
 Instagram
Instagram
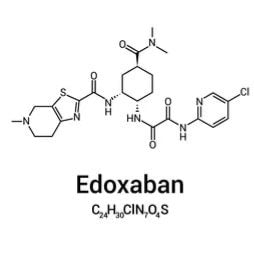
Edoxaban: Side Effects, Dosage, and Uses
Related products
The oral anticoagulant medication edoxaban is an essential tool for both treating and preventing serious blood clots. It is primarily used by patients with conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Aside from that, it works rather well at reducing the risks of stroke and systemic embolic events that come with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
The recommended dosage for edoxaban is one dose per day, either with or without food. However, these are often customised to address the unique health needs of each patient; hence, physicians emphasise the significance of regular diagnostic tests to closely monitor patient progress.
Edoxaban, like every other pharmaceutical prescription drug available today, may have adverse effects, nevertheless. These can be minor, such as skin rashes and bleeding, or more serious, such as liver problems or protracted episodes of excessive bleeding.
Furthermore, even while statistical evidence indicates that the possibility of these side effects occurring is quite low, one should not entirely discount the reality of their potential for deadly consequences.
What is Edoxaban?

Edoxaban, an oral anticoagulant medication, functions as a type of blood thinner. It works by selectively inhibiting factor Xa, an enzyme in the coagulation cascade that prevents platelet aggregation and thrombus formation. Its mechanism of action makes it crucial for averting hazardous blood clots in conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). Moreover, Edoxaban dramatically lowers the stroke risk associated with people who have non-valvular atrial fibrillation due to its efficient mode of action. Careful dosing and regular monitoring are still necessary to support the therapeutic value of this medication because of the potential for side effects including severe bleeding or liver problems.
Uses
Preventing blood clots is one of the main goals of the potent oral anticoagulant medication edoxaban. It is commonly administered to patients who have deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and who are at risk of pulmonary emboli (PE). It also has a critical role in reducing the incidence of stroke and systemic embolic events in individuals with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Its mode of action is centred on inhibiting the Factor Xa enzyme, which stops clotting and suppresses platelet aggregation. Because serious bleeding or liver-related issues are common side effects of this method, it has proven beneficial when used under strict supervision.
How Does It Work?
Edoxaban, an oral anticoagulant that belongs to the direct factor Xa inhibitor family, works by selectively inhibiting Factor Xa. It is important to note that Factor Xa is involved in the coagulation cascade, which is a sequence of events that ultimately leads to the formation of a clot. One of the critical steps in blood clotting, platelet aggregation, is inhibited by edoxaban by blocking this cascade process's function. Therefore, it reduces the risks associated with hazardous clots while treating conditions like deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism along with strokes among patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation thanks to its efficient preventive mechanism against thrombus formation.
Dosage
Medical recommendations generally propose a dosage of 60 mg of Edoxaban once daily. It's important to keep in mind that this recommended dosage frequently needs to be modified due to patient-specific factors. For instance, individuals with lower body weights or renal impairment could only require a daily dose of less than 30 mg. Occasionally, similar modifications are necessary because of the potency of other concurrent medications.
Because edoxaban is taken orally, with or without food, patients will find the administration schedule and manner extremely convenient.
The patient's response informs the supervising physician's final decision regarding dosage, and tailored monitoring helps each patient's specific therapeutic needs be met while prioritising safety. In addition to ensuring maximal effectiveness of the treatment, it is important to monitor for any side effects, such as severe bleeding.
Edoxaban Side Effects
One of the most common side effects of Edoxaban is mild bleeding. This could affect any part of the body, including the gums when brushing teeth and nosebleeds. Even while it normally doesn't cause much trouble and goes away on its own in a short while, if it continues longer than usual, immediate medical attention is needed.
An additional harmless but frequent adverse effect of this drug is a skin rash that can take many different forms, including redness, itching, or flaking. Patients with severe cases involving blisters, peeling, and fever should promptly visit their primary care physicians for guidance on the best course of corrective action, even though moderate occurrences are usually only symptoms of allergic response medication.
However, some side effects can have more severe clinical consequences. For example, heavy, prolonged bleeding can lead to anaemia, which is a lack of healthy blood cells in the body that causes weakness, exhaustion, dizziness, elevated heart rate, and other symptoms. In such cases, prompt corrective action should be taken as soon as these symptoms appear.
The hepatic issues associated with usage are another significant concern. Edoxaban described symptoms such as extreme fatigue, loss of appetite, yellowing of the eyes, dark urine, abdominal pain, etc. that call for a prompt therapeutic withdrawal and a careful medical evaluation in order to stop further damage and restore normal functionality of the organ as soon as possible, all the while carefully and most importantly putting the patient's welfare and safety first.
In rare cases, people have reported experiencing allergies to drugs that cause obvious symptoms like oedema in the face, lips, tongue, and throat, which necessitates quick emergency care and rules out any issues. extreme emotions at all, taking into account each unique circumstance, personal requirement, sensitive topic, and the health and wellbeing of every user across a broad spectrum of diverse communities worldwide.
Edoxaban drug interaction
Edoxaban's effectiveness may be altered or the likelihood of adverse side effects may increase when it is combined with other drugs. For instance, due to their additive anticoagulation effects, co-administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), other anticoagulants, and some antiplatelet therapies raises the risk of bleeding.
Furthermore, erythromycin, dronedarone, and ketoconazole—strong inducers or inhibitors of the P-glycoprotein transport system—dramatically modify the plasma concentrations of edoxaban, increasing the risk of exposure and the potential for adverse effects, including serious bleeding.
Although carefully thought-out combinatory applications have been shown to be advantageous in some documented cases, it is not a good idea to rely solely on one's opinion in these scenarios. Expert medical advice is always required when deciding whether any specific medications taken concurrently pose substantial hazards that call for immediate treatment.
Takeaway
The main purpose of the oral anticoagulant medication edoxaban is to treat and prevent hazardous blood clots that result from conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). It effectively reduces non-valvular atrial fibrillation's risk of stroke. Although the typical dosage guidelines call for daily ingestion, they frequently need to be modified to account for the individual health needs of each person. Common side effects include minor bleeding and skin rashes; severe repercussions, however, may include prolonged severe bleeding or liver problems.
Notably, the drug interacts differently with other medications, such as antiplatelet agents and NSAIDs, and can occasionally have deleterious consequences. One such impact is an increased risk of bleeding, therefore using the drug requires strict monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the long term side effects of edoxaban?
Among the long-term side effects of Edoxaban are severe anaemia, prolonged episodes of heavy bleeding, and liver problems or jaundice (yellowing of the skin or eyes).
What are the most common side effects of edoxaban?
Minor bleeding, such as nose and mouth bleeds, and easily bruised areas are the most common side effects. Skin rashes and nausea are two more.
What foods to avoid when taking edoxaban?
When using Edoxaban, foods high in vitamin K should be consumed in moderation as they may interfere with the medication's ability to work as intended. Among them are leafy green veggies like kale or spinach.















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews