
 Instagram
Instagram
Related products
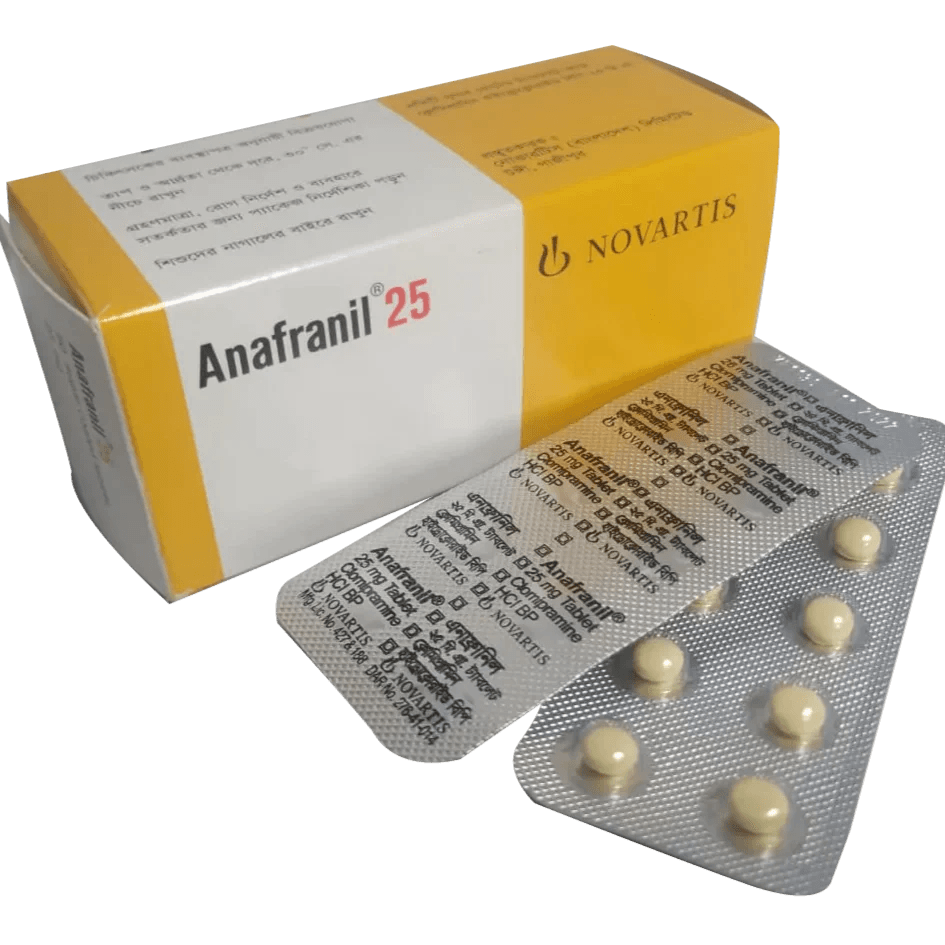
Generic name: clomipramine.
Clomipramine is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA), which is marketed under the brand names Anafranil and others. Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), panic disorder, major depressive disorder, and chronic pain are all treated with it. It can be injected into a muscle or taken orally. Although not thoroughly researched, use during pregnancy seems to be safe, whereas use while nursing is not advised. Serotonin and norepinephrine are prevented from reabsorbing by clomipramine.
The first anafranil was created in 1961, and its medical use was authorized in 1964. It is accessible as a generic drug. With more than a million prescriptions written in 2018, it was the 288th most frequently prescribed drug in the US.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is the main condition that anafranil is used to treat. Obsessions, or recurrent, unwanted thoughts, and compulsions, or repetitive behaviors, are two symptoms of OCD, a type of anxiety disorder. Obsessions and compulsions are frequently present in OCD sufferers. Obsessions are intrusive, unwanted thoughts that can range in severity from mild to extreme. People with OCD feel they must perform repetitive behaviors as compulsions in an effort to reduce their anxiety. Major depressive disorder and panic disorders are also managed with anafranil.
Pharmacokinetics
Clomipramine's pharmacokinetics are linear and dose-dependent. The medication has a 100% oral bioavailability and is well absorbed from the GI tract. Only a tiny fraction (less than 1%) of the unchanged drug, clomipramine, is excreted in the urine because it is extensively metabolized in the liver. Clomipramine has a half-life in plasma of roughly 24 hours. .
Indications
Anafranil is a medication that is prescribed to treat OCD and panic disorder.
Contraindications
Anafranil should not be used by patients with a history of hypersensitivity to clomipramine or any of the other formulation ingredients.
Side Effects
The most frequent negative effects of anafranil are as follows:
- Constipation,
- Trouble sleeping,
- Impotence, and
- Perspiration
Other, less common side effects include weight gain, blurry vision, and dizziness. A rare side effect is mania/hypomania, along with seizures.
Warnings and Precautions
Anafranil should only be used with caution by patients who have a history of seizure disorders or other conditions that lower the seizure threshold. Additionally, the drug should be used with caution by people who have cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, or a history of stroke. Anafranil usage should be cautious in patients who have liver or renal impairment.
Drug interactions
Anafranil may interact with SSRIs, MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and other medications that affect the serotonin neurotransmitter system, among others.
Pregnancy and Lactation
Pregnant women have not been sufficiently and thoroughly studied in relation to anafranil. The drug should only be used while pregnant if the potential benefits outweigh the potential risks to the fetus. Anafranil should not be used by nursing mothers because it excretes in breast milk.
Pediatric use
Anafranil is not supposed to be used by kids.
Geriatric use
Anafranil should be used cautiously because older people are more likely to experience side effects like seizures, cardiovascular collapse, and coma.
Dosage and Administration
Anafranil is available as a capsule or oral solution. For the treatment of OCD, a dosage of 25 mg twice or three times daily is advised. Anafranil is recommended to be taken in doses of 10 mg three times daily for the treatment of panic disorder.
Overdose
An overdose of anafranil is characterized by seizures, coma, and cardiovascular collapse. Supportive and symptomatic treatments are used to treat anafranil overdose. There is no particular treatment for anafranil overuse.














 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews