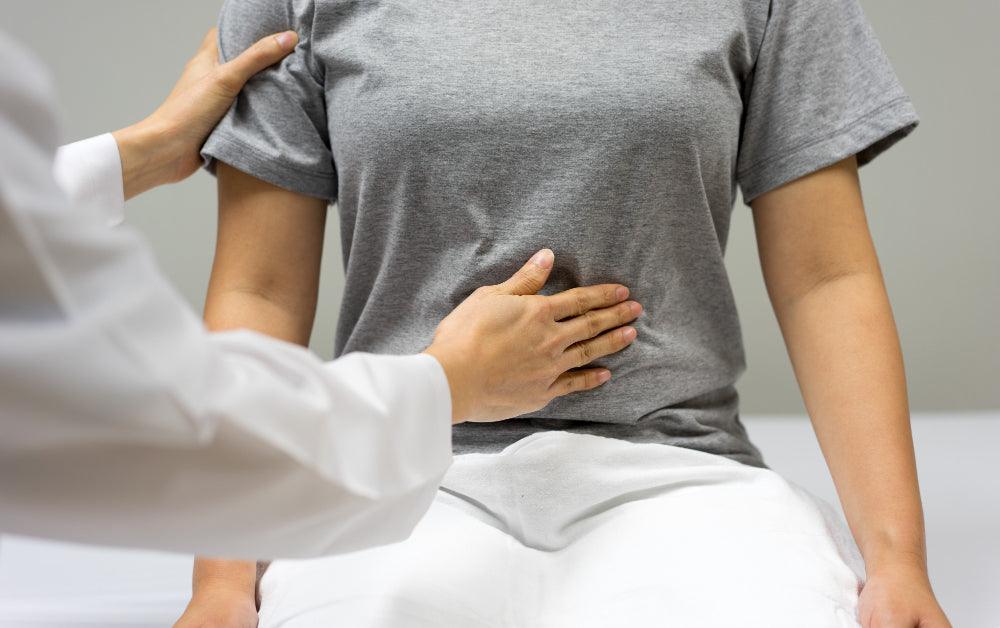
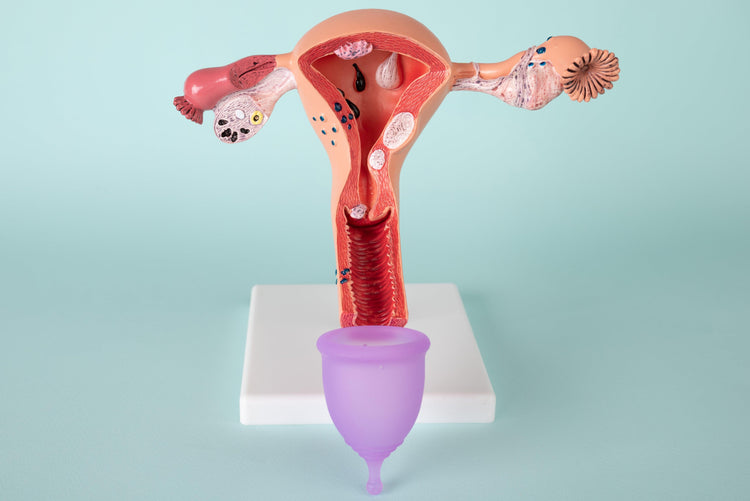
Sudden stabbing pain in the pelvic area
.png?v=1669111892533)

Related products
What’s covered?
Sudden stabbing pain in the pelvic area
Pelvic pain is an area of concern for everyone. If it worries you or someone you know, keep reading this article to clear all your health queries and concerns.
Sharp Pelvic Pain
Pain in the pelvic region isn't necessarily always related to reproductive organs. In fact, referred pain is the kind of painful sensation that can be due to an underlying condition in one part of the body while the pain is felt in any other region. However, it is wise to look out for severe pain as this may signify something more.

Stabbing Acute Pelvic Pain
It is still important to understand that not all but many diseases in the reproductive organs can present themselves as pelvic pain.
1. Severe Abdominal Pain
In certain cases, the abdominal pain can be so severe that the patient would also feel a dull pain in the pelvis.
-
Abdominal pain can be related to a perforated stomach, inflamed appendix, gas problem, irritable bowel syndrome, diarrhoea, constipation, colon inflammation, etc. These are the conditions that need to be immediately treated by the doctor.
-
Females of reproductive age can also experience period cramps, which are painful sensations in the abdomen and pelvis. This pain can be normal when less severe; however, consulting an OB/GYN expert would be a healthy choice if the pain is unbearable.
-
The related cause of sudden abdominal pain can be detected by abdomen palpation, vaginal examination, routine tests, or an ultrasound to detect whether the pain is primarily due to a disease condition in the pelvis or the abdomen.
2. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
As the name suggests, pelvic inflammatory disease is the inflammation of female reproductive organs, including the uterus, attached fallopian tubes, and ovaries.
-
PID is commonly due to a group of sexually transmitted bacteria that stay in the vagina and reach the uterus and ovaries by climbing up the cervix of the female.
-
The doctor should investigate PID thoroughly as untreated cases may lead to infertility due to fallopian tube narrowing, ovaries inflammation, or other uterine deformities.
-
PID can be diagnosed by specimen taken from vaginal examination and sent to a laboratory for culture and identification of the bacteria involved.
-
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor will draw the treatment plan, including antibiotics, according to the cause involved.
3. Painful Bladder Syndrome
Painful bladder syndrome is a spectrum of disorders that ultimately lead to problems associated with urinary bladder pain and dysfunction. Bladder pain is localized, ranging from mild discomfort to excruciating pain.
-
Inflammation of the urinary bladder, also known as interstitial cystitis, causes pressure and pain in the pelvic region due to the inflamed bladder. This pain can also be felt between the vaginal and anal opening in females, while in males, this pain is felt between the scrotum and the anus.
-
The confirmed cause of this condition is not known yet. Still, many experts believe that it is due to the local irritation of urothelium (inner lining of the bladder), hereditary causes, allergies, or other autoimmune conditions.
4. Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
UTI is the infection and inflammation of the urinary tract. A bladder infection is most common along the urinary tract. However, the kidneys may also be affected in some cases.
-
The main cause of UTI is poor hygiene. The proximity of the anus to the vagina makes female populations more prone to suffer from frequent UTIs.
-
Symptoms of UTI include pelvic pain, fever, urge to urinate even when the bladder is empty, burning sensation in the urethra, and bloody urine.
-
UTIs that cause kidney inflammation (pyelonephritis) will also present with pain in the lower back.
5. Ruptured Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are small fluid-filled sacs that rupture during ovulation to release the egg. This occurs 14 days before menstruation in females of a normal and regular menstrual cycle.
-
Rupture ovarian cyst may pass unnoticed or present with mild pain. However, in some cases, this pain may be severe enough with bleeding it needs immediate medical attention, as it may even lead to death in the worst cases.
-
Symptoms of ruptured ovarian cysts usually include sudden stabbing pain and tenderness in the pelvic region, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and bleeding through the vagina.
-
This may be due to trauma to the abdomen or in patients on anticoagulation therapy.

6. Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is the implantation or fixation of the fertilized egg inside the fallopian tube instead of the uterine cavity. Fallopian tube pregnancy may go unnoticed in the initial weeks, but pelvic pain increases to an unbearable length as the fertilised egg continues to grow there.
-
The pain is very severe and requires immediate hospitalization and mass removal.
-
In some cases, the fallopian tube may rupture, which will cause the cutting and removal of the involved fallopian tube, also called salpingectomy.
7. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are fibrous and muscular outgrowths that grow inside or outside the uterus.
-
Uterine fibroids are common in females that present with severe pelvic pain and heavy bleeding during menstruation. Females with uterine fibroids share characteristic iron deficiency anaemia. Thus, these females usually complain of easy fatiguability.
-
Once the fibroids are diagnosed through an ultrasound scan, they can be either treated easily.
-
Treatment aims to remove or constrict the blood supply to these fibroids with the help of prescribed medications or through surgical interventions.
8. Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)
Females with active sexual lives with multiple partners or a single diseased partner can cause sexually transmitted infections.
-
These infections are due to bacteria and viruses that reside in the male and female genital tracts and can get transferred from one partner to another through sexual contact.
-
Chronic pelvic pain and fever are common complaints of females with STIs.
-
STIs are difficult to treat or eradicate completely in cases where most females are unknown to them. However, a doctor may still prescribe certain antibiotics to halt the progression of the bacteria that caused the disease condition.
If you are concerned about your health in any way, you should consult with a doctor. To learn more about women's health, read our Women's Health Hub here.































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews