
 Instagram
Instagram
Thrush and Sexual health: Transmission and Prevention

Related products
Connection between thrush &
sexual health
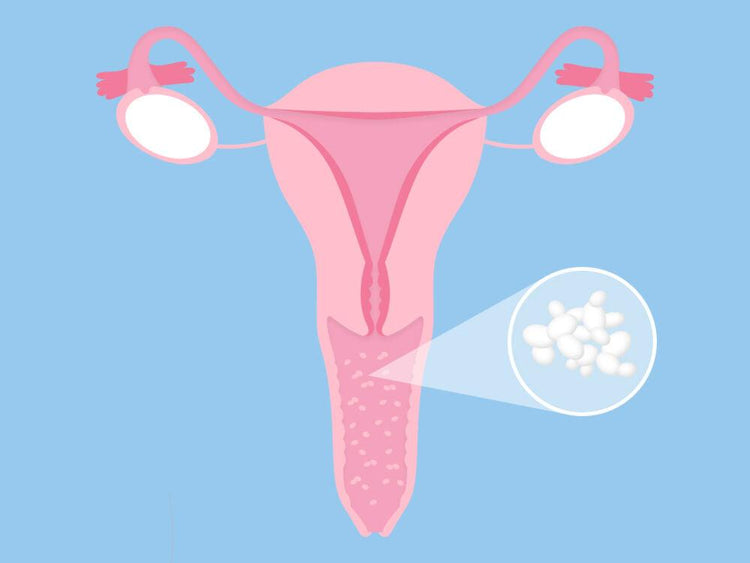
Thrush is a common fungal infection caused by the overgrowth of Candida yeast, which normally resides in small amounts on the skin, mouth, and genital areas. When it comes to sexual health, thrush can cause discomfort, itching, and irritation, impacting the quality of one's intimate relationships. It is essential to be aware of the connection between thrush and sexual health, as well as the strategies for prevention & treatment.
Importance of awareness and prevention strategies
Raising awareness about thrush and its connection to sexual health can help individuals recognise the signs and symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and adopt prevention strategies. In doing so, they can maintain their overall sexual health & minimise the risk of transmission to their partners.
Thrush Transmission through Sexual Activity
Potential for transmission during sexual intercourse
Although thrush is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection (STI), it can still be passed between partners during sexual intercourse. The close contact between the genital areas can facilitate the transfer of Candida yeast, increasing the risk of infection for both partners.
Risk factors for contracting thrush sexually
Certain factors can increase the risk of contracting thrush through sexual activity, such as having a weakened immune system, using antibiotics, or having poorly controlled diabetes. In addition, engaging in sexual activities with a partner who has an active thrush infection can also increase the likelihood of transmission.
Differences in susceptibility between men and women
Women are generally more susceptible to developing thrush due to hormonal fluctuations, particularly during pregnancy or when using hormonal contraceptives. However, men can also develop thrush, often presenting as balanitis (inflammation of the head of the penis).
Prevention Strategies for Thrush in Relation to Sexual Health
Maintaining good genital hygiene
Proper washing techniques
To reduce the risk of thrush, it is important to maintain good genital hygiene by washing the area daily with mild soap and water. Avoid using harsh chemicals or scented products that can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms and contribute to yeast overgrowth.
Choosing appropriate clothing and underwear
Wearing breathable cotton underwear and avoiding tight-fitting clothing can help prevent the warm, moist environment in which Candida thrives. Opt for loose-fitting garments that allow air circulation and keep the genital area dry.
Using barrier protection during sexual activity
Condoms and dental dams
Using barrier protection methods, such as condoms and dental dams, during sexual activity can help reduce the risk of transmitting thrush between partners. Barrier protection can also prevent the spread of other STIs and promote overall sexual health.
Proper use and storage of protection
To ensure the effectiveness of barrier protection, follow the manufacturer's instructions for use and storage. Check the expiration date and dispose of any damaged or expired protection products.
Open communication with sexual partners
Discussing history of thrush or other infections
Open and honest communication with sexual partners about one's history of thrush or other infections can help prevent transmission and encourage responsible sexual behaviour. Sharing this information allows both partners to take appropriate precautions and seek treatment if necessary.
Encouraging partners to seek treatment if needed
If a partner is experiencing symptoms of thrush or has been diagnosed with the infection, encourage them to seek treatment and follow their healthcare provider's recommendations. This can help prevent the spread of the infection and promote overall sexual health for both partners.
IV. Treatment Options for Thrush in Sexual Partners
A. Antifungal medications
1. Topical treatments
Topical antifungal medications, such as creams, ointments, or pessaries, can be applied directly to the affected area to treat thrush. These treatments are often available over-the-counter, but it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment advice.
2. Oral medications
In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed to treat thrush. These medications are typically taken as a single dose or a short course, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's medical history.
B. Importance of treating both partners simultaneously
If one partner is diagnosed with thrush, it is crucial for both partners to receive treatment simultaneously to prevent re-infection. Even if one partner is asymptomatic, they may still carry the Candida yeast and can pass it back to their partner during sexual activity.
C. Following medical advice for the duration of treatment
It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's recommendations and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before the treatment is finished. This ensures that the infection is effectively treated and reduces the risk of recurrence.
V. Maintaining Sexual Health after Thrush Treatment
A. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional
Scheduling regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor one's sexual health & detect any potential issues, such as recurrent thrush or other infections. These appointments provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns and receive appropriate guidance and support.
B. Monitoring for recurrent infections
After receiving treatment for thrush, it is important to monitor for any signs of recurrent infection. If symptoms reappear or persist, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
C. Continuing to practice prevention strategies
To maintain sexual health and minimise the risk of future thrush infections, continue to practice the prevention strategies discussed earlier. This includes maintaining good genital hygiene, using barrier protection during sexual activity, and maintaining open communication with sexual partners.
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the relationship between thrush and sexual health
Thrush is a common fungal infection that can impact one's sexual health, causing discomfort and irritation during intimate activities. Although not classified as an STI, thrush can still be transmitted between partners during sexual intercourse.
B. Importance of transmission prevention and proper treatment
Understanding the connection between thrush and sexual health is crucial for preventing transmission and ensuring appropriate treatment. Practicing good genital hygiene, using barrier protection, and communicating openly with sexual partners can help reduce the risk of infection and maintain overall sexual health.
C. Encouragement of open communication and ongoing vigilance in maintaining sexual health
Promoting open communication with sexual partners and staying vigilant about one's sexual health can help prevent the spread of thrush and other infections. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional and monitoring for recurrent infections can further support a healthy and satisfying intimate life.
IV. Treatment Options for Thrush in Sexual Partners
A. Antifungal medications
1. Topical treatments
Topical antifungal medications, such as creams, ointments, or pessaries, can be applied directly to the affected area to treat thrush. These treatments are often available over-the-counter, but it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment advice.
2. Oral medications
In some cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed to treat thrush. These medications are typically taken as a single dose or a short course, depending on the severity of the infection and the individual's medical history.
B. Importance of treating both partners simultaneously
If one partner is diagnosed with thrush, it is crucial for both partners to receive treatment simultaneously to prevent re-infection. Even if one partner is asymptomatic, they may still carry the Candida yeast and can pass it back to their partner during sexual activity.
C. Following medical advice for the duration of treatment
It is essential to follow the healthcare provider's recommendations and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before the treatment is finished. This ensures that the infection is effectively treated and reduces the risk of recurrence.
V. Maintaining Sexual Health after Thrush Treatment
A. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional
Scheduling regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor one's sexual health and detect any potential issues, such as recurrent thrush or other infections. These appointments provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns and receive appropriate guidance and support.
B. Monitoring for recurrent infections
After receiving treatment for thrush, it is important to monitor for any signs of recurrent infection. If symptoms reappear or persist, consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
C. Continuing to practice prevention strategies
To maintain sexual health and minimise the risk of future thrush infections, continue to practice the prevention strategies discussed earlier. This includes maintaining good genital hygiene, using barrier protection during sexual activity, and maintaining open communication with sexual partners.
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the relationship between thrush and sexual health
Thrush is a common fungal infection that can impact one's sexual health, causing discomfort and irritation during intimate activities. Although not classified as an STI, thrush can still be transmitted between partners during sexual intercourse.
B. Importance of transmission prevention and proper treatment
Understanding the connection between thrush and sexual health is crucial for preventing transmission and ensuring appropriate treatment. Practicing good genital hygiene, using barrier protection, and communicating openly with sexual partners can help reduce the risk of infection and maintain overall sexual health.
C. Encouragement of open communication and ongoing vigilance in maintaining sexual health
Promoting open communication with sexual partners and staying vigilant about one's sexual health can help prevent the spread of thrush and other infections. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional and monitoring for recurrent infections can further support a healthy and satisfying intimate life.
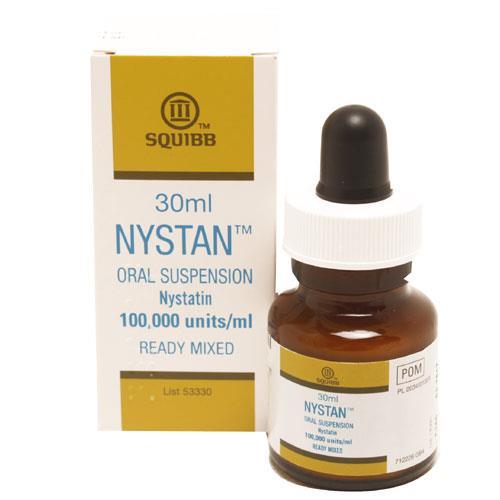















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews