Everything you need to know about a COVID booster
.png?v=1673516427809)
Related products
Everything you need to know about a COVID booster
COVID-19 vaccines need regular booster doses for the immunity to remain effective.
Vaccines form the mainstay of protection from infections, including the notorious COVID-19. They are used throughout the world for disease control. What are vaccines and vaccinations? A vaccine is developed from dead or weakened germs or their segments. It is a type of active immunity which causes the host immune system to produce antibodies. These antibodies protect against future infections.
But do the effects of a vaccine last forever? The answer is 'No'. Even the most potent vaccines provide immunity for a certain period, after which the immunity begins to fade away. At that moment, a booster vaccine is needed to restore immunity. Why do you need a booster shot? Are you eligible for a booster shot? How a 'booster shot' differs from an 'additional shot'?
Read more about COVID-19 including its emergence, causes, symptoms, control measures, different variants, and available vaccines at Welzo.
What is a COVID booster?
A COVID booster is an additional dose of the COVID-19 vaccine, which is given as soon as the protection provided by the original shot begins to fade away. It is provided when the antibody titre from the first dose is expected to fall.
A booster shot refreshes the immune response, making the infection less likely.
Why is a booster shot needed?
Many COVID vaccines have entered the market months after the outbreak's start. The studies have found that the first shot effectively reduced the disease morbidity, mortality and severity. But, depending on age, immune status and overall health, the effectiveness vanes over time. Moreover, with time, more and more COVID variants (e.g., alpha, delta, omicron etc.) emerged against whom the immune system was not prepared.
The subsequent booster shot covers up this immunity dip and lengthens the immunity duration. The new boosters offer a broader protection spectrum against novel virus variants.
Are you eligible for a booster shot?
The eligibility for a booster shot is decided based on the time gap from the first shot. However, a doctor can give recommendations after viewing the health status, age and pregnancy. The recommendation also depends upon the vaccine used. For example, the WHO has provided different guidelines for different vaccines.
Moderna vaccine
It is an RNA vaccine developed by Moderna, an American biotechnology and pharmaceutical company. It is used in adults over 12 years of age. The guidelines for primary and booster shots are;
-
The first booster shot is required for the high-risk population (frontline health workers, people with a severely weakened immune system and older adults) after 4-6 months of the primary shot. If more time has passed, the vaccine should be given as soon as available.
-
For all of the population over 12 years of age, the booster dose should be given at the same time (4-6 months) after the primary dose.
-
The WHO provides no recommendations for primary or booster shots for children under 12 years.
Pfizer BioNTech
It is also an RNA vaccine developed by Pfizer, an American multinational biotechnology pharmaceutical company. The guidelines for primary and booster doses are the same as for the Moderna vaccine.

Janssen vaccine
It is a vector vaccine developed by Janssen vaccines, Netherlands. The guidelines for use are;
-
This vaccine is recommended for individuals who are aged 18 or more.
-
The WHO recommends administering a booster dose after 2-6 months of the primary dose.
-
The immunogenicity of the vaccine tends to improve with an increased interval. Therefore, the WHO recommends increasing the inter-dose interval to 6 months.
Novavax vaccine
It is a sub-unit vaccine developed by Novavax, an American biotechnology company. It was introduced in late 2021 and showed excellent efficacy in preventing disease and death from COVID-19. The guidelines for primary and booster shots are;
-
This vaccine is recommended for people who are aged 12 or more.
-
A first booster shot is recommended after 4-6 months of the primary shot. The first booster dose should be given to the high-risk group on a priority basis.
-
To further reduce the risk of serious illness and death, the second booster shot is recommended after 4-6 months of the first booster.
-
The clinical trials have generated insufficient information about a booster shot in adolescents (12-18 years).
AstraZeneca vaccine
This vaccine is developed from a modified virus by AstraZeneca, a British-Swedish multinational biotechnology and pharmaceutical company. The guidelines for primary and booster doses are;
-
This vaccine is recommended for all individuals aged 18 or above.
-
A booster dose is recommended after 4-6 months of the primary shot, starting from the high-priority group.
-
The use of this vaccine and its booster dose in children (5-11 years of age) has not been determined.
Do you need a second booster shot?
If you are immunocompromised, the immunity will not develop adequately after the first booster. Therefore, if you are aged 50 or more or are experiencing immunosuppression due to any reason, you need a second booster after 4 months of the first booster for all of the vaccines (Moderna, Johnson and Johnson, Pfizer etc.).
The common indications for a second booster are;
-
The people receiving an organ transplant or stem cell therapy
-
The people undergoing cancer therapy in the recent past
-
People having advanced or untreated HIV.
-
The people using some immunosuppressant drugs, e.g., corticosteroids etc.
Booster shot Vs. Additional shot?
Have you know-how about the additional shot? It is technically not a booster shot, but some people say it is so. It is an additional shot recommended by healthcare authorities in some situations.
The additional booster is often needed because of the following reasons;
-
A weaker immune system will not develop adequate immunity even with a good vaccine. It means it will not be able to produce enough antibodies to combat the infections or reduce the disease severity.
-
A person with a weaker immune system is likely to experience a far more dangerous form of the disease.
-
The natural ability of the immune system to cope with the challenge also decreases with age. So, one or two booster doses may not give full protection.
Keep in mind that the booster and additional shots differ from each other. The booster shot is administered to those who have received the first vaccination and whose immunity has been diminished over time. In contrast, the additional shot is recommended for the people who have received the booster shot, but their poor immune system has dictated the need to receive the additional shot to supplement the effects of the basic vaccination series.
So, an additional shot is not for everyone, and you should consult the local health authorities to know your eligibility for this shot.
Monovalent Vs. Bivalent boosters
Recently, a new booster, the mRNA booster shot, has entered the market, which is often recommended for people with a weak immune system and who have received a third dose of the Moderna or Pfizer vaccine. These bivalent boosters have gained importance since the emergence of COVID variants. What are these?
A bivalent booster vaccine combines two viral strains, while a monovalent booster contains only one strain or viral component.

The coronavirus genome is rapidly changing and giving rise to many new variants. We have detailed the differences between the three common variants, delta, omicron and deltacron in another article. Click here to read it.
How are bivalent vaccines useful?
The bivalent boosters are named because they provide protection against the original virus and are effective against the new omicron variants BA.4, BA.5. The previous 'monovalent' boosters provided immunity only against the original virus.
The older monovalent boosters also provided protection against the omicron, but the level of protection is lower than that of the bivalent boosters. Two COVID-19 vaccine manufacturers, Moderna and Pfizer have developed the bivalent boosters.
Can a booster shot cause any side effects?
COVID-19 vaccine boosters can cause some side effects in the initial days similar to those caused by the primary vaccine, e.g., a swollen arm and soreness at the local site. Some people may experience tiredness, headaches, body aches, swollen lymph nodes, joint or muscle pain and fever.

However, there is little to worry about these symptoms as they don't reflect a disease; they mean that your immune system is responding to the vaccine and rapidly developing antibodies. These effects are not experienced by all people and will disappear with time. However, serious side effects, e.g., severe allergic reactions, should be reported to the doctor.
How to know if your COVID-19 vaccination status is up to date?
The information changes from time to time, and only the local health authorities have the mandate to provide recommendations. But the current recommendations by the WHO are;
-
Your COVID-19 vaccination status is considered up to date if you have completed the basic series of the COVID vaccines and received the most recent monovalent or bivalent booster as recommended.
-
You have received the primary shot but are not eligible for the booster doses.
-
After receiving all the recommended doses, you suffered from a COVID-19 infection. You no longer need any additional booster shots.
However, continue to consult with the local health authorities, who will decide the recommendations for you based on your age, the vaccine to be used and the time duration from the last dose.
Do you need boosters if you have had a COVID-19 infection in the past?
A natural infection works similarly to a vaccine. It also provides active immunity. So, the recommendations for a basic or a booster dose should also consider your infection status. The recommendation by the WHO is;
-
Suppose you have recently had a coronavirus infection. In that case, you can delay your next dose (both primary and a secondary booster) for 3 months starting from the day when the signs and symptoms of infection appeared or, in case of asymptomatic infection, start from the day when you have tested positive.
What is the rationale behind it?
A natural infection also produces strong immunity, and the risk of reinfection is lower in the weeks and months after a natural infection. However, vaccination may be recommended sooner due to some reasons, e.g., a higher personal risk of getting a severe infection, a higher risk of severe disease in the close ones and the emergence of novel variants that may cause an infection earlier than expected.
Consult the local health authorities for better advice.
What are the seasonal boosters?
The concept of seasonal boosters is very similar to an additional shot except that a seasonal booster is recommended before the expected onset of a seasonal spike in the cases, while the additional shot is recommended to provide more immunity to the immunocompromised people.

The seasonal boosters are recommended for the following people;
-
People who are aged 50 or more
-
People aged less than 50, but some factors, e.g. the use of immunosuppressant drugs, circulatory and heart diseases, etc., have rendered them more susceptible.
-
The people who are aged 5 or more but are living with some elder who has a weak immune system and are at a higher risk of infection.
-
For pregnant women
-
For front-line social and health workers
How long do the effects of a booster last?
The protection provided by a booster shot lasts for a considerable length of time provided that you have a sound immune system and all the protocols of the vaccination handling and administration were strictly followed.
The effectiveness of the mRNA-1273 booster shot against the coronavirus infection in immunosuppressed adults was evaluated in a study published in the Clinical Infectious Diseases (the official journal of the Infectious Disease Control Society of America) in 2022. The data was compared to the people receiving 2-dose mRNA-1273 primary series. It was noted that the booster dose effectively protected against infections, hospitalisations and deaths.
How long does a booster shot take to provide effective protection?
The booster shot provides a high degree of protection within 1-2 weeks of administration, and many studies have proved it. But, it again depends upon your health condition, the dose administered, the vaccine used, etc.
What should you do in case you have missed the booster?
Although the Government has made rigorous efforts to ensure vaccine availability, you can still miss a dose for various reasons. What should you do? Should you restart the vaccination program?
There is no need to repeat the earlier dose even if you have missed the booster dose at any time. You can book a booster dose as long as you are eligible for it and at least three months (depending upon the vaccine used) have passed since the earlier dose.
Bottom-line
The widespread vaccination was started to combat the coronavirus infection (like the flu vaccine in the past).
The immunity provided by the primary shot vanes after some time. So, a booster shot is needed to cope with the expected dip in immunity.
Some people may need a third additional or seasonal shot as recommended by the local health authorities after a thorough review of their health status and relative risk. A booster shot doesn't mean you have no risk of getting an infection; it reduces the risk of acquiring it.
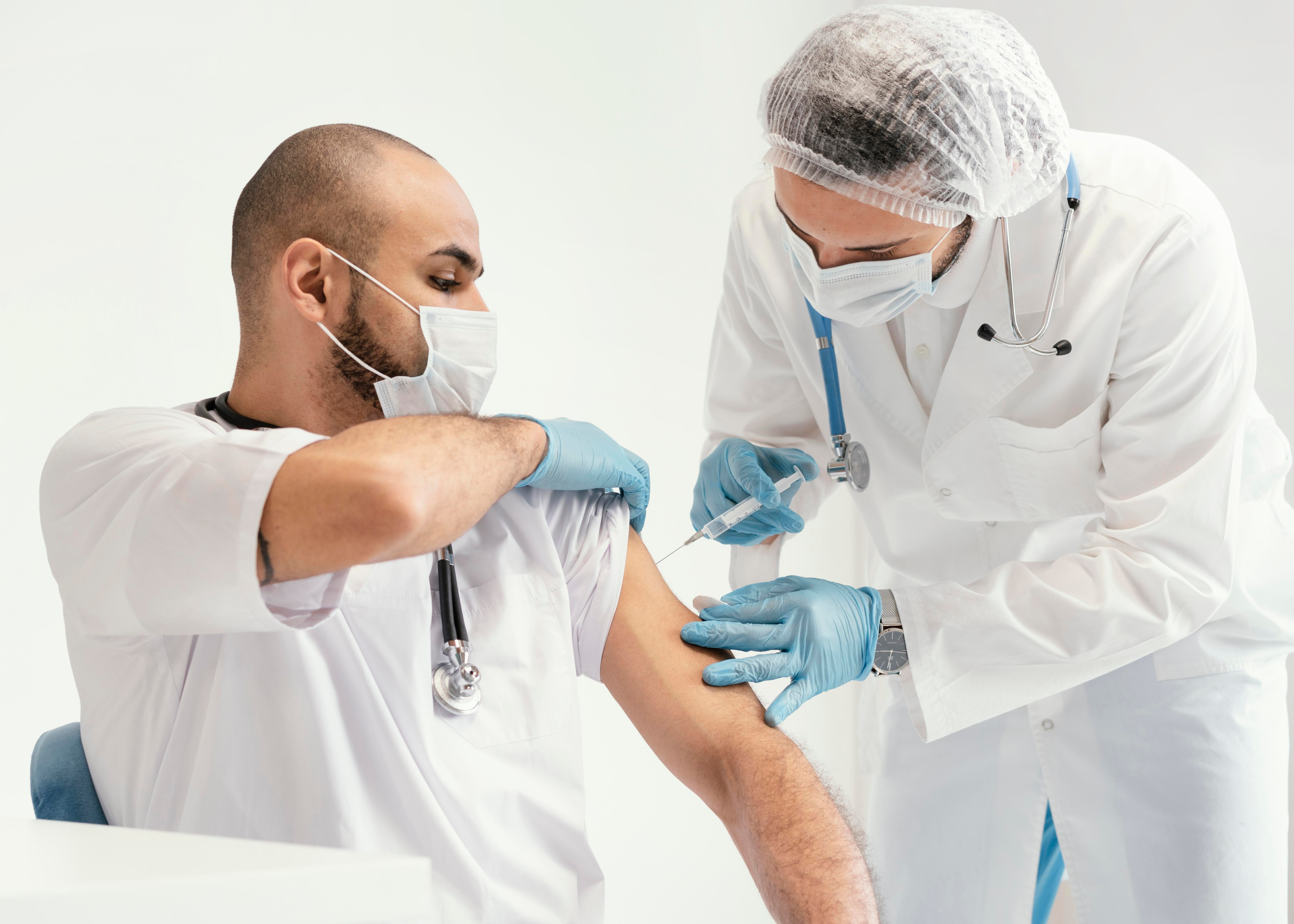
The article has detailed some important information related to the COVID boosters, their types, administration schedules and other recommendations. This information should be viewed as a guide only, and only the local health authorities have the ultimate authority to recommend the boosters.
At Welzo, we have products to help you with your symptoms. Click here to learn more.
If you have symptoms of the coronavirus infection, you need a screening test for diagnosis. Our COVID-19 Antibody Blood Test is an accurate and fast test that can help you detect antibody levels over time. The test can be conducted at home and need a single finger prick. Click here to order your test kit.
Find more products and information at our online pharmacy, click here to learn more.







 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews