Follow us:

 Instagram
Instagram

 Instagram
Instagram
×
Related products
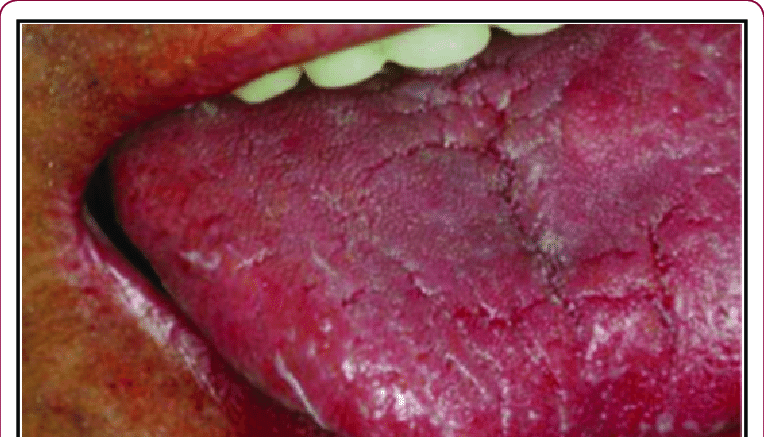
Thrush and Bleeding
Thrush, also known as a yeast infection or candidiasis, is a common fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of the Candida species, primarily Candida albicans. While it is most commonly associated with itching, redness, and discomfort, thrush can also cause bleeding in some cases. In this article, we will explore the potential causes of bleeding related to thrush and discuss the importance of seeking medical advice for proper diagnosis and treatment.Understanding Thrush
A. Causes of thrush
Thrush occurs when there is an imbalance in the body's natural microorganisms, allowing the Candida species to multiply and cause an infection. Factors that can contribute to this imbalance include: Weakened immune system Antibiotic use Hormonal changes (e.g., pregnancy, hormonal contraceptives) Diabetes and uncontrolled blood sugar levels Poor personal hygiene Wearing tight, non-breathable clothing Using scented soaps or feminine hygiene productsB. Symptoms of thrush
The symptoms of thrush can vary depending on the affected area but may include: Itching and irritation Redness and swelling White, curd-like discharge (vaginal thrush) Pain during urination or sexual intercourse Cracked, sore skin (oral thrush)Can Thrush Cause Bleeding?
A. The link between thrush and bleeding
While bleeding is not the most common symptom of thrush, it can occur in some cases. The constant itching and irritation caused by the infection can lead to scratching or rubbing the affected area, which can cause the delicate skin to break and bleed. Additionally, the inflammation associated with thrush can make the skin more prone to tearing, particularly during sexual intercourse or when wiping after using the toilet.B. Distinguishing between thrush and other conditions
It is essential to note that bleeding related to thrush can be easily confused with other conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), or even cervical or vaginal cancer. Therefore, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if you experience bleeding, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms like pain, fever, or foul-smelling discharge.Treatment and Prevention of Thrush-Related Bleeding
A. Treatment options for thrush
If you suspect that you have thrush, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Common treatments for thrush include: Antifungal medications (e.g., fluconazole, clotrimazole) Topical creams or ointments (e.g., miconazole, nystatin) Oral antifungal medication (e.g., fluconazole) for more severe casesB. Preventing thrush-related bleeding
To prevent thrush and the associated bleeding, consider the following strategies: Maintain good personal hygiene: Keep the genital area clean and dry, and avoid using scented soaps or shower gels. Choose breathable clothing and underwear: Opt for loose-fitting, breathable clothing and underwear made from natural fibres like cotton to help prevent moisture build-up. Avoid douching: Douching can disrupt the balance of good and bad bacteria in the vagina, increasing the risk of thrush. Manage underlying medical conditions: Properly managing conditions like diabetes can help reduce the risk of thrush. 5. Seek medical advice promptly: If you experience symptoms of thrush, including bleeding, consult a healthcare professional as soon as possible to receive appropriate diagnosis and treatment.When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is essential to seek medical advice: Persistent or recurrent thrush symptoms, despite treatment Bleeding unrelated to your menstrual cycle Pain, fever, or foul-smelling discharge accompanying the bleeding A history of sexually transmitted infections or other risk factors Symptoms that worsen or do not improve after treatment A healthcare professional will be able to diagnose the cause of your symptoms and recommend the appropriate course of action.The Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Thrush
A. Diet and thrush
Diet can play a role in the development of thrush, as certain foods can promote the growth of Candida. Consuming a balanced diet and avoiding excessive sugar, refined carbohydrates, and processed foods can help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms in the body and reduce the risk of thrush.B. Stress and thrush
Stress can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infections, including thrush. Practising stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or exercise, can help maintain a healthy immune system and reduce the likelihood of developing thrush.C. Sleep and thrush
Adequate sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system, which can help prevent thrush. Establishing a regular sleep routine and ensuring you get enough rest each night can support your overall health and reduce the risk of infections.Thrush in Different Populations
A. Thrush in pregnant women
Pregnant women are at a higher risk of developing thrush due to hormonal changes that can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body. It is essential for pregnant women experiencing symptoms of thrush to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, as some antifungal medications may not be safe for use during pregnancy.B. Thrush in infants and children
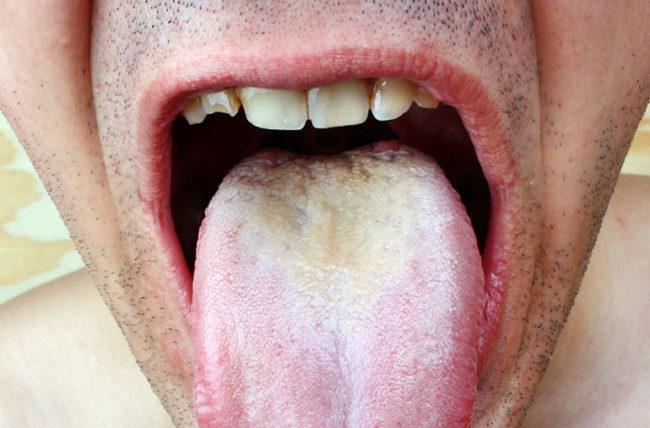
Thrush can also affect infants and young children, particularly in the form of oral thrush. Symptoms may include white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, or gums, and difficulty feeding. If you suspect your child has thrush, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options.C. Thrush in men
Although thrush is more commonly associated with women, men can also develop the infection. Symptoms of thrush in men may include itching, redness, and discomfort on the head of the penis or foreskin. Men experiencing these symptoms should consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.Misconceptions about Thrush
A. Thrush as a sexually transmitted infection
While thrush can be transmitted between sexual partners, it is not classified as a sexually transmitted infection (STI). However, if you or your partner have an active thrush infection, it is essential to seek treatment and avoid sexual intercourse until the infection has cleared to prevent transmission.B. Thrush is only a female issue
As previously mentioned, both men and women can develop thrush. It is essential for individuals of any gender to be aware of the risk factors, symptoms, and treatments associated with thrush.
Thrush is a common fungal infection that can cause a range of symptoms, including bleeding. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatments for thrush, as well as the impact of lifestyle choices and the risk factors in different populations, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage the condition effectively. If you suspect that you have thrush, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment to ensure a full recovery and prevent complications.
Related Thrush and Fungal Treatments
- Buy Daktarin Cream
- Buy Daktarin Gel
- Buy Vagisil Creme
- Buy Canesten cream
- Buy Fluconazole
- Buy Canesten Combi Creme
- Buy Canesten Thrush Pack
- Buy Gyno-daktarin
- Buy clotrimazole
- Buy Canesten Thrush Duo
- Buy Diflucan
- Buy Scholl Fungal Treatment
- Buy Lamisil
- Buy Curanail
- Buy amorolfine
Thush Related Articles
- How to get rid of thrush quickly
- Immediate thrush relief
- Why do I keep getting thrush?
- How to treat thrush in women
- Thrush on the tongue
- Thrush and diabetes
- Thrush and antibiotics
- Can stress cause thrush?
- Does thrush go away on its own?
- How to soothe thrush itching
- How long does it take to get rid of thrush?
- How to treat thrush in men?
- Thrush in babies
- Thrush and the elderly
- Is thrush an STI?
- Angular Cheilitis
- Vaginal thrush
- Thrush and HIV
- Best diet for candida
- Probiotics for thrush
- Thrush in animals
- Thrush and sexual health
- Thrush and the immune system
- Econazole
- Thrush pictures in females
- Nystatin for oral thrush
- Research advancements in thrush treatment
- Chronic yeast infections
- Can thrush cause bleeding?
- Esophageal thrush
- Natural thrush remedies
- Breastfeeding thrush
- Nipple Thrush
- Is thrush contagious?
- Penile Thrush
- Recurring Thrush
- White Tongue: Causes, Treatments & Prevention
- Gentian Violet















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews