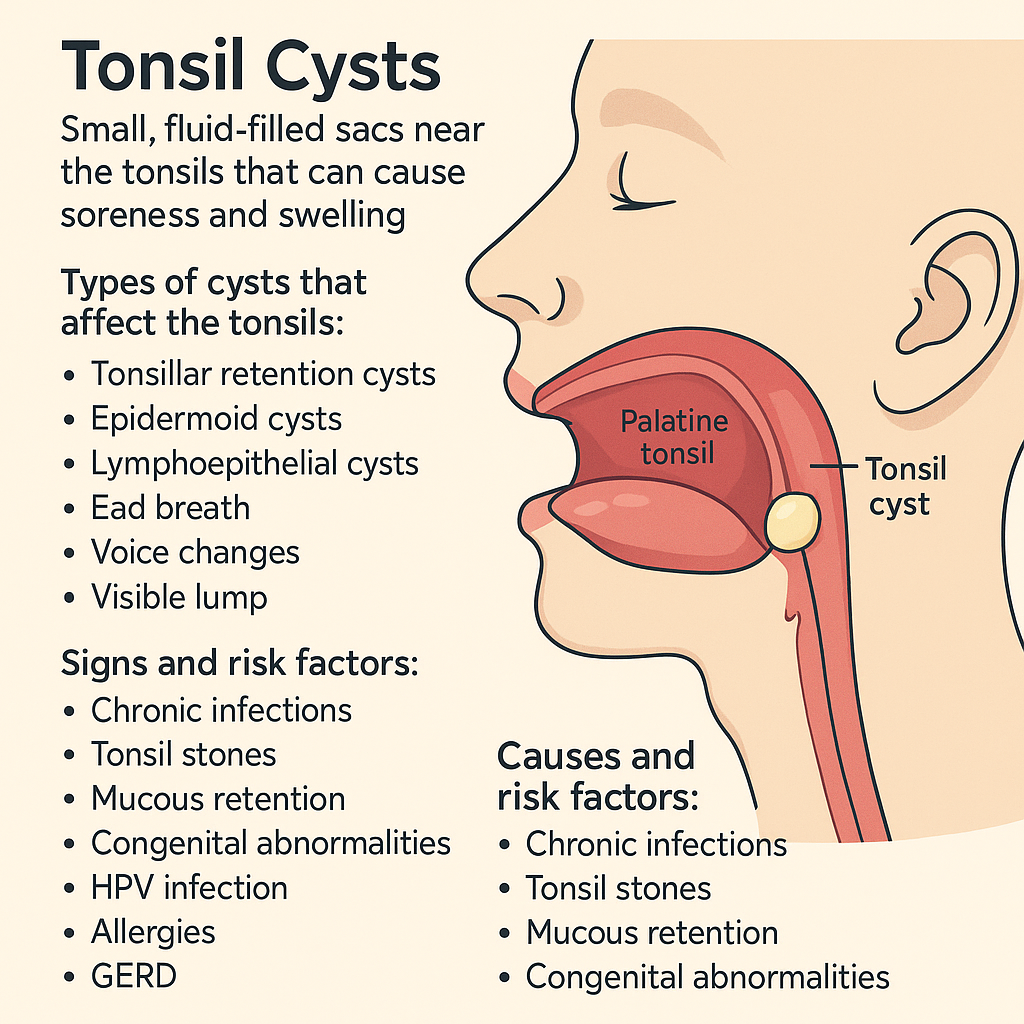
Tonsil Cyst: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment

Tonsil cysts are small, fluid-filled sacs near the tonsils that can cause soreness and swelling, prompting a medical visit. Though less common than tonsillitis, they affect the palatine tonsils—key lymph glands at the back of the throat involved in immune defence. This article covers tonsil cysts’ symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
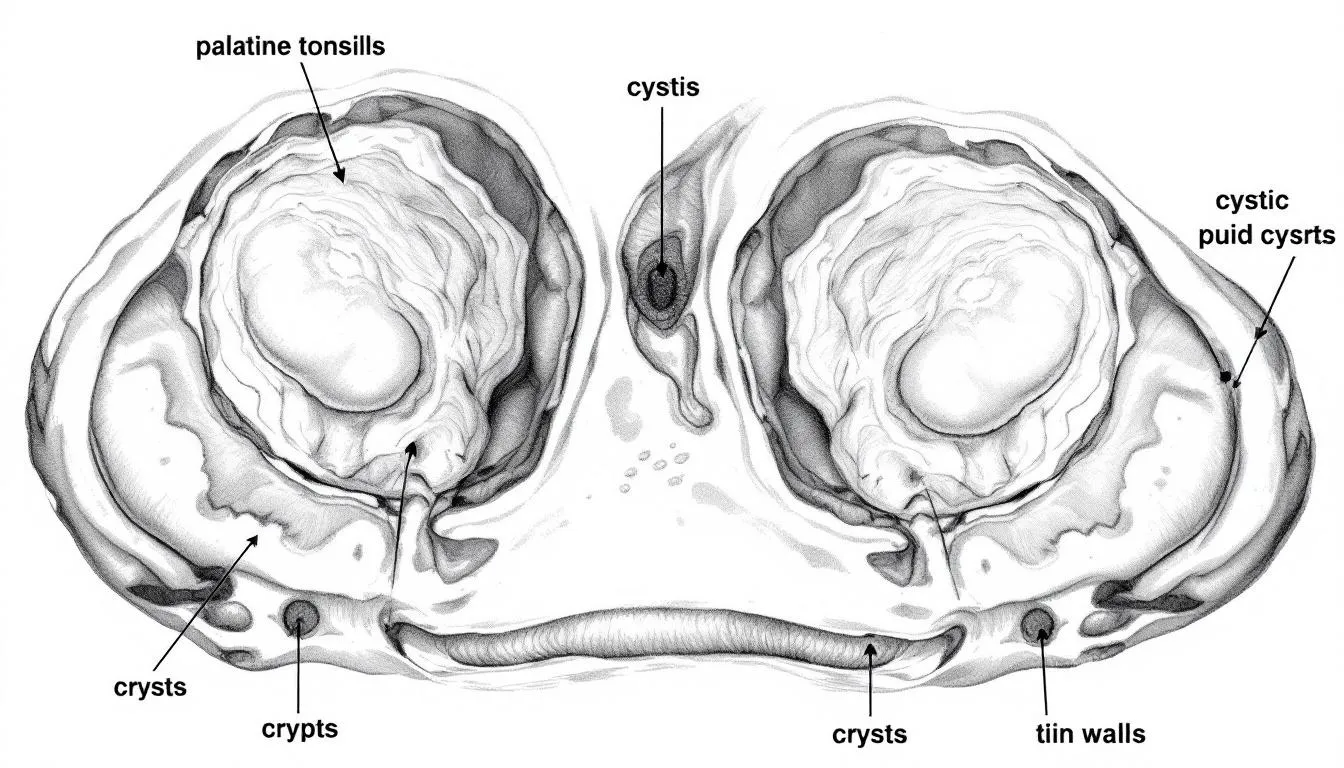
Types of cysts that affect the tonsils include:
Tonsillar retention cysts: These are the most common type, originating from blocked mucus glands in the palatine tonsil, and often lead to dysphagia.
Epidermoid cysts: These benign, keratin-filled lesions are rare in the palatine tonsil, though more commonly seen in other body regions such as the stomach.
Lymphoepithelial cysts: While they often present as papillomatous lesions under the tongue or on the floor of the mouth, they can rarely occur as a cyst in the palatine tonsil. A literature review and case report by Moon JY and Kim JS have described such rare occurrences.
Hydatid cysts: These are also rarely involved in tonsillitis pathology. They develop as a result of a tapeworm known as Echinococcus granulosus.
An epidermoid cyst in the tonsil is a benign, slow-growing, painless mass typically treated by surgical removal or tonsillectomy. A lymphoepithelial cyst is a rare, benign lesion lined with squamous epithelium and lymphoid tissue. The term "tonsillar cyst" broadly refers to any cystic lesion of the tonsil, with tonsillar retention cysts being the most common type caused by blocked mucus glands. Occasionally, tonsil cysts develop without any clear cause.
If you have a sore throat and white or yellow spots or pus on your tonsils, you could have:
Tonsillitis: Swollen tonsils with some yellow or white patches or coating usually characterise this inflammation of the tonsils.
Strep throat: Ear infections can cause this type of bacterial tonsillitis, including large, coated white tonsils.
Infectious mononucleosis: Some of the signs of this virus are recorded to have included the inflammation of the tonsils.
Tonsil stones (tonsilloliths): These are hard deposits of calcium formed from the accumulation of food particles, bacteria, and mucus that become trapped in the tonsil crypts.
A tonsil cyst often appears as a noticeable swelling at the back of the throat. Even if small, it can cause the affected tonsil to enlarge. When only one tonsil is swollen or looks different from the other, it may indicate an underlying issue. If the cyst is on one side, swelling is usually more pronounced on that side. In some cases, the enlarged tonsil can block the airway, making breathing or swallowing difficult. Doctors typically examine the surrounding tissues to evaluate the extent of the swelling or cyst.
A sore throat often accompanies tonsillar cysts, caused by inflammation of the cyst. The pain is typically mild to moderate but can become severe if the cyst becomes infected. Unlike general tonsillitis, the discomfort is usually localised around the cyst area.
As the cyst grows, it can cause dysphagia, making swallowing food difficult. Enlarged tonsils may block the throat, complicating eating and drinking. Some individuals also experience pain while swallowing or a sensation of food being stuck in the throat.
Tonsil cysts can trap germs and debris, leading to halitosis or bad breath. Bacterial buildup, especially if the cyst is infected, causes an unpleasant odour. Even without infection, accumulated mucus and dead cells can produce this symptom.
Though the cyst is located in the throat, it can cause referred ear pain due to shared nerve pathways. Many people with tonsil cysts report dull or sharp pain in one or both ears without any ear infection.
Tonsillar cysts, especially larger ones, can affect the voice by pressing on the vocal cords or blocking airflow, causing the voice to sound weak, hoarse, or nasal.
A tonsil cyst may appear as a swollen white or yellow lump at the back of the throat, often noticed during a routine check or self-examination with a mirror. However, a painless lump in the neck could indicate lymph node involvement and should be promptly evaluated by a doctor, as it may signal cancer spread.
There are several causes which lead to the formation of tonsil cysts. Knowing the causes can assist in the prevention of cyst formation as well as proper care for patients with cysts.
Understanding the risk factors and associated health conditions, such as distinguishing between benign and malignant issues, can help guide the prevention and early detection of tonsil cysts.
Recurring infections in the tonsils cause cysts to form. Inflammation and obstruction of tonsil crypts, which are small spaces in the tonsils, result from recurrent tonsillitis or other infections. Such blockages progress and form cysts because fluid begins to collect in them.
Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are small, usually harmless deposits that form in the tonsil crypts. When they grow or block these spaces, they can contribute to cyst development. Tonsilloliths arise from the buildup of food particles and dead cells.
Tonsil cysts form when mucus builds up in blocked tonsil crypts. Since the tonsils naturally secrete mucus, any obstruction causes it to collect and create a cyst, similar to mucous retention cysts found in other areas, like the sinuses.
Some individuals are genetically predisposed to tonsil cysts due to congenital abnormalities that alter tonsil structure, leading to blockages and fluid buildup.
HPV infection has been associated with cyst formation in the throat, including the tonsils. Certain HPV types can cause benign tumours that develop into cysts. While less common than other causes, HPV should be considered in patients with a history of infection. Additionally, HPV is a known risk factor for oropharyngeal cancer, which can involve the tonsils and nearby tissues.
Prolonged exposure to allergens or irritants can inflame the tonsils, leading to cyst formation. Individuals with chronic rhinitis or postnasal drip are particularly prone to developing tonsil cysts due to ongoing inflammation.
GERD causes acid to reflux into the throat, inflaming the tonsils and potentially leading to cyst formation. Chronic acid reflux increases this risk as the tonsil tissues are repeatedly exposed to stomach acid.

Tonsil cysts can be diagnosed through physical examination, medical history, and some diagnostic tests. In some cases, a doctor may need to order imaging tests to determine the nature of the cyst and rule out malignancy. Therefore, it is important to make the right diagnosis to determine the right treatment.
First, a primary care provider will examine the patient's throat and tonsils physically. If the cyst is large enough, one may be able to see it as a small lump on the tonsil. The doctor might use a tongue depressor to better view the throat. Sometimes, a little camera called an endoscope is used to get a better look at the throat.
If the cyst cannot be easily seen, further diagnostic tests, including ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI, are done to reveal and determine its size. Such tests reveal detailed images of the tonsils and adjacent tissues, which help determine whether the cyst is benign or requires further referral.
If the cyst appears unusual or cancer is suspected, a biopsy will be performed. This involves removing a small tissue sample from the cyst for laboratory analysis to determine whether it is benign, cancerous, or infected.
If an infection is suspected, the doctor may perform throat or blood tests to identify bacterial or viral causes. Determining the exact cause helps guide appropriate treatment, such as prescribing antibiotics or antiviral medications if needed.
There are several ways through which doctors treat tonsil cysts. Most of the time, tonsil cysts do not need intervention; they heal on their own. However, available treatments for tonsil cysts depend on the size, symptoms, and underlying cause. Tonsil cyst treatment may include both non-invasive options, such as observation and medication, and surgical interventions like drainage or tonsillectomy. If the cyst is painful or creates some disturbance, one must visit a doctor or a surgeon.
In rare cases, a tonsil cystic lesion may be diagnosed as tonsil cancer, which requires a different treatment approach. Depending on the stage, treatment may involve surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Early diagnosis is crucial for improved outcomes.
If a tonsil cyst is small and symptom-free, doctors usually recommend monitoring rather than immediate treatment. This approach is common for cysts found during routine exams or when symptoms are mild. Regular check-ups every 3–6 months help track any changes. Many small cysts resolve on their own without intervention, and studies in NHS clinics show that 40–50% of asymptomatic cysts do not progress or require treatment. Routine monitoring is typically sufficient unless new symptoms develop.
Antibiotics are prescribed if the tonsil cyst is caused by or has developed a bacterial infection. This treatment is especially effective for cysts linked to tonsillitis, peritonsillar abscess, or chronic tonsillitis.
Common Antibiotics: Penicillin or amoxicillin is usually taken, but doctors opt for clarithromycin for patients with penicillin allergies.
Duration of Treatment: The average period of antibiotic treatment is 7 to 10 days. For chronic infections, the treatment takes longer or has to be repeated several times.
Efficacy: Antibiotics can help reduce inflammation and pain and prevent the growth of bacteria. Nonetheless, antibiotics cannot remove the cyst unless an infection is present.
Complications: Misuse of antibiotics is one reason antibiotic resistance is a big problem in the UK. In the current world, healthcare providers do not easily prescribe antibiotics to patients since they are unsure of the infection.
Surgical drainage is recommended for large or painful tonsil cysts. This outpatient procedure involves making a small incision to drain the trapped fluid, relieving symptoms like pain, swallowing difficulty, or obstruction. Usually performed under local anaesthesia, recovery is quick, with most patients resuming normal activities within a day or two. While pain relief is immediate, drainage is not a cure; cysts can recur if the underlying cause isn’t treated. Studies show a 20-30% relapse rate after drainage, and in UK clinics, about 15-20% of severe tonsil cyst cases undergo this procedure.
If drainage is ineffective or the cyst recurs, surgical excision may be recommended to fully remove the cyst.
This procedure is usually done for patients who have recurrent cysts in the tonsils or chronic tonsillitis. This is a surgical procedure in which all the tonsils are removed, and it is a permanent solution to cysts and recurrent infections. Even after the tonsils are surgically removed, there is still a small risk of developing cancer in the oropharynx due to possible residual tissue.
Tonsillectomy is performed under general anaesthesia, typically requiring a one-night hospital stay. It is a common procedure, with recovery taking one to two weeks. This surgery is highly effective, curing over 90% of cyst-related issues, especially in patients with chronic tonsillitis. Main risks include post-surgical bleeding and infection, while anaesthesia-related side effects are rare due to advances in surgical techniques. The procedure remains prevalent in the UK, with the NHS performing over 35,000 tonsillectomies annually, primarily for chronic tonsillitis and recurrent tonsil cysts.
Laser ablation is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses laser light to break down and remove cysts. It is a newer treatment option, typically used for minor or superficial cysts as an alternative to traditional surgery.
Laser ablation is usually performed under local anaesthesia, targeting the cyst precisely without damaging surrounding tissues. This reduces inflammation and scarring, leading to faster recovery—most patients resume normal activities within a day or two. Key benefits include high accuracy, shorter rehabilitation, and a lower recurrence rate (10-15%) compared to traditional surgical drainage. Although available in some UK ENT clinics, laser ablation is less common than tonsillectomy or conventional surgery due to higher costs and specialised equipment requirements.
Several home remedies can help ease the symptoms of small tonsil cysts, or for those avoiding surgery, but they only provide symptom relief and do not cure the cyst.
Rinsing the throat with warm saline water can reduce swelling and pain while keeping the area clean and lowering the risk of infection. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are recommended for managing pain and inflammation at home. Staying hydrated and using a humidifier can also soothe a dry or sore throat, helping to ease symptoms.
Tonsil cysts are usually benign but can cause issues if left untreated, especially when large or infected. They often develop slowly as painless lumps and may remain symptom-free until they grow or become infected.
In severe cases, large tonsil cysts can block the airway, causing breathing difficulties. This is a medical emergency requiring immediate attention. Symptoms may include laboured breathing, wheezing sounds, or a sensation of suffocation.
If a tonsil cyst becomes infected, it is called a tonsillar abscess or peritonsillar abscess, where pus collects around the affected tonsil. This condition can cause severe pain, fever, and difficulty swallowing. Medical treatment to drain the abscess is recommended to prevent the infection from spreading.
An infected cyst causes significant discomfort and pain, particularly when swallowing. This can be debilitating, often affecting one’s ability to eat, speak, or sleep properly.
Tonsil cysts may recur after treatment, particularly if the underlying cause isn’t addressed. Factors like chronic infections, allergies, or tonsil stones increase the risk of recurrent cysts.

While it’s not always possible to prevent tonsil cysts completely, addressing the underlying causes can reduce their risk. The following measures can help prevent cyst formation:
Tonsil care focuses on preventing bacterial buildup and debris that cause cysts by maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash help keep the mouth and throat clean.
Patients with chronic allergies should consult their doctor for management strategies. Reducing allergen exposure, using antihistamines, and using nasal sprays can help prevent tonsillitis.
GERD can be managed with diet changes, medication, and lifestyle adjustments to help prevent tonsil cyst formation.
A checkup with a primary care provider can diagnose tonsil cysts early, allowing prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Most tonsil cysts are asymptomatic, so many people do not seek treatment, making their true prevalence unclear. Tonsillar retention cysts, caused by blocked mucus glands, are the most common type. Epidermoid cysts in the mouth and throat are rare, accounting for less than 0.01% of cystic lesions. Authoritative case reports and reviews on tonsil cysts are available from sources like Wolters Kluwer Health.
Tonsils are two oval-shaped lymph glands at the back of the throat that help protect the body by trapping germs entering through the mouth or nose. Tonsil cysts are small, rounded sacs filled with clear fluid that form in or around the tonsils. Although less common than conditions like tonsillitis, they can cause soreness, swelling, and other symptoms that may require medical attention. Types of tonsil cysts include tonsillar retention cysts, epidermoid cysts, lymphoepithelial cysts, and hydatid cysts.
Signs of tonsil cysts include swelling or enlargement of the affected tonsil, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, bad breath, ear pain, voice changes, and a visible lump. Causes range from chronic infections, tonsil stones, mucus retention, congenital abnormalities, HPV infection, allergies, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), to chronic irritation. If you notice these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for diagnosis, which typically involves a physical exam, imaging, lab tests, and possibly a biopsy.
Common complications of tonsil cysts include airway obstruction, recurrent throat infections, chronic pain, and recurrence, making medical attention essential to prevent these issues. Treatment options range from watchful waiting and home care to symptomatic relief, antibiotics, surgical drainage, laser ablation, or tonsillectomy (removal of the affected tonsil).
Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.