Volume Eating: What Is It and Does It Work?


Related products

What is Volume Eating?
Volume eating, also known as energy density eating or Volumetrics, is a plan or diet that focuses on eating large portions of filling food to maintain weight or to lose it. Volume eating works by including high-volume foods in one’s diet to help them feel full longer. The volume eating method has been used for decades, however, it has recently picked up popularity on TikTok, let’s find out if it actually works.
Does Volume Eating Work for Weight Loss?
Yes, volume eating is considered effective for weight loss. Volume eating allows people to eat more high-volume and low-calorie foods while making them feel full longer. It is important to note that the type of foods eaten falls under the recommended kinds, the goal is to eat foods that are low in carbs and low in calories.
A Penn State University study, done by Dr Barbara Rolls and colleagues, found that individuals who consumed low-calorie-density diets lost more weight over a 12-month period compared to those who consumed high-calorie-density diets, even when both groups consumed the same number of calories, suggesting that this method significantly and positively influences weight loss.
What are the Benefits of Volume Eating?
The benefits of volume eating include weight loss and management, psychological and nutritional benefits, as well as appetite control. Volume eating helps a person maintain their weight or lose it by making them feel fuller for much longer than if they would eat a full-carb diet, for example.
Psychologically, compared to other restrictive diets, the volume eating diet involves larger portions of food which helps a person avoid the feeling of deprivation. Since you can physically see more food on the plate, it does not feel like a typical diet.
Nutritionally, because the volume eating approach involves eating more vegetables, fruits, whole grains and overall nutrient-dense foods, the outcome is eating more nutrients and variety.
Lastly, going hand in hand with the other benefits, volume eating helps with appetite and satiety control as the foods eaten are high in fibre and water which reduces one’s hunger and prevents overeating.
What are the Potential Drawbacks of Volume Eating?
The potential drawbacks of volume eating are nutrient imbalance, digestive issues, socialising challenges, time-consuming, and overeating. As with most diets, there are often possible drawbacks that impact the success of its results.
When limiting the types of foods eaten, it may lead to nutritional imbalances, for example, the volume diet involves healthy carbs which leave out healthy fats. Along the same lines, although the foods eaten are high in fibre, eating too much fibre can cause some discomfort such as bloating and gas.
Depending on how one socialises, volume eating may have an impact on social life if a person finds it difficult to go out to eat or find healthy options on the menu. Following the diet guidelines may also be time-consuming when prepping and even eating high-volume meals. Finally, overeating is still a possibility, because the foods eaten on this diet are considered healthy, and moderation may be ignored leading to gain weight.
How to Volume Eat?
The main step in volume eating is eating high-volume food that is also low-calorie, however, listening to your body is also important and helps prevent overeating. It is helpful to take a look at the Healthy Eating Plate Template or if you need help with 7 healthy Eating Habits. The following include helpful steps to consider:
Choose Low-Calorie-Dense Foods
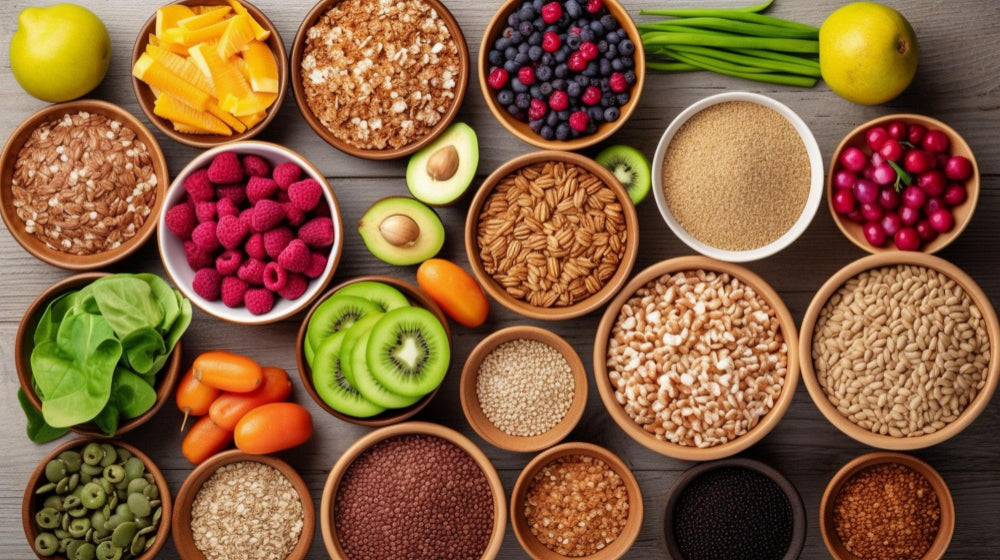
Fruits and Vegetables: Add a variety of fruits and vegetables into your meal, be sure to choose the ones high in fibre and water, such as leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, cucumbers, and tomatoes.
Whole Grains: Eat whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, barley, and oats. Whole grains provide more volume and nutrients compared to their refined counterparts.
Lean Proteins: Add lean proteins into your diet such as chicken breast, fish, beans, turkey, and legumes. Lean proteins are filling and provide essential nutrients without adding an excess in calories.
Broth-Based Soups: Start meals with broth-based soups or include them as part of your meal. They are typically low in calories but can help you feel fuller faster.
Adding High-Fibre Foods
Legumes: Legumes like beans, lentils, and chickpeas are a great source of fibre and protein, which helps you stay full longer.
Whole Fruits: Adding whole fruits over fruit juices helps you get more fibre, which also helps with your digestion and promotes the feeling of fullness.
Vegetables: Prioritise eating vegetables with high fibre content such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, and sweet potatoes.
Practical Meal Planning and Preparation
Meal Prep: Plan and prepare meals in advance to ensure you have access to low-calorie, high-volume foods throughout the week. This can help avoid the temptation of high-calorie, convenience foods.
Portion Control: By using smaller plates and bowls you will be able to control your portion sizes, which helps avoid overeating. Controlling portion size can visually trick your brain into feeling satisfied with less food.
Balanced Meals: Make sure to aim for well-balance meals that includes proteins, healthy carbohydrates, and healthy fats. Even in volume eating, it's important to maintain nutritional balance to avoid deficiencies.
Smart Food Substitutions
Swap High-Calorie Foods: Replace high-calorie ingredients with low-calorie alternatives, such as using cauliflower rice instead of white rice, or instead of pasta, you can use zucchini noodles.
Healthy Snacks: Choose snacks that align with volume eating principles, such as air-popped popcorn, sliced veggies with hummus, or fruit salad.
Mindful Eating Practices
Eat Slowly: By eating slowly you will not only feel full faster and prevent overeating, it will also help you enjoy and savour your food.
Listen to Your Body: Listening to your body is the best guide in figuring out when you are feeling hungry or full, there is no need to eat when you are no longer hungry. Overeating can result in gaining weight and probably a stomach ache.
Hydration: As with most things, drinking water helps immensely. Sometimes, when you are feeling hungry, it might actually mean that you are thirty and after drinking plenty of water your hunger might disappear. Drinking water also helps you feel fuller, which can positively help your diet.
Example Meal Plan
Breakfast: Greek yoghurt with berries and a sprinkle of granola. A side of sliced fruit.
Lunch: Large salad with mixed greens, assorted vegetables, grilled chicken, chickpeas, and a light vinaigrette dressing.
Dinner: Broth-based vegetable soup, a side of quinoa, and steamed broccoli with a lean protein like grilled fish.
Snacks: Carrot sticks with hummus, an apple, or a handful of nuts.

People Also Ask
What are the foods for volume eating?
The main foods for volume eating include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, broth-based soups and high-fibre foods.
Does volume eating stretch your stomach?
No, volume eating does not stretch your stomach. As with most diets no matter what you eat, the stomach expands when one eats but will go back to normal after the food is digested.
Conclusion
Volume eating, or volumetrics, is not a new concept, although it has become popular on TikTok recently. Although volume eating comes with many benefits, it also has some drawbacks and whether it works or not depends on many factors, including personal preference.
Whether you are looking to volume eat or just want to clean up your diet, you can learn about 8 Tips for Healthy Eating and more on Welzo.


































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews