
 Instagram
Instagram
Related products

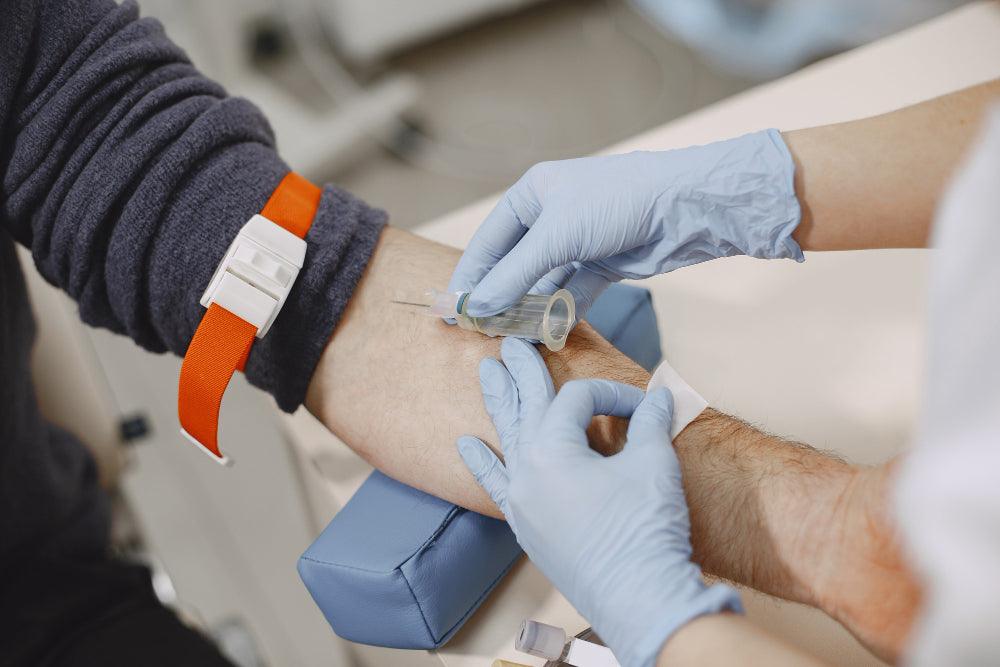
A serological test, also known as a serology test or serological assay, is a laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of antibodies or antigens in a person's blood serum. This type of test is used to diagnose various diseases and infections, including viral infections such as COVID-19, bacterial infections such as syphilis, and autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
When a person is exposed to a foreign substance, such as a virus or bacteria, their immune system produces specific proteins called antibodies that recognize and neutralize the invading pathogen. These antibodies can remain in the bloodstream for weeks, months, or even years after the initial infection, providing long-term protection against future infections from the same pathogen.
Serological tests work by detecting the presence of these antibodies in a person's blood serum. The test involves taking a sample of the person's blood, which is then processed in a laboratory to isolate the serum. The serum is then mixed with a specific antigen or pathogen, and the mixture is observed for any reaction that indicates the presence of specific antibodies.
There are several different types of serological tests, each of which uses a different method to detect and measure antibodies or antigens in a person's blood serum. The most commonly used types of serological tests include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), indirect fluorescent antibody (IFA) test, and western blot test.
ELISA is a widely used serological test that is used to detect the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a person's blood serum. This test works by coating a microplate with a specific antigen or antibody, then adding a sample of the person's blood serum to the plate. If the sample contains the specific antibody or antigen, it will bind to the plate, and the presence of the antibody or antigen can be detected using a colorimetric or fluorescent assay.
IFA is another commonly used serological test that uses fluorescent-labeled antibodies to detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies in a person's blood serum. This test involves applying the fluorescent-labeled antibody to a sample of the person's blood serum, then observing the sample under a microscope for any fluorescence that indicates the presence of the antigen or antibody.
Western blotting is a more advanced serological test that is used to confirm the presence of specific antibodies in a person's blood serum. This test involves separating the person's blood serum proteins using gel electrophoresis, then transferring the proteins to a membrane. The membrane is then exposed to a specific antigen or pathogen, and any antibodies that recognize and bind to the antigen or pathogen can be detected using a colorimetric or fluorescent assay.
Serological tests are an important tool in the diagnosis of many diseases and infections, as they can provide valuable information about a person's immune response to a specific pathogen. They are also used to monitor the progression of some diseases, such as HIV, and to evaluate the effectiveness of vaccines.
In conclusion, a serological test is a laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of antibodies or antigens in a person's blood serum. This type of test is used to diagnose various diseases and infections and provides valuable information about a person's immune response to a specific pathogen. There are several different types of serological tests, each of which uses a different method to detect and measure antibodies or antigens in a person's blood serum. Serological tests are an important tool in the diagnosis and monitoring of many diseases and infections, and they continue to be a valuable resource in the fight against infectious diseases.
Please note that this quiz is for informational purposes only and should not replace a consultation with a healthcare professional.
Serological Test Quiz



































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews