13 Top Vitamin B12 Foods to Add to Your Diet

Related products

It is absorbed in the body using an intrinsic factor which binds to the B12 molecules and helps the cells and the body to absorb it. The excess B12 moves to the liver for future storage. Vitamin B12 supplements are necessary if the body can't get enough from the diet.

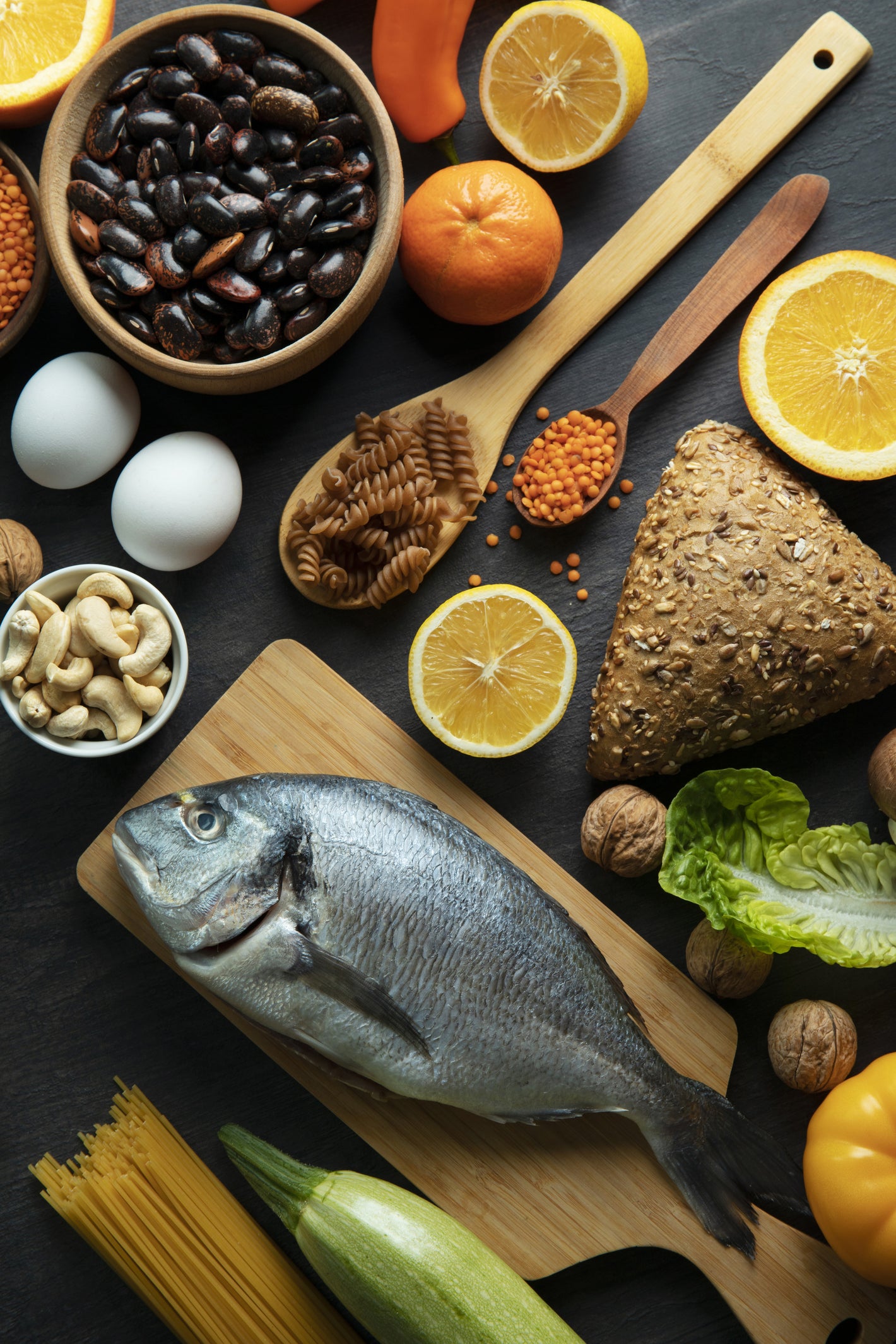
We are summarising the 14 best B12 foods to ensure enough B12 intake. Add these foods to the diet for better results.
Top Vitamin B12 Foods
The best B12-rich foods with the daily value (DV%) and nutritional information are;
Clams
Clams are chewy and small shellfish packed with rich nutrients. It is a mollusc, a source of lean proteins, and is particularly rich in vitamin B12. Eating 11 smaller clams (100g) provides 4120 DV% of B12. The whole baby clams are particularly important, as besides B12, they provide much-needed iron (200% DV in 100g serving) and are a rich source of antioxidants.
Interestingly, all forms and types of clam dishes are rich in B12, and even clam broth is rich in B12 as the canned clam broth provides 113-588% DV of B12 per 3.5-ounce serving (100g). So, add clams to the diet for this delicious source of B12. Make B12-rich foods a staple in the diet and experience the difference in energy levels.
Liver & Kidneys
Organic meats are rich in vital minerals and vitamins. The kidneys and liver of animals are rich sources of B12. The lamb liver is a rich source of vitamin B12, and a 3.5-ounce (100g) lamb liver serving provides 3571% DV of B12. Besides the lamb liver, the other options are veal and beef liver, and a serving of both provides about 3000% DV of B12.
Lamb liver is a rich source of nutrients, e.g., vitamins B2, A, selenium, and copper. Likewise, the kidneys of these animals are rich in B12 as a 100g (3.5 ounces) lamb kidney provides around 3000% DV of B12 and more than 100% DV of selenium and B2. Add this B12 powerhouse to your meals and boost overall health.
Fortified cereals
This B12 source works well for vegans and vegetarians as it is synthetic and not animal-derived. Fortified cereals are not recommended as a part of a regular and healthy diet. Yet, they contain a good amount of B vitamins, e.g., B12, as food fortification adds the necessary nutrients to otherwise nutrient-deficient diets. The research shows that adding fortified cereals to the diets boosts B12 intake.

Although fortified cereals boost the B12 intake, choose only the products higher in whole grains and fibre and lower in added sugars. Don't wait—start adding B12-rich foods into the diet now for better health and vitality.
Beef
Beef is a good source of B12, and 100g of grilled flat steak provides 3.17 mcg (121% DV) of B12. It contains many valuable nutrients, e.g., B3, B3 & B2, and delivers more than 100% DV of zinc and selenium. The lower fat cuts are necessary for people looking for higher amounts of B12.
It is better to roast and grill it instead of frying it to preserve the B12 content in the beef. Take the first step towards a healthier life by including more B12-rich foods in your daily routine.
Sardines
Sardines are soft, bony and smaller saltwater fishes. They are canned in water, sauce and oil, although sometimes, they are used fresh. They are very delicious as they contain healthy amounts of nutrients, and a cup-sized (150g) serving of drained sardines provides about 550% DV of B12.
Besides B12, sardines are a good source of Omega-3 fatty acids, with numerous health benefits, e.g., better heart health and lower inflammation. Boost your energy and improve your health by adding this B12-packed food to your menu,
Fortified yeast
Nutritional yeast is an excellent source of many minerals, vitamins and proteins. This yeast species is specially grown as a food and a leavening agent in beer and bread. Naturally, it contains a low amount of B12 and, is fortified to make it a good source of B12. Like the fortified cereals, the B12 in the fortified yeast is vegan-friendly, as it is synthetic and eating two tablespoons (about 15g) of nutritional yeast provides about 733% DV of B12.
Another older study noted an increased B12 level and lower biomarkers of B12 deficiency by adding nutritional yeast. Elevate your nutrition by making B12-rich foods a regular part of the diet.

Tuna
Tuna is a common fish species and is a good source of many nutrients, e.g., minerals, vitamins and proteins. It is rich in B12 vitamins, especially in the dark muscles under the skin. A 100g (3.5 ounces) serving of tuna provides 453% DV of B12. The same serving also provides vitamin B3, A, selenium, phosphorus and lean proteins.
Canned tuna is also a good source of B12 as one cup (165g) serving of canned tuna contains 152% DV of B12. Feel the benefits of increased energy and improved health by Tuna as a B12-rich food.
Milk
One cup of low-fat milk provides 1.15 mcg (46% DV) of B12. Besides B12, milk is a good source of potassium, vitamin D and calcium. Besides this, milk has many other benefits, e.g., it causes lower blood pressure and lower risk of heart disease and diabetes.
There are many ways to add milk to the diet. Try making a smoothie using milk, cinnamon, butter, ginger, almond and frozen fruits and relish every sip. Transform your health with the power of B12—add milk to your life today.
Yoghurt
One container (170g) of low-fat Greek yoghurt provides about 55% DV of B12. Besides, it provides other nutrients, e.g., protein, magnesium and calcium. It is beneficial as a probiotic. Moreover, it is a digestive aid and helps balance the microflora in the gut and eases the symptoms of digestive Illnesses, e.g., IBS.

Low-fat or no-fat varieties of organic Greek yoghurt are preferable for this purpose. Mixing Greek yoghurt with fruits, oats, herbs, e.g., fresh mint, nuts, and fruits, and smoothies are great food ideas.
Start enjoying the health benefits of B12-rich foods and see the difference for yourself.
Turkey meat
Turkey is not a good source of B12, and it delivers a lower dose of B12 than many other nutritional sources. A 100g serving of Turkey meat provides one mcg (40% DV) of B12. However, it is a valuable source of many other minerals. For example, its one serving provides nearly 50% DV of selenium, a trace mineral that boosts immunity. Incorporate it into the food ideas, e.g., oven-roasted Turkey breast on a garden salad with fingerling potatoes and Brussels sprouts.
The lean Turkey meat can also be cooked with marinara sauce and served with spaghetti squash. The skin contains saturated fats, and only the white meat in the breast is preferable. Make a healthy choice today and incorporate more B12-rich foods into your diet.
Eggs
Eggs are a great source of vitamins, e.g., B12 & B2, minerals and proteins. Two large eggs (100mg) provide 46% DV of B12 and 39% DV of B2. Furthermore, the research shows that egg yolk is a richer source of B12 than egg white, and the B12 in the egg yolk also absorbs more rapidly.
So, consuming whole eggs is preferable over egg whites for this purpose.
Besides providing a healthy dose of B12, it also delivers vitamin D, and two large eggs provide 11% DV of vitamin D. Don't miss out on the health benefits of B12—make these foods a part of your diet now.
Fortified Tempeh
Tempeh is a soy product and a rich source of B12. It is a part of Indonesian cuisine, prepared from fermented soybeans and resembles a loaf or cake. The fermentation adds more B12 and some brands fortify it with B12. Each 100g serving of tempeh provides about 0.7-0.8mcg of B12 (33% DV).
However, choose a fortified product with higher B12 contents. It is eaten uncooked or cooked on salad and sandwiches. Enhance your well-being by making B12-rich foods a key component of your nutrition plan.

Mackerel
It includes more than 30 fatty fish species and is extremely rich in B12. A 3-ounce serving of mackerel delivers approximately 16.2 mcg (675% DV) of B12. Like tuna, it is a good source of many other nutrients, e.g., vitamin A, potassium, selenium and Omega-3 fatty acids/ It has a milder flavour than many other oily fishes, e.g., salmon.
It pairs well with garlic, lemon, dill and parsley and is eaten pan-seared, broiled or roasted. Take charge of your health and add it to your diet for a more energetic life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can one raise the B12 levels quickly?
Eating foods containing higher amounts of B12 restore its normal levels. The foods worth considering are liver, chicken, beef, shellfish and fish, e.g., tuna fish, clams, salmon and trout, fortified cereals, cheese, yoghurt and low-fat milk and eggs.
How many eggs are necessary to boost the B12 intake?
Eggs are a great source of B12, and two large boiled eggs (100g) supply 46% DV of B12. So, it is necessary to take more eggs for Optimum vitamin B12 intake.
Which juices are rich in B12?
Pomegranate and orange juice are a rich source of B12, energy and antioxidants. Drinking a glass full of pomegranate juice regularly or sprinkling them over foods are the best choices.
Which foods are poor for B12 deficiency?
Many foods don't go well with the B12 vitamins. These include folate (too much folic acid masks the B12 deficiency) and alcohol. Taking too much alcohol reduces B12 levels.
How can one check the B12 levels at home?
Many at-home B12 testing kits help test it. These kits are mostly purchased online, and a small amount of blood from a finger prick is all they need. Welzo offers a Folate Blood Test for this purpose. Visit the page to review and buy it.
What are the warning signs of B12 deficiency?
Vitamin B12 deficiency causes signs that develop gradually and worsen only if left untreated. These are headaches, breath shortness, increased heart rate, numbness, rapid breathing, poor/ loss of appetite, poor vision, diarrhoea and feeling tired and weak.
What are the four stages of B12 deficiency?
In stage 1, the B12 level falls in the blood, while lower B12 levels and associated metabolic abnormalities occur in stage 2. In stage 3, various psychological and neurological signs appear, e.g., poor vision, anxiety and confusion. In stage 4, macrocytic anaemia, characterised by large red blood cells develops.

Bottom-line
B12 is an essential nutrient that maintains nerve cells, aids DNA synthesis and supports the formation of red blood cells. An adequate intake of B12 is necessary, particularly for vegans, vegetarians, and other people with deficiency signs and risks. The top B12 foods are dairy products, fortified cereals, eggs, meat, liver, clams and plant-based milk alternatives for people following a plant-based diet.
Including these foods in the diet supports overall well-being by fulfilling B12 demands. Read our informative article to learn more about B12, its sources and uses. We have detailed the benefits, deficiency symptoms and sources of B12 in another must-read article.
































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews