Allergic Asthma: Understanding and Managing Asthma Triggered by Allergens

Related products
Definition of Allergic Asthma
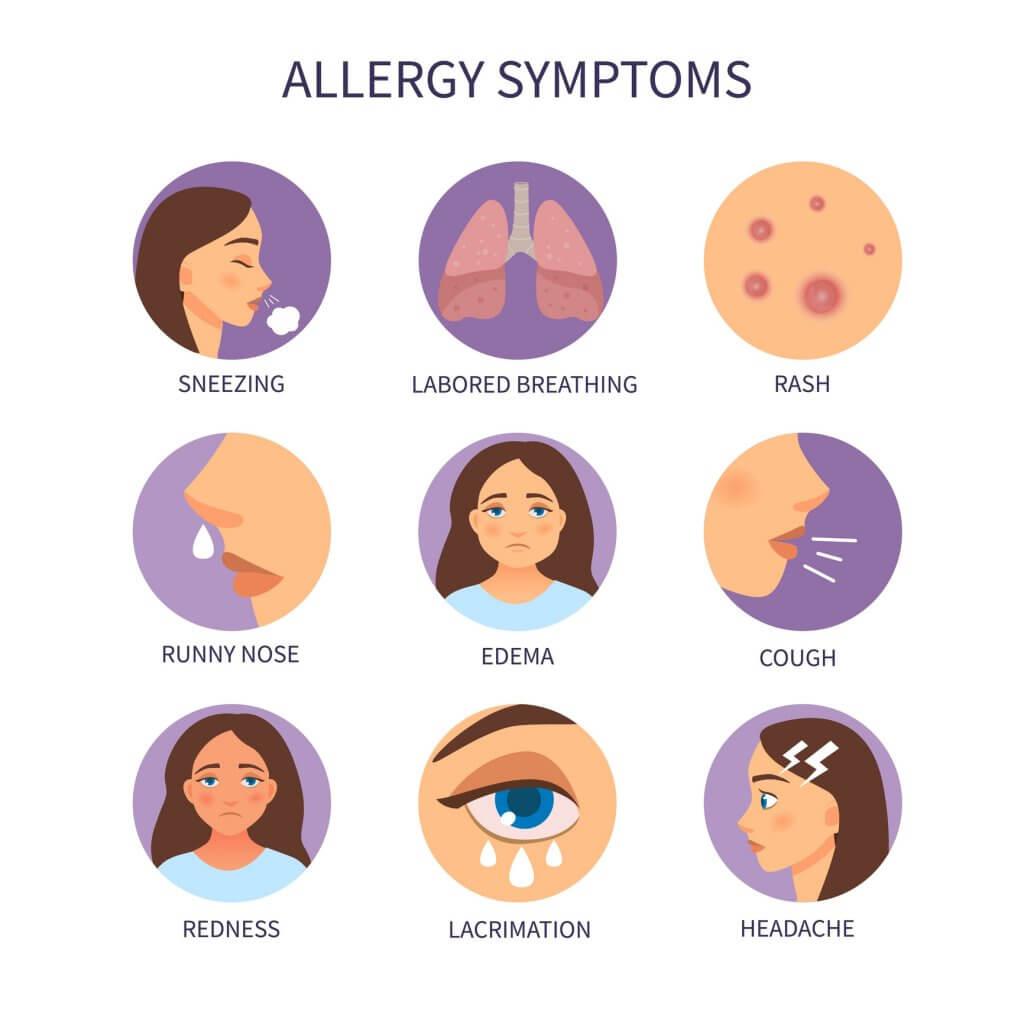
Allergic asthma, a common form of asthma, is a chronic respiratory condition triggered by exposure to allergens. When an individual with allergic asthma encounters allergens, their immune system overreacts, resulting in inflammation of the airways and difficulty breathing. According to Dr. Samantha Walker, Deputy Chief Executive of Asthma UK, "Allergic asthma is a type of asthma where a person’s symptoms are triggered by allergens, which can cause the airways to become inflamed and narrow, leading to asthma symptoms such as wheezing, coughing and difficulty breathing.".
What is Allergic Asthma?
Allergic asthma is a type of asthma in which an individual's asthma symptoms are triggered by exposure to specific allergens. When a person with allergic asthma comes into contact with these allergens, their immune system overreacts, leading to inflammation and constriction of the airways. This results in difficulty breathing, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath, which are all common symptoms of an asthma attack.Managing allergic asthma starts with identifying and avoiding allergens. In many cases, over-the-counter products can play a big role in controlling symptoms and preventing reactions.
-
Piri Allergy Relief is a trusted antihistamine brand that helps manage common allergy symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes—reducing the likelihood of asthma flare-ups caused by seasonal or environmental allergens.
-
Becodefence is a preventative nasal spray that forms a barrier against airborne allergens, helping to stop symptoms before they start. This makes it ideal for people with allergic asthma who want to take a proactive approach to allergy control.
Both products support allergy prevention and symptom relief—key components in effectively managing allergic asthma.
What other terms for allergic asthma?
Other terms for allergic asthma include extrinsic asthma or allergy-induced asthma. These terms emphasise the fact that the condition is triggered by external allergens rather than factors internal to the body, such as stress or exercise, which can also trigger asthma symptoms in some individuals (referred to as intrinsic asthma or non-allergic asthma). To learn more about asthma, read our comprehensive guide that covers: Asthma - Symptoms, Causes and Treatments. To learn more about Allergies, read our comprehensive guide that covers: Allergies:, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment options. If you are looking for treatments for hay fever or general allergens, then visit our extensive page with allergy and hayfever medication and tablets.
Prevalence of Allergic Asthma
It is estimated that around 60-80% of people with asthma suffer from allergic asthma (European Respiratory Journal). In the UK, approximately 5.4 million people are affected by asthma, with a significant proportion experiencing symptoms triggered by allergens. Understanding and managing allergens are crucial for individuals with allergic asthma to prevent exacerbations and improve their quality of life.
Importance of Understanding and Managing Triggers
Effectively managing allergic asthma begins with understanding the allergens that trigger symptoms. Dr. Robert Wood, President of the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, emphasises the importance of identifying triggers, stating, "Knowing what allergens are causing your symptoms is the first step towards effectively managing your allergic asthma" (AAAAI). By identifying and avoiding allergens, individuals with allergic asthma can significantly reduce the risk of asthma attacks and improve their overall health. In many cases, individuals use supportive treatments such as antihistamine-based sprays like Otrivine Allergy Relief Nasal Spray (10ml), which can relieve nasal symptoms related to allergic rhinitis—often a comorbidity of allergic asthma.
Causes of Allergic Asthma
Overview of Allergens
Allergens are substances that can trigger an allergic reaction in susceptible individuals. In the context of allergic asthma, allergens cause the immune system to overreact, resulting in inflammation and constriction of the airways. Professor Stephen Durham, Head of Allergy and Clinical Immunology at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London, explains, "In allergic asthma, the immune system mistakenly identifies a usually harmless substance as a threat, producing an inappropriate response that leads to the symptoms of asthma" (RBHT).
Common Allergens that Trigger Asthma
There are numerous allergens that can provoke allergic asthma symptoms. The following are some of the most common:
Pollen
Pollen from trees, grasses, and weeds can trigger allergic asthma symptoms in sensitive individuals. According to Asthma UK, around 80% of people with asthma report that their symptoms worsen during the pollen season (Asthma UK). Pollen can be inhaled directly or carried indoors on clothing, pets, and through open windows, making it difficult to avoid completely.
Animal Dander
Animal dander, or microscopic skin particles shed by animals with fur or feathers, is another common allergen that can trigger allergic asthma. Dr. Graham Roberts, Consultant in Paediatric Allergy and Respiratory Medicine at Southampton General Hospital, highlights the impact of animal allergens on allergic asthma, stating, "Pet allergens are a major trigger for allergic asthma, with cats and dogs being the most common sources" (UHS). Allergic reactions to animal dander can be immediate or delayed, making it challenging to identify the source of the problem.
Mould Spores
Mould spores, tiny reproductive units produced by mould and fungi, can also cause allergic asthma symptoms. Mould spores are prevalent in damp or humid environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Dr. Andy Whittamore, Clinical Lead for Asthma UK, explains the link between mould and asthma, stating, "Mould spores can trigger asthma symptoms in some people, especially if they are allergic to mould or have a sensitivity to damp environments" (Asthma UK). Proper ventilation and moisture control are essential to reduce mould growth and mitigate allergic asthma symptoms.
Cockroach Droppings
Lastly, cockroach droppings are another allergen capable of triggering allergic asthma. According to a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, exposure to cockroach allergens significantly increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalisations and emergency room visits (JACI). Effective pest control measures and maintaining a clean environment are crucial to minimise exposure to cockroach allergens.
Nasal sprays like Olbas Nasal Spray (20ml) can help relieve congestion caused by some of these allergens, improving breathing comfort.
Identifying Your Allergic Asthma Triggers
Importance of Knowing Your Triggers
Knowing your specific allergic asthma triggers is essential for effective management of the condition. By identifying and avoiding allergens, you can reduce the likelihood of asthma attacks and improve your overall quality of life. Dr. Samantha Walker of Asthma UK emphasises the importance of identifying triggers, stating, "Understanding the specific allergens that trigger your asthma is the first step towards tailoring your treatment and reducing your risk of symptoms and asthma attacks" (Asthma UK).
Allergy Testing
To identify your allergic asthma triggers, a healthcare professional may recommend allergy testing. There are several types of allergy tests available:
Skin Prick Test
The skin prick test is a common method for identifying allergens. During the test, a small amount of allergen extract is placed on the skin, which is then pricked with a needle. If a raised, red bump appears, it indicates an allergic reaction to the allergen. This test can help identify triggers such as pollen, dust mites, and animal dander.
Animal Dander
Animal dander, or microscopic skin particles shed by animals with fur or feathers, is another common allergen that can trigger allergic asthma. Dr. Graham Roberts, Consultant in Paediatric Allergy and Respiratory Medicine at Southampton General Hospital, highlights the impact of animal allergens on allergic asthma, stating, "Pet allergens are a major trigger for allergic asthma, with cats and dogs being the most common sources" (UHS). Allergic reactions to animal dander can be immediate or delayed, making it challenging to identify the source of the problem.
Mould Spores
Mould spores, tiny reproductive units produced by mould and fungi, can also cause allergic asthma symptoms. Mould spores are prevalent in damp or humid environments, such as bathrooms, kitchens, and basements. Dr. Andy Whittamore, Clinical Lead for Asthma UK, explains the link between mould and asthma, stating, "Mould spores can trigger asthma symptoms in some people, especially if they are allergic to mould or have a sensitivity to damp environments" (Asthma UK). Proper ventilation and moisture control are essential to reduce mould growth and mitigate allergic asthma symptoms.
Cockroach Droppings
Lastly, cockroach droppings are another allergen capable of triggering allergic asthma. According to a study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, exposure to cockroach allergens significantly increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalisations and emergency room visits (JACI). Effective pest control measures and maintaining a clean environment are crucial to minimise exposure to cockroach allergens.
How Allergens Trigger Asthma Symptoms
When an individual with allergic asthma encounters an allergen, their immune system reacts inappropriately, leading to inflammation and constriction of the airways. This process can be broken down into two main components:
The Immune System's Response
In individuals with allergic asthma, the immune system mistakenly identifies harmless allergens as harmful substances, resulting in an overreaction. When exposed to an allergen, the immune system produces immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies. These antibodies bind to the allergen and cause the release of inflammatory chemicals, such as histamine, from immune cells called mast cells. Dr. Samantha Walker of Asthma UK explains, "The release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals leads to the classic symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as itching, redness, and swelling" (Asthma UK).
Inflammation of the Airways
The release of histamine and other inflammatory chemicals causes the airways to become inflamed, making them more sensitive and prone to constriction. Inflammation can also lead to an increase in mucus production, further narrowing the airways and making it difficult to breathe. Professor Stephen Durham, Head of Allergy and Clinical Immunology at the Royal Brompton Hospital, London, states, "In allergic asthma, the inflammation of the airways caused by the immune system's response to allergens results in the classic symptoms of asthma, such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath" (RBHT).
Identifying Your Allergic Asthma Triggers
Importance of Knowing Your Triggers
As previously mentioned, knowing your specific allergic asthma triggers is essential for effective management of the condition. By identifying and avoiding allergens, you can reduce the likelihood of asthma attacks and improve your overall quality of life.
Allergy Testing
When identifying your allergic asthma triggers, a healthcare professional may recommend allergy testing. As previously discussed, there are several types of allergy tests available, including the skin prick test, blood test, and challenge test. These tests can help pinpoint the allergens responsible for your symptoms and guide the development of a tailored treatment plan.
Maintaining a Symptom Diary
Keeping a symptom diary is another valuable tool for identifying allergic asthma triggers. By recording your symptoms, their severity, and the circumstances surrounding each episode, you can help your healthcare professional identify potential allergens and implement effective strategies to avoid them.
Correlating Allergens and Asthma Attacks
Once you have identified your allergic asthma triggers, it's essential to recognise the correlation between allergen exposure and asthma attacks. Understanding these connections can help you implement effective strategies to avoid allergens and reduce the risk of future asthma exacerbations.
Managing Allergic Asthma Triggers
General Strategies for Allergen Avoidance
As previously mentioned, there are several general strategies for allergen avoidance that can benefit individuals with allergic asthma. These include regular cleaning, using allergen-proof mattress and pillow covers, opting for hard flooring instead of carpets, using air purifiers with HEPA filters, and maintaining proper ventilation.
Specific Allergen Avoidance Measures
In addition to general strategies, there are specific allergen avoidance measures you can take based on your identified triggers, such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, mould spores, and cockroach droppings. Implementing these measures can help reduce your exposure to allergens and minimise the risk of asthma attacks.
Medications to Control Symptoms
Alongside allergen avoidance, various medications can help control allergic asthma symptoms:
Inhaled Corticosteroids
Inhaled corticosteroids are commonly prescribed for allergic asthma to reduce inflammation in the airways. These medications, such as fluticasone and budesonide, help to prevent asthma symptoms and improve lung function. Medications such as Clenil Modulite are commonly used to reduce inflammation in the lungs and prevent asthma symptoms. Dr. Andy Whittamore of Asthma UK emphasises the importance of inhaled corticosteroids, stating, "Inhaled corticosteroids are the cornerstone of asthma management, helping to reduce airway inflammation and prevent asthma attacks".
Short-Acting Beta-Agonists (SABAs): For quick relief, a bronchodilator like the Ventolin Inhaler is widely used to open up airways during an asthma attack.
Long-Acting Beta-Agonists
Long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs) are bronchodilator medications that relax the muscles around the airways, improving airflow and making it easier to breathe. LABAs, such as salmeterol and formoterol, are often prescribed in combination with inhaled corticosteroids for individuals with moderate to severe allergic asthma.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines, such as cetirizine and loratadine, can help relieve allergy symptoms by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released during an allergic reaction. Antihistamines may be taken orally or used as nasal sprays, and are often used alongside other asthma medications to help manage allergic asthma.
Leukotriene Modifiers
Leukotriene modifiers, such as montelukast and zafirlukast, are oral medications that work by blocking the action of leukotrienes, chemicals involved in the inflammatory response. These medications can help reduce asthma symptoms and improve lung function in individuals with allergic asthma.
Another option for immediate symptom relief is the Salamol Inhaler, which acts quickly to ease breathing by relaxing muscles around the airways.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots or desensitisation, is a treatment option for some individuals with allergic asthma. This therapy involves gradually
introducing small amounts of an allergen to the body, allowing the immune system to become desensitised to it over time. This can help reduce the severity of allergic reactions and improve asthma symptoms. According to Professor Stephen Durham of the Royal Brompton Hospital, London, "Immunotherapy can be a highly effective treatment for certain individuals with allergic asthma, particularly those who have not responded well to conventional medications".
Immunotherapy is typically administered as a series of injections or sublingual (under the tongue) tablets, depending on the allergen and the patient's individual needs. It's important to note that immunotherapy should only be considered under the guidance of an experienced healthcare professional, as it carries a risk of severe allergic reactions.
Immunotherapy Options
As mentioned earlier, immunotherapy is a treatment option for some individuals with allergic asthma. There are two primary forms of immunotherapy:
Allergy Shots
Allergy shots, also known as subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT), involve injecting gradually increasing amounts of allergens under the skin. This treatment typically begins with weekly injections, followed by monthly maintenance injections once the optimal dose is reached. Allergy shots can be effective in reducing allergy symptoms and asthma attacks, but treatment can take up to three to five years to reach maximum effectiveness.
Sublingual Immunotherapy
Sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT) involves placing allergen-containing tablets under the tongue. The tablets dissolve, allowing the allergen to be absorbed by the immune system. SLIT is typically administered daily and can be done at home, making it a more convenient option for some individuals. While SLIT may be less effective than allergy shots, it still offers potential benefits for those with allergic asthma.
Developing an Asthma Action Plan
An asthma action plan is a written document that outlines how to manage your allergic asthma, including instructions for monitoring symptoms, taking medications, and addressing emergencies. Working with your healthcare professional to develop a personalised asthma action plan can help you take control of your condition and improve your overall well-being.
Living with Allergic Asthma
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare professional are essential for individuals with allergic asthma. These appointments allow your healthcare team to monitor your condition, make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan, and provide guidance on managing your asthma effectively.
Adapting Your Lifestyle
Adapting your lifestyle to better manage allergic asthma can include adopting allergen avoidance strategies, maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and reducing exposure to tobacco smoke and other environmental irritants. Making these changes can significantly improve your asthma control and overall quality of life.
Support from Friends, Family, and Healthcare Professionals
Living with allergic asthma can be challenging, but support from friends, family, and healthcare professionals can help you navigate the ups and downs of your condition. Communicating your needs, seeking advice, and sharing your experiences with others can provide invaluable emotional support and practical guidance.
Coping with Emotional Aspects of Allergic Asthma
Dealing with the emotional aspects of allergic asthma is an essential part of managing your condition. Anxiety, stress, and depression are common among individuals with asthma, and addressing these issues can help improve your overall well-being. Consider talking to a mental health professional or joining a support group to help cope with the emotional challenges associated with allergic asthma.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Allergic asthma is a prevalent condition that requires ongoing management and awareness of potential triggers. Identifying allergens, adopting avoidance strategies, using appropriate medications, and working closely with your healthcare professional can help you take control of your asthma and maintain an active, healthy life.
Encouragement to Take Control Allergic Asthma
It is essential to take a proactive approach to managing your allergic asthma. By being well-informed about your condition and actively engaging in your treatment plan, you can significantly improve your quality of life and reduce the impact of asthma on your daily activities.
Importance of Working with a Healthcare Professional for Optimal Management
Collaborating with your healthcare professional is crucial for effective allergic asthma management. They can provide guidance on identifying triggers, tailoring your treatment plan, and developing an asthma action plan to help you take control of your condition. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your healthcare team can help ensure your allergic asthma is well-managed and that you receive the support you need.



































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews