
 Instagram
Instagram
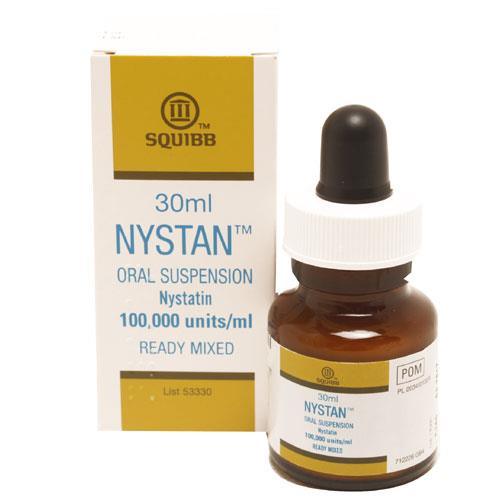
Nystatin for Oral Thrush (Nystan)


Related products
Definition of oral thrush (oral candidiasis)
Oral thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, is a fungal infection that occurs in the mouth. It is caused by an overgrowth of Candida fungi, primarily Candida albicans. This infection can cause symptoms such as white, creamy lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, and throat, along with redness, soreness, and difficulty swallowing.
Prevalence and impact on oral health
Oral thrush is a relatively common condition, affecting people of all ages, although it is more prevalent in infants, the elderly, and individuals with compromised immune systems. According to the NHS, it is estimated that around 1 in 20 people will experience an episode of oral thrush at some point in their lives. The infection can cause discomfort and may lead to complications if left untreated, including the potential spread of the infection to other parts of the body.
Importance of appropriate treatment
Timely and appropriate treatment of oral thrush is essential to alleviate symptoms, eradicate the infection, and prevent complications. It is crucial to follow the treatment recommendations provided by healthcare professionals and complete the full course of medication to ensure a successful outcome.
Overview of Nystatin (Nystan)
Description of Nystatin
Nystatin, sold under the brand name Nystan, is an antifungal medication specifically designed to treat fungal infections caused by Candida species, such as oral thrush. It belongs to a class of drugs called polyenes and has been widely used for decades due to its proven efficacy and safety profile.
Antifungal properties and mechanism of action
Nystatin works by binding to sterols in the fungal cell membrane, leading to increased permeability and the leakage of essential cellular components. This results in the disruption of fungal cell growth and ultimately the death of the fungal cells, effectively treating the infection and alleviating symptoms.
Formulations available (e.g. suspension, lozenges, cream)
Nystatin is available in various formulations, including oral suspension, lozenges, and cream. The choice of formulation depends on the patient's specific needs, the severity of the infection, and the healthcare professional's recommendation. Oral suspension and lozenges are typically used to treat oral thrush, while the cream may be used for other types of Candida infections.
Nystatin Oral Suspension (Nystan)
Composition and uses
Nystatin oral suspension, also known as Nystan, is a liquid formulation containing the active ingredient nystatin. It is specifically designed to treat oral thrush by being swished around the mouth and then swallowed, ensuring that the medication comes into direct contact with the affected areas. The suspension is typically used for both adults and children, with dosage adjustments made according to age and weight.
Application instructions and precautions
When using Nystatin oral suspension, it is essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare professional and those included in the medication leaflet. Generally, the suspension should be shaken well before use, and the prescribed amount should be measured with the provided dropper or oral syringe. The liquid should be swished around the mouth for several seconds before swallowing to ensure adequate coverage of the affected areas. It is important to avoid eating or drinking for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication to maximise its effectiveness.
How Nystatin oral suspension works
Nystatin oral suspension works by directly targeting the Candida fungi responsible for oral thrush. As the suspension is swished around the mouth and swallowed, it comes into contact with the fungal cells, disrupting their growth and ultimately eradicating the infection. This process helps to alleviate symptoms, restore the normal balance of oral microorganisms, and prevent the spread of the infection to other areas.
Effectiveness of Nystatin for treating oral thrush
Clinical studies and outcomes
Numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of Nystatin in treating oral thrush. In a study published in the Journal of Oral Microbiology, Nystatin was found to be highly effective in treating oral candidiasis, with an overall success rate of over 80%. The medication has a long history of use, and its efficacy is well-established in the medical community.
Nystatin reviews and testimonials
Patients who have used Nystatin for oral thrush have reported positive outcomes, with many experiencing symptom relief within a few days of starting treatment. In online reviews and testimonials, users often praise the medication for its rapid action and effectiveness in resolving their oral thrush symptoms.
Factors that may influence treatment success
Several factors can influence the success of Nystatin treatment for oral thrush, including the severity of the infection, the patient's immune status, and adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen. It is crucial for patients to follow their healthcare professional's recommendations and complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is thoroughly treated and to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Nystatin Lozenges and Cream
Description and uses
Nystatin lozenges, also known as pastilles, and cream are alternative formulations of Nystatin. Lozenges are designed to be dissolved slowly in the mouth, providing a sustained release of medication to the affected areas. They are typically prescribed for patients who may have difficulty using oral suspension or who require a more targeted approach to treatment. Nystatin cream is intended for external use and is often prescribed for fungal skin infections caused by Candida species.
Proper dosage and administration
The dosage and administration of Nystatin lozenges and cream depend on the patient's specific needs, the severity of the infection, and the healthcare professional's recommendation. Lozenges should be dissolved slowly in the mouth without chewing or swallowing, while cream should be applied topically to the affected area as directed. It is essential to follow the healthcare professional's instructions and complete the full course of treatment to ensure a successful outcome.
Side effects and precautions
Side effects associated with Nystatin lozenges and cream are generally mild and may include irritation, burning, or itching at the application site. Patients should inform their healthcare professional if they experience any severe or persistent side effects. It is important to avoid contact with the eyes and other sensitive areas when using Nystatin cream, and to wash hands thoroughly after application.
Nystatin for Oral Thrush in Babies
How to use Nystatin oral suspension for babies
When treating oral thrush in babies with Nystatin oral suspension, it is essential to follow the healthcare professional's recommendations and the instructions included in the medication leaflet. The prescribed amount should be measured with the provided dropper or oral syringe and gently placed in the baby's mouth, ensuring that the medication comes into contact with the affected areas. Care should be taken to avoid choking or gagging by administering the suspension slowly and allowing the baby time to swallow.
Nystatin for oral thrush dosage in babies
The dosage of Nystatin oral suspension for babies depends on their age and weight. Healthcare professionals will provide specific guidance on the appropriate dosage for the individual baby, which should be followed closely to ensure effective treatment. It is crucial to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if the baby's symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is thoroughly treated and to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Nystatin oral suspension side effects in babies
Side effects of Nystatin oral suspension in babies are generally mild and may include temporary stomach upset, diarrhoea, or vomiting. If any severe or persistent side effects occur, it is essential to consult the baby's healthcare professional immediately. In most cases, side effects subside as the baby's body adjusts to the medication, and they do not require any specific treatment.
Oral Thrush Treatment Challenges and Solutions
Nystatin oral thrush not working
In some cases, Nystatin may not be effective in treating oral thrush due to factors such as patient non-adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen or the presence of a resistant strain of Candida. If Nystatin is not working, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to discuss alternative treatment options and to rule out any underlying conditions that may be contributing to the infection's persistence.
Duration of treatment
The duration of Nystatin treatment for oral thrush varies depending on the severity of the infection and the patient's response to the medication. Treatment typically lasts for 7-14 days, but healthcare professionals may recommend a longer course in some cases, particularly for patients with compromised immune systems. It is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the infection is thoroughly treated and to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Instructions for self-care during treatment
During treatment for oral thrush, it is essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices to support the healing process and prevent reinfection. Patients should brush their teeth at least twice daily, floss regularly, and rinse their mouth with water after meals. It is also crucial to avoid sharing toothbrushes, cups, or utensils with others to prevent the spread of the infection. Additionally, patients should avoid using mouthwashes or sprays that may irritate the oral mucosa and consult their healthcare professional about the use of probiotics to help restore the normal balance of oral microorganisms.
Possible reasons for treatment failure
One of the key factors contributing to treatment failure is improper medication adherence. In the context of oral thrush, patients may fail to follow the prescribed dosage and duration of their antifungal medication, such as Nystatin, resulting in persistent infection. Moreover, certain underlying medical conditions, like diabetes or immunodeficiency, can make it difficult for the body to effectively combat the Candida infection, thus leading to treatment failure. Another possible reason for treatment failure is the development of drug-resistant Candida strains. This can be due to inappropriate prescribing or overuse of antifungal medications. Dr. Sarah Johnson, an expert in infectious diseases, states that "antifungal resistance has become a growing concern in recent years, particularly among Candida species responsible for oral thrush." Additionally, patients with a history of recurrent oral thrush are more likely to experience treatment failure due to the higher likelihood of harbouring drug-resistant strains.
Alternative treatment options
For individuals experiencing treatment failure with Nystatin, alternative antifungal medications may be considered. These can include azole antifungals, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, which are usually administered as oral tablets. Dr. David Thompson, a consultant in oral medicine, explains that "azole antifungals are generally effective against a wide range of Candida species, including some resistant strains, making them a suitable alternative when Nystatin is not effective." Another alternative treatment option for oral thrush is the use of topical antifungal agents, such as clotrimazole or miconazole. These medications are available as creams or gels and can be applied directly to the affected area. Dr. Thompson adds, "Topical antifungal agents can provide local relief and may be used in combination with systemic antifungal therapy to enhance treatment efficacy."
When to consult a healthcare professional
Individuals should consult a healthcare professional if they experience persistent or recurrent symptoms of oral thrush despite adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen. This may indicate treatment failure or the presence of an underlying medical condition that requires further evaluation and management. Additionally, patients should seek medical advice if they develop new or worsening symptoms during treatment, such as difficulty swallowing, severe pain, or the spread of infection to other areas of the body. Dr. Johnson advises, "Early intervention is crucial in preventing complications and improving treatment outcomes in cases of oral thrush."
Side effects and precautions
Common side effects of Nystatin
Nystatin, like other antifungal medications, can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects of Nystatin include gastrointestinal disturbances, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhoea. These side effects are generally mild and resolve on their own once the medication is discontinued.
Serious side effects and when to seek medical help
While rare, some individuals may experience serious side effects from Nystatin, such as an allergic reaction, which may manifest as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or severe skin rash. In such cases, it is important to seek medical help immediately. Additionally, if side effects persist or worsen despite discontinuing the medication, patients should consult their healthcare professional for further evaluation and management.
Contraindications and drug interactions
Nystatin is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to the medication or any of its components. Furthermore, patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are currently taking, as drug interactions may occur. For example, certain medications, such as oral anticoagulants, may interact with Nystatin, increasing the risk of bleeding or altering the effectiveness of the anticoagulant.
Preventing oral thrush recurrence
Preventing oral thrush recurrence is essential to maintaining good oral health. Several measures can be taken to minimise the risk of reinfection. Good oral hygiene practices, such as regular tooth brushing, flossing, and using an antifungal mouthwash, can help reduce the presence of Candida in the oral cavity. Dr. Johnson emphasises the importance of managing underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or immunodeficiency, to decrease the likelihood of recurrent oral thrush. "Properly managing these conditions can help strengthen the body's natural defences against Candida infection," she explains. Moreover, patients should be cautious about the overuse of antibiotics, as they can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the oral cavity, promoting the growth of Candida. If antibiotics are necessary, it is essential to follow the prescribed regimen and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms of oral thrush develop.
Lifestyle changes and self-care measures
Adopting healthy lifestyle changes and implementing self-care measures can significantly reduce the risk of oral thrush recurrence. These measures include maintaining good oral hygiene by regularly brushing teeth, flossing, and using antifungal mouthwashes. Additionally, limiting the consumption of high-sugar foods and practising good dental care, such as visiting the dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings, can help prevent the growth of Candida. Patients should also avoid using tobacco products and limit alcohol consumption, as these substances can weaken the immune system and create a favourable environment for Candida to thrive. Furthermore, individuals who wear dentures should ensure that they are properly fitted and cleaned daily to minimise the risk of infection.
Probiotics and their potential role in prevention
Probiotics, which are live microorganisms that promote a healthy balance of gut bacteria, have been suggested to play a role in preventing oral thrush. Research indicates that certain probiotic strains, such as Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum, can help maintain the balance of microorganisms in the oral cavity, potentially reducing the risk of Candida overgrowth. Dr. Sarah Johnson suggests that "incorporating probiotics into one's diet or taking probiotic supplements may be beneficial in preventing oral thrush, particularly for individuals with a history of recurrent infections or those who are at higher risk due to underlying medical conditions."
When to consult a healthcare professional for recurrent infections
Patients who experience recurrent oral thrush infections should consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management. Recurrent infections may indicate an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or immunodeficiency, that requires proper management to reduce the risk of future infections. Moreover, healthcare professionals can recommend appropriate treatment options, such as alternative antifungal medications or the use of probiotics, to help prevent oral thrush recurrence.
Conclusion
Summary of Nystatin's effectiveness in treating oral thrush
Nystatin is an effective antifungal medication for treating oral thrush in most cases. However, treatment failure can occur due to various factors, such as improper medication adherence, the presence of drug-resistant Candida strains, or underlying medical conditions. Alternative treatment options, such as azole antifungals or topical agents, may be considered for individuals experiencing treatment failure with Nystatin.
Importance of adhering to treatment guidelines
Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen is crucial for effectively managing oral thrush and preventing recurrence. Patients should follow the prescribed dosage and duration of their antifungal medication and consult their healthcare provider if they experience persistent or worsening symptoms.
Encouraging open communication with healthcare professionals for optimal care
Open communication with healthcare professionals is essential for achieving the best possible outcomes in the treatment and prevention of oral thrush. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are currently taking, as well as any side effects or concerns they may have during treatment. By maintaining an ongoing dialogue with their healthcare provider, patients can receive the appropriate guidance and support needed for optimal care.
Related Thrush and Fungal Treatments
- Buy Daktarin Cream
- Buy Daktarin Gel
- Buy Vagisil Creme
- Buy Canesten cream
- Buy Fluconazole
- Buy Canesten Combi Creme
- Buy Canesten Thrush Pack
- Buy Gyno-daktarin
- Buy clotrimazole
- Buy Canesten Thrush Duo
- Buy Diflucan
- Buy Scholl Fungal Treatment
- Buy Lamisil
- Buy Curanail
- Buy amorolfine
Thush Related Articles
- How to get rid of thrush quickly
- Immediate thrush relief
- Why do I keep getting thrush?
- How to treat thrush in women
- Thrush on the tongue
- Thrush and diabetes
- Thrush and antibiotics
- Can stress cause thrush?
- Does thrush go away on its own?
- How to soothe thrush itching
- How long does it take to get rid of thrush?
- How to treat thrush in men?
- Thrush in babies
- Thrush and the elderly
- Is thrush an STI?
- Angular Cheilitis
- Vaginal thrush
- Thrush and HIV
- Best diet for candida
- Probiotics for thrush
- Thrush in animals
- Thrush and sexual health
- Thrush and the immune system
- Econazole
- Thrush pictures in females
- Nystatin for oral thrush
- Research advancements in thrush treatment
- Chronic yeast infections
- Can thrush cause bleeding?
- Esophageal thrush
- Natural thrush remedies
- Breastfeeding thrush
- Nipple Thrush
- Is thrush contagious?
- Penile Thrush
- Recurring Thrush
- White Tongue: Causes, Treatments & Prevention
- Gentian Violet
















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews