
 Instagram
Instagram
What Is the Candida Diet?


Related products
The Candida diet explained
The Candida diet is a specialised eating plan designed to help individuals suffering from Candida overgrowth. Candida is a type of yeast found naturally in the human body, particularly in the mouth, gut, and vagina. When Candida overgrows, it leads to various health issues. The Candida diet aims to restore balance within the body by eliminating foods that promote Candida growth and replacing them with healthier alternatives.
The Candida Diet as a potential solution
Candida overgrowth leads to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, digestive issues, and recurrent yeast infections. The Candida Diet offers a potential solution by addressing the root cause of the problem – an imbalance in the body's natural microbiome. Individuals experience relief from these symptoms and improve their overall health by following the Candida Diet.
What does the Candida diet consist of?
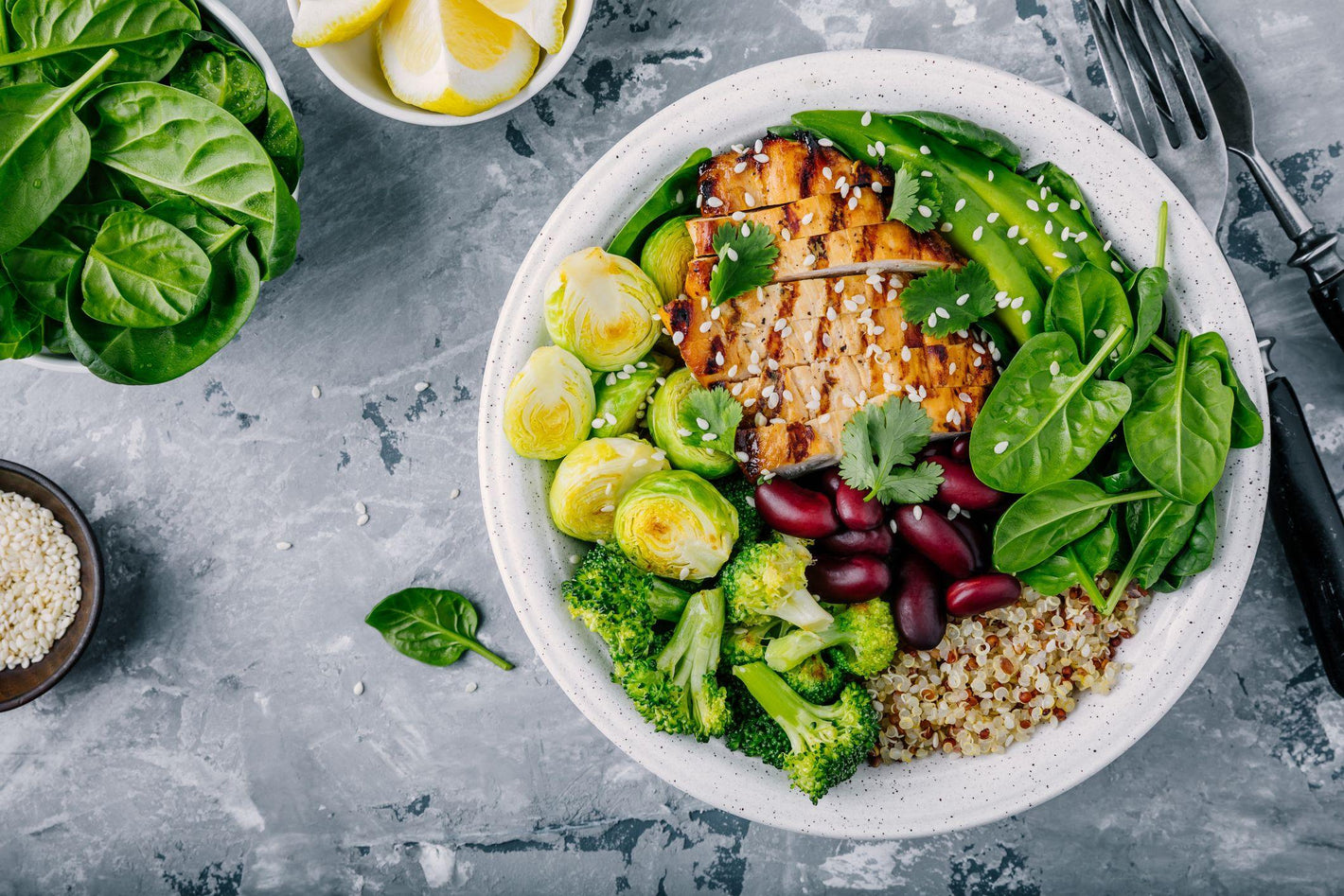
The Candida Diet primarily consists of whole, unprocessed foods that do not promote Candida growth, including non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, low-sugar fruits, nuts, seeds, and fermented foods. Foods to avoid on the Candida Diet include sugars, processed and refined foods, high-lactose dairy products, gluten-containing grains, alcohol, and caffeinated beverages.
Purpose of the Candida Diet
The main purpose of the Candida Diet is to restore balance within the body's natural microbiome by eliminating foods that feed Candida and promote its overgrowth. Doing so helps alleviate symptoms related to Candida overgrowth, improve gut health, and enhance overall wellbeing.
Understanding Candida Overgrowth
Definition and causes of Candida overgrowth
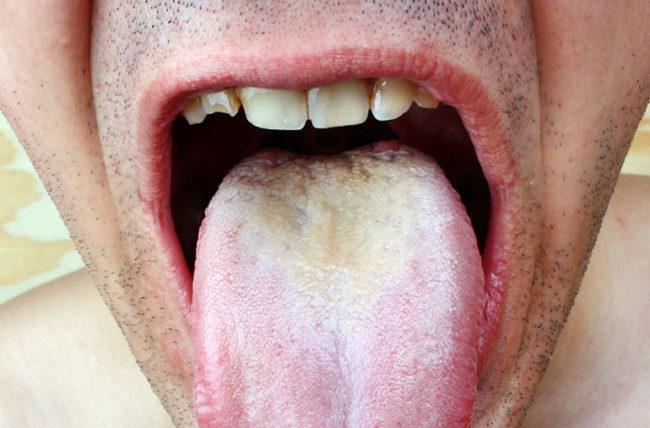
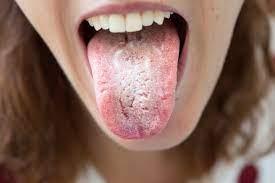
Candida overgrowth, known as Candidiasis, occurs when the naturally occurring Candida yeast in the body multiplies uncontrollably. Resulting from various factors, such as a weakened immune system, long-term antibiotic use, poor diet, and hormonal imbalances. When left untreated, Candida overgrowth leads to numerous health problems. To find out more about thrush treatment, visit the Welzo thrush section.
How the Candida Diet works to combat Candida overgrowth
The Candida Diet works by starving Candida yeast of the nutrients it needs to thrive and multiply. By eliminating certain foods, particularly sugars and refined carbohydrates, the Candida Diet helps to create an environment in which the yeast cannot grow. Simultaneously, the diet encourages the consumption of foods that support a healthy microbiome, such as fermented foods containing beneficial probiotics.
What is the candida cleanse and how do I do it?
The Candida cleanse is an initial phase of the Candida Diet, typically lasting one to two weeks. During this time, individuals focus on consuming a limited number of foods to support detoxification and encourage a healthy gut environment. Foods include consuming mainly non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats while avoiding sugars, grains, and other potential allergens. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a Candida cleanse, as it might not be appropriate for everyone.
Candida Diet principles, goals, effectiveness
The primary principles of the Candida Diet involve eliminating foods that contribute to Candida overgrowth and incorporating foods that support gut health. The goals of the diet include reducing Candida overgrowth, alleviating symptoms, and improving overall health. The effectiveness of the Candida Diet varies among individuals, and scientific evidence supporting its efficacy is limited. However, many people report experiencing relief from Candida-related symptoms after following the diet.
Foods to Include
What is the best food to eat for Candida?
The best foods to eat for Candida are those that do not promote Candida growth and support a healthy microbiome. These include:
Non-starchy vegetables: Leafy greens, broccoli, cauliflower, cucumber, and zucchini are low in carbohydrates and do not promote Candida growth.
Lean proteins: High-quality sources of protein, such as chicken, turkey, fish, and eggs, help maintain a balanced diet while fighting Candida.
Healthy fats: Avocado, olive oil, and coconut oil provide essential fatty acids and helps keep the body satisfied without feeding Candida.
Low-sugar fruits: Berries, green apples, and grapefruit are lower in sugar and are included in moderation on the Candida Diet.
Nuts and seeds: Almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds are good sources of healthy fats, protein, and fibre, supporting gut health without feeding Candida.
Fermented foods: Foods like sauerkraut, kimchi, and plain yoghurt contain beneficial probiotics that help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria.
By incorporating these foods into one's diet and avoiding those that contribute to Candida overgrowth, supports the body in its fight against Candida and improve one's overall gut health.
Foods to Avoid on the Candida Diet
What is the number one food to avoid Candida?
The number one food to avoid on the Candida Diet is sugar, as it directly feeds Candida yeast and promotes its growth. Other foods to avoid include:
Sugars and sweeteners: Refined sugars, artificial sweeteners, and natural sweeteners like honey and maple syrup must be avoided. Sugar is Candida's favourite food, according to Dr Amy Myers, a functional medicine physician.
Processed and refined foods: Processed foods, such as fast food, packaged snacks, and refined grains, contributes to Candida overgrowth by promoting inflammation and weakening the immune system.
High-lactose dairy products: Milk, soft cheeses, and other high-lactose dairy products promotes Candida growth due to their sugar content. Low-lactose dairy products, like plain yoghurt, are included in moderation as they contain probiotics that support gut health.
Gluten-containing grains: Grains like wheat, barley, and rye contribute to gut inflammation, which exacerbate Candida overgrowth. Opt for gluten-free grains like quinoa, millet, or buckwheat instead.
Alcohol and caffeinated beverages: Alcohol and caffeine weaken the immune system and impair the liver's ability to detoxify the body, making it harder to fight off Candida overgrowth.
Certain fruits, vegetables, and legumes: High-sugar fruits like bananas, grapes, and mangoes must be avoided, as well as starchy vegetables like potatoes and legumes like beans and lentils, which feed Candida.
Candida Diet restrictions, sugars, processed foods, dairy: By following these restrictions, individuals starve Candida yeast and promote a healthier gut environment.
Candida Diet Meal Plan and Recipes
Sample meal plan for a week on the Candida Diet
A well-planned meal plan helps a person stay on track with the Candida Diet. Here's a sample one-week meal plan:
Day 1: Breakfast: Vegetable omelette with avocado Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with mixed greens and olive oil dressing Dinner: Baked salmon with steamed broccoli and cauliflower rice
Day 2: Breakfast: Chia seed pudding with unsweetened almond milk and berries Lunch: Turkey lettuce wraps with cucumber and bell pepper slices Dinner: Spaghetti squash with homemade pesto sauce and grilled shrimp For days 3-7, continue to vary the meal choices, incorporating a range of non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Recipe suggestions for breakfast, lunch, and dinner
Breakfast: Coconut flour pancakes with almond butter and a small handful of berries.
Lunch: Quinoa salad with mixed vegetables, grilled chicken, and lemon-tahini dressing.
Dinner: Slow-cooker beef stew with a variety of non-starchy vegetables.
Snack ideas for the Candida Diet
- Snack ideas for the Candida Diet include the following:
- Celery sticks with almond butter
- A handful of mixed nuts and seeds
- Cucumber slices with hummus (made without tahini)
- A small serving of low-sugar fruit, such as berries or green apple slices
- Coconut yoghurt with a sprinkling of cinnamon and chia seeds by incorporating a variety of meal options and snacks, it's easier to maintain a diverse and enjoyable Candida Diet.
The Importance of Consistency and Personalisation
Sticking to the Candida Diet
Consistency is key when it comes to the Candida Diet. Results might not be immediate, and it might take some time for the body to rebalance its gut flora. It's important to be patient and consistent in following the diet to achieve long-term success, as stated by Dr Josh Axe, a clinical nutritionist.
Personalising the Candida Diet
The Candida Diet needs to be tailored to an individual's specific needs and preferences. Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian helps ensure the diet is appropriate and well-balanced, taking into account any allergies or sensitivities.
The Role of Probiotics and Antifungal Supplements
Probiotics for Candida
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria, helps support a healthy gut microbiome and assist in fighting Candida overgrowth. Including probiotic-rich foods like yoghurt, kefir, and sauerkraut in the Candida Diet is beneficial. Probiotic supplements might be recommended by healthcare professionals for targeted support.
Antifungal Supplements
In some cases, healthcare professionals recommend anti-fungal supplements in addition to the Candida Diet. These supplements, such as caprylic acid, garlic extract, and grapefruit seed extract, helps to eliminate Candida overgrowth and restore balance to the gut.
Potential Benefits and Risks of the Candida Diet
What are the symptoms of Candida in the gut?
Symptoms of Candida overgrowth in the gut include bloating, gas, constipation, diarrhoea, food cravings, fatigue, and brain fog.
How do you starve out Candida?
Starving Candida involves eliminating its food sources, such as sugars and processed foods, from the diet while promoting gut health through the consumption of nutrient-dense, whole foods.
Benefits of the Candida Diet
- Reduction of Candida overgrowth: By avoiding foods that feed Candida yeast, the Candida Diet aims to limit its growth and restore balance in the gut.
- Improved gut health: The Candida Diet promotes the consumption of fibre-rich, nutrient-dense foods that support a healthy gut microbiome.
- Enhanced immune function: A balanced gut microbiome is essential for a strong immune system, which help to prevent further Candida overgrowth.
Risks and considerations of the Candida Diet
- Nutrient deficiencies: Restricting certain food groups lead to nutrient deficiencies if the diet is not well-planned and balanced.
- Difficulty adhering to the diet long-term: The Candida Diet is restrictive, making it challenging for some people to maintain over an extended period.
- Limited scientific evidence supporting the Candida Diet: While anecdotal evidence suggests the Candida Diet is beneficial, there is limited scientific research to support its effectiveness.
Candida Diet benefits, risks, evidence
Despite potential benefits, it is important to weigh the risks and consider the limited scientific evidence when deciding whether to follow the Candida Diet.
Consultation with Healthcare Professionals
Importance of seeking professional advice before starting the Candida Diet
Consulting with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting the Candida Diet helps ensure the diet is appropriate, well-balanced, and tailored to an individual's specific needs.
Monitoring progress and making adjustments to the diet
Regular check-ins with a healthcare professional helps monitor progress on the Candida Diet and make any necessary adjustments to ensure optimal results.
Considering alternative treatments and interventions
In some cases, healthcare professionals recommend alternative or complementary treatments, such as anti-fungal medications or probiotics, to address Candida overgrowth more effectively.
Healthcare professionals, Candida Diet guidance, adjustments
Working closely with healthcare professionals provides valuable guidance and support throughout the Candida Diet journey.
Recap of the Candida Diet and its potential benefits
The Candida Diet is a dietary approach designed to combat Candida overgrowth by eliminating foods that feed Candida yeast and promoting a healthier gut environment. Potential benefits include reduced Candida overgrowth, improved gut health, and enhanced immune function.
Importance of professional guidance and personalised approach
Seeking professional guidance and adopting a personalised approach to the Candida Diet helps ensure its effectiveness and avoid potential risks, such as nutrient deficiencies.














 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews