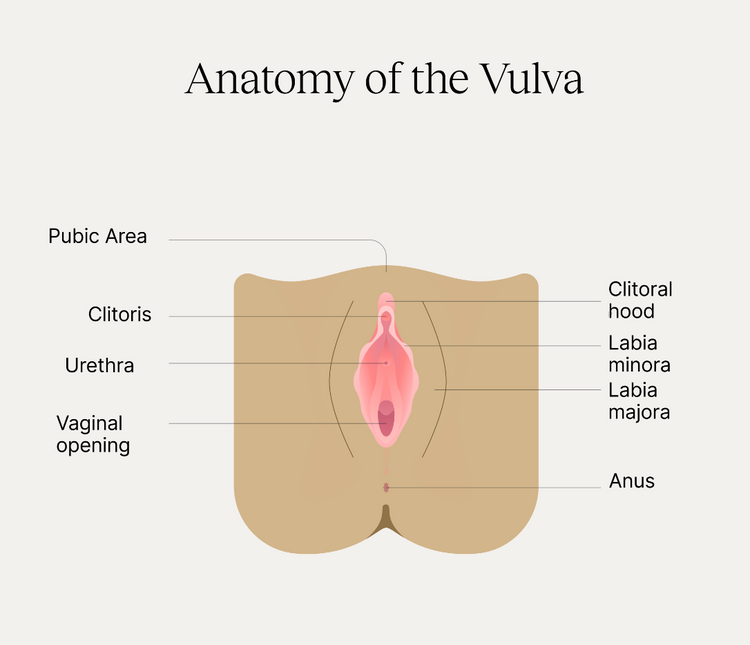
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is defined by a combination of symptoms and signs that are primarily related to hormonal imbalances. These imbalances manifest in various ways, including irregular or absent menstrual periods, which are a direct result of anovulation. Infertility issues commonly arise as ovulation is unpredictable or non-existent in many cases. Excessive hair growth (hirsutism), severe acne, and weight gain are also typical, driven by elevated androgen levels, which are a hallmark of PCOS.
"PCOS symptoms can significantly affect a patient's psychological and physical health, often leading to increased stress, anxiety, and depression," notes Dr. Thompson. This statement underlines the broader impacts of PCOS symptoms on overall quality of life.
Hormonal and Metabolic Impact
PCOS significantly affects hormone levels and metabolism, leading to insulin resistance in approximately 70% of cases. Insulin resistance is a key factor in many of the condition's metabolic issues, including weight gain and the increased risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Moreover, PCOS is associated with abnormal levels of gonadotropins (LH and FSH), which disrupt the natural menstrual cycle.
"The dysregulation of insulin and other hormones in PCOS not only complicates fertility but also contributes to a higher risk of metabolic syndrome," explains Dr. Laura Hughes, a gynaecologist. This metabolic dysfunction can further complicate the management of PCOS, necessitating a comprehensive approach to treatment.
Long-Term Risks
Women with PCOS are at an elevated risk for several serious health conditions, including Type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer. These risks are exacerbated by the associated metabolic syndrome components, such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and obesity, common in PCOS patients.
Statistics indicate that women with PCOS are three times more likely to develop endometrial cancer compared to women without PCOS. "Monitoring and managing these long-term risks is crucial in the care of PCOS patients," asserts Dr. Hughes. This necessity underscores the importance of comprehensive health monitoring for women affected by this condition.
How Does Birth Control Manage PCOS?
Birth control is a cornerstone treatment for managing Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) due to its effectiveness in addressing several core aspects of the condition. Birth Control for PCOS is used to manage PCOS, combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and progestin-only pills are commonly employed. These hormonal contraceptives help regulate the menstrual cycle by providing consistent levels of hormones, which the body is unable to produce reliably on its own due to PCOS. Here are the key ways in which hormonal contraceptives can help manage PCOS:
Regulation of Menstrual Cycles and Symptom Improvement
By administering regular doses of estrogen and progestin, birth control pills help to regulate menstrual cycles, thereby reducing the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer. "Hormonal birth control is effective in reducing the severity of PCOS symptoms, such as hirsutism and acne, by decreasing androgen levels," highlights Dr. Thompson. This benefit is particularly valuable for managing the external manifestations of PCOS.
Beyond Symptom Management
In addition to symptom relief, the use of hormonal contraceptives in PCOS patients provides benefits that extend beyond direct symptom management. These include a potential reduction in the risk of ovarian and endometrial cancers. Dr. Hughes notes, "The protective effect of birth control against certain types of cancer cannot be understated, especially in a PCOS context where the risk of endometrial cancer is significantly heightened."
In conclusion, while hormonal birth control serves as a cornerstone in the management of PCOS, understanding the broader implications of discontinuing such treatment is crucial. This insight is essential for those considering this change, underscoring the importance of a carefully managed transition under medical guidance.
What Happens When You Have PCOS and Go Off Birth Control?
When you have PCOS and stop taking birth control, you may experience a return to irregular menstrual cycles and a resurgence of symptoms such as acne, weight fluctuations, and increased hair growth due to a rebound in androgen levels. Additionally, there might be changes in fertility as natural ovulation can become more unpredictable, potentially improving for some but remaining challenging for others. Managing these changes typically requires a combination of lifestyle adjustments, such as diet and exercise, possibly supplemented by other medical treatments to address specific symptoms or health concerns.
Immediate Changes in Menstrual Regularity
Upon discontinuation of hormonal birth control, individuals with PCOS often experience an immediate return to irregular menstrual cycles. Dr. Helen Foster, a specialist in reproductive endocrinology, explains, "The artificial hormones in birth control provide a semblance of regularity that ceases when the medication is stopped, often leading to the resurgence of irregular periods typical of PCOS." This change is critical as it affects the body's natural hormonal balance and can disrupt daily life.
Resurgence of Symptoms
The cessation of birth control can lead to the re-emergence of typical PCOS symptoms such as acne, excessive hair growth, and significant weight fluctuations. "These symptoms are primarily driven by a rebound increase in androgens, which were previously suppressed by birth control," notes Dr. Foster. Managing these symptoms requires a reassessment of treatment approaches, including both pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical interventions.
Changes in Fertility
Fertility may increase after stopping birth control, as ovulation may resume, albeit irregularly. Dr. Anita Patel, a fertility expert, states, "Many women with PCOS may experience improved fertility upon stopping birth control, but this can vary widely among individuals." Understanding these changes is crucial for those hoping to conceive, as it influences decisions regarding family planning and fertility treatments.
How to Manage PCOS After Stopping Birth Control?
Managing PCOS after discontinuing birth control involves a holistic approach focused on lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Key strategies include adopting a balanced diet with a low glycemic index to control insulin levels, engaging in regular physical activity to help with weight management, and possibly using medications such as Metformin to improve insulin sensitivity or anti-androgens for symptoms like hirsutism and acne. Additionally, regular medical check-ups are crucial to monitor any metabolic changes or cardiovascular risks, and alternative therapies such as herbal supplements and stress management techniques like mindfulness may also be beneficial in alleviating symptoms.
Lifestyle Modifications
Diet Recommendations
A diet with a low glycemic index and anti-inflammatory properties is beneficial in managing insulin resistance associated with PCOS. Nutritionist Sarah Gilbert advises, "Foods that are low in sugar and high in fibre can help manage blood sugar levels, which is crucial for PCOS management." Such dietary changes can also aid in weight management, another significant aspect of PCOS care.
Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is essential in managing weight and improving insulin sensitivity. "Exercise can help mitigate several PCOS symptoms, including weight gain and insulin resistance," says Dr. Foster. A routine that combines aerobic and resistance training is often recommended.
Weight Management Strategies
Effective weight management is critical in reducing the severity of PCOS symptoms and managing insulin resistance. Regular consultations with a dietician or a nutritionist can provide tailored advice to help maintain a healthy weight.
Medications and Supplements
Metformin
Metformin is commonly prescribed to manage insulin resistance in PCOS. "It helps in improving the body's sensitivity to insulin, which can be beneficial in regulating menstrual cycles and promoting ovulation," explains Dr. Patel.
Anti-androgens
For symptoms such as hirsutism and acne, anti-androgen medications can be effective. These medications help reduce the levels of male hormones, which are typically elevated in PCOS.
Inositol Supplements
Inositol, particularly in the form of myo-inositol, is often recommended to enhance fertility in women with PCOS. "Inositol can play a role in improving the quality of eggs and restoring ovulation," says Dr. Patel.
Monitoring and Managing Long-Term Health Risks
Regular health screenings are essential to monitor the risks of diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol. Additionally, due to an increased risk of osteoporosis with PCOS, bone health strategies are critical. Dr. Foster recommends, "Regular calcium and vitamin D intake along with bone density scans can be integral to maintaining bone health in PCOS patients."
What are Alternative Therapies for PCOS?
Alternative therapies for managing PCOS include a range of non-pharmaceutical options that can complement conventional treatments. Herbal remedies, such as spearmint tea, which may reduce androgen levels, and saw palmetto, used for its potential anti-androgen effects, are popular choices. Acupuncture is another alternative therapy that might help in balancing hormone levels and reducing PCOS symptoms like menstrual irregularity and pain.
Additionally, incorporating mindfulness practices and yoga can aid in stress management, which is crucial given the impact of stress on hormonal balance and overall PCOS symptomatology. These alternative approaches can offer supportive benefits and are often used in conjunction with traditional medical treatments.
Herbal Remedies and Acupuncture
Herbal remedies such as spearmint tea and saw palmetto can be used to manage mild symptoms of PCOS. Acupuncture has also been found to help in reducing stress and balancing hormone levels. Dr. Gilbert notes, "These alternative therapies can complement traditional treatments for PCOS, providing holistic care."
Mindfulness and Stress Management
Stress exacerbates PCOS symptoms; therefore, techniques such as mindfulness meditation can be beneficial. "Mindfulness can significantly reduce stress and improve the overall quality of life for those with PCOS," says Dr. Foster.
People Also Ask
How can I live with PCOS without birth control?
Living with PCOS without relying on birth control involves a multifaceted approach. Key strategies include adopting a balanced, low-glycemic diet to manage insulin levels and reduce inflammation, engaging in regular exercise to improve insulin sensitivity and maintain a healthy weight, and possibly using non-hormonal medical treatments such as Metformin to help with insulin resistance. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like mindfulness and yoga can also positively impact PCOS symptoms. Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential to tailor a comprehensive plan that addresses individual symptoms and needs.
How long should you take birth control with PCOS?
The duration for taking birth control to manage PCOS symptoms varies depending on individual health goals, symptom severity, and side effects. For many, birth control is used long-term to help regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and decrease the risk of endometrial cancer. However, if fertility becomes a goal or if significant side effects occur, discontinuation might be considered. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial to evaluate the benefits and potential risks of continued use of birth control.
Why am I gaining weight after stopping birth control PCOS?
Weight gain after stopping birth control in individuals with PCOS can occur due to several factors. One major reason is the potential return of insulin resistance and hormonal imbalances that can increase weight gain, which were previously mitigated by the hormonal regulation provided by birth control. Additionally, stopping birth control may lead to a resurgence of hormonal fluctuations that impact metabolism, appetite, and fat storage. It's important to manage weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise, and to consult with a healthcare provider for strategies tailored to individual metabolic needs and PCOS management.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of PCOS, especially after discontinuing birth control, demands a well-rounded and personalized management strategy. It is essential for individuals to embrace a comprehensive approach that includes both lifestyle modifications and medical interventions. Adjusting one's diet, increasing physical activity, and possibly incorporating medications are all pivotal in managing the symptoms and metabolic challenges of PCOS.
Additionally, exploring alternative therapies can provide supplementary relief and holistic benefits. By maintaining regular consultations with healthcare providers, individuals can ensure that their management plan is effectively tailored to their unique health needs. The journey with PCOS is highly individual, but with the right support and strategies, it is manageable, empowering individuals to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews