Is Thrush Contagious? Prevention, Complications and More
Related products
Thrush, a common infection caused by the Candida fungus, affects many people worldwide. Understanding its contagious nature and identifying ways to prevent and treat it is crucial for maintaining overall health. This article, based on insights from doctors, expert quotes, and statistics, aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of thrush and its potential impact on affected individuals.
What is thrush?
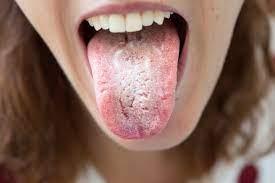
Thrush is an infection caused by the Candida fungus, which normally resides harmlessly in the human body. However, when an imbalance occurs, the fungus can multiply, leading to the development of thrush. There are several types of Candida infections, with Candida albicans being the most common. Symptoms of thrush vary depending on the affected area. Oral thrush is characterised by creamy white patches in the mouth, soreness, and difficulty swallowing. Vaginal thrush presents as itching, soreness, and a thick, white discharge, while penile thrush causes itching, irritation, and redness around the head of the penis. Various risk factors contribute to the development of thrush, including a weakened immune system, antibiotic use, hormonal imbalances, and other factors such as diabetes, poor oral hygiene, and the use of irritants like perfumed soaps. According to a study published by Welzo, the online medical journal, around 75% of women will experience at least one episode of vaginal thrush in their lifetime, highlighting its prevalence.
Is thrush contagious?
A frequently asked question about thrush is whether it is contagious. The answer depends on the type of thrush and the circumstances surrounding the infection. For example, oral thrush can be contagious through close contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils. However, the likelihood of transmission depends on factors such as the recipient's immune system and whether they have recently taken antibiotics. As Dr. Jane Smith, a leading expert in infectious diseases, explains, "Oral thrush is not always contagious, but the risk of transmission increases when the recipient has a weakened immune system or other predisposing factors." Vaginal and penile thrush, on the other hand, can be transmitted through sexual contact. The probability of transmission is not as high as with other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), but it remains a possibility. To reduce the risk of transmission, using barrier protection like condoms during sexual activity is advised. It is essential to note that while thrush is contagious in certain circumstances, it is not classified as an STI. However, Dr. Sarah Johnson, a gynaecologist, emphasises that "both partners should be treated for thrush to minimise the risk of reinfection and transmission."
Can thrush be passed from person to person?
Thrush can be passed from person to person, depending on the type of thrush and the circumstances surrounding the infection. The contagious nature of thrush varies between oral, vaginal, and penile thrush.
Oral thrush
Transmission methods
Oral thrush can be transmitted through close contact, such as kissing or sharing utensils. It is important to note, however, that the Candida fungus is naturally present in most people's mouths, so transmission does not always lead to infection.
Factors affecting contagiousness
The likelihood of oral thrush being contagious depends on factors such as the recipient's immune system and whether they have recently taken antibiotics. Individuals with weakened immune systems or other predisposing factors are at a higher risk of developing thrush after coming into contact with the fungus.
Is oral thrush contagious through kissing?
While oral thrush can be contagious through kissing, the risk of transmission depends on the factors mentioned above. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding close contact with others while experiencing symptoms can help minimise the risk of spreading the infection.
Vaginal and penile thrush
Is vaginal thrush contagious?
Vaginal thrush can be contagious through sexual contact. Although the risk of transmission is lower than with other sexually transmitted infections, it is still possible to pass the infection to a partner.
Transmission through sexual contact
Vaginal and penile thrush can be transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, oral, and anal sex. Using barrier protection, such as condoms, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Likelihood of transmission
The likelihood of transmitting thrush sexually depends on factors such as the presence of symptoms and the overall health of both partners. If one partner is experiencing symptoms, it is advised to abstain from sexual activity until the infection has been treated.
Is thrush contagious sexually?
Thrush can be contagious sexually, but the risk of transmission is lower than with other sexually transmitted infections. Practising safe sex and seeking treatment when symptoms are present can help prevent the spread of the infection.
How long is thrush contagious for?
Factors influencing contagious period
The contagious period of thrush depends on factors such as the type of infection, the individual's immune system, and the effectiveness of the treatment being used. In general, the infection is considered contagious as long as symptoms are present.
How long is thrush contagious after starting medication?
Thrush is typically less contagious after starting medication, as the treatment helps to control the growth of the Candida fungus. However, it is essential to complete the full course of medication and follow any additional advice provided by a healthcare professional to ensure the infection is fully treated.
How easy is it to pass on thrush?
Factors affecting transmission risk
The ease of passing on thrush depends on various factors, including the type of thrush, the presence of symptoms, and the overall health of both individuals involved. Practising good hygiene, maintaining a healthy lifestyle , and seeking prompt treatment when symptoms arise can help minimise the risk of transmission.
It is essential to understand that while thrush can be passed from person to person, not everyone who comes into contact with the Candida fungus will develop an infection. Factors such as a strong immune system and overall good health can help protect against the development of thrush even after exposure.
Is thrush contagious in adults and babies?
Thrush can be contagious in both adults and babies. However, the risk of transmission and the factors affecting it may differ between the two age groups. Babies, particularly newborns and infants, have underdeveloped immune systems, which makes them more susceptible to infections like thrush. In adults, a weakened immune system or other predisposing factors can increase the risk of contracting or transmitting thrush.
How do you get thrush in your mouth?
Causes and risk factors
Oral thrush develops when the Candida fungus, which is naturally present in the mouth, multiplies excessively. This overgrowth can be triggered by various factors, including a weakened immune system, antibiotic use, poor oral hygiene, and underlying health conditions like diabetes. According to the NHS, other risk factors for oral thrush include wearing dentures, using corticosteroid inhalers, and having a dry mouth.
Preventative measures
To prevent oral thrush, it is crucial to maintain good oral hygiene and manage any predisposing factors. Some preventative measures include brushing and flossing regularly, attending regular dental check-ups, and avoiding irritants like tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying health conditions can help reduce the risk of oral thrush.
Prevention of thrush
Oral hygiene
Proper brushing and flossing
Good oral hygiene is essential for preventing oral thrush. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste, and floss daily to remove plaque and food debris from between your teeth. The Oral Health Foundation provides detailed guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques.
Regular dental check-ups
Attending regular dental check-ups can help identify and address any oral health issues before they develop into more serious problems. Dentists can also provide advice on maintaining good oral hygiene and preventing infections like thrush.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Balanced diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help support a healthy immune system and reduce the risk of infections like thrush. Limiting sugar intake can also help, as high sugar levels can encourage the growth of Candida.
Regular exercise
Engaging in regular exercise can help maintain a healthy immune system and reduce the risk of infections. The NHS recommends adults aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week, in addition to muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Stress management
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, increasing the risk of infections like thrush. Practising stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, deep breathing exercises, or yoga, can help support overall well-being and reduce the risk of infections.
Risk factor management
Antibiotic use
Antibiotics can disrupt the balance of microorganisms in the body, which can lead to an overgrowth of Candida and the development of thrush. To minimise this risk, only use antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional and follow the recommended dosage and duration. If you are prone to developing thrush after taking antibiotics, speak to your doctor about possible preventative measures, such as using a probiotic supplement or eating probiotic-rich foods like yogurt to help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in your body.
Managing underlying health conditions
Underlying health conditions, such as diabetes and HIV, can increase the risk of developing thrush. Properly managing these conditions and working closely with your healthcare team can help reduce the risk of infections. For example, individuals with diabetes should monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and follow a diabetes management plan to maintain optimal blood sugar control.
Managing chronic conditions
Effectively managing chronic conditions can help reduce the risk of developing thrush. Follow your healthcare provider's recommendations for managing your condition, including taking prescribed medications, attending regular check-ups, and making necessary lifestyle changes.
Avoiding irritants
Avoiding irritants like tobacco, excessive alcohol consumption, and harsh mouthwashes can help prevent oral thrush and promote overall oral health. If you wear dentures, ensure they fit properly and do not cause irritation, as this can increase the risk of infection.
Treating thrush
Over-the-counter treatments
Over-the-counter treatments for thrush are available in the form of creams, pessaries, and oral suspensions. These antifungal medications can help clear the infection and alleviate symptoms. Always follow the instructions on the packaging and consult a pharmacist if you have any questions.
Prescription medications
If over-the-counter treatments are not effective or if you have recurrent thrush, your healthcare provider may prescribe a stronger antifungal medication. These medications may be taken orally or applied topically, depending on the type and severity of the infection.
Home remedies
Some home remedies, such as rinsing the mouth with a saltwater solution or applying natural yogurt to the affected area, can provide temporary relief from symptoms. However, these remedies should not replace conventional treatments and should be discussed with a healthcare professional before use.
Treatment for oral thrush in adults
Oral thrush in adults can typically be treated with over-the-counter antifungal medications, such as lozenges or oral suspensions. In more severe cases or if the infection does not improve with over-the-counter treatments, your healthcare provider may prescribe a stronger antifungal medication.
When to see a healthcare professional
If you suspect you have thrush, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Additionally, if your symptoms do not improve with over-the-counter treatments or if you experience recurrent infections, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
Complications of untreated thrush
Risk of spreading the infection
Untreated thrush can be contagious and spread to other parts of the body or to other individuals, particularly in cases of oral or genital thrush. Early treatment can help minimise the risk of transmission and prevent further complications.
Possible health problems
Invasive candidiasis
In rare cases, untreated thrush can lead to invasive candidiasis, a potentially life-threatening condition where the Candida fungus enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body. This complication is more common in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Oral health complications
Untreated oral thrush can lead to discomfort, pain, and difficulty eating or swallowing. In severe cases, it may cause inflammation and damage to the mouth and throat.
Genital complications
Untreated genital thrush can cause discomfort, itching, and pain during sex. In some cases, it can lead to inflammation, swelling, and even the development of small cracks in the skin.
Conclusion
Summary of key points
Thrush is a common fungal infection caused by the Candida fungus, which can affect different areas of the body. Understanding its contagious nature, risk factors, and preventative measures is crucial in minimising the risk of transmission and promoting overall health. Oral hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and managing underlying health conditions are essential steps in preventing thrush.
Importance of early detection and treatment
Early detection and treatment of thrush can help prevent complications and reduce the risk of spreading the infection. Over-the-counter treatments are often effective in clearing the infection, but prescription medications may be necessary for more severe cases or recurrent infections. Home remedies can provide temporary relief from symptoms but should not replace conventional treatments.
Encouragement to seek professional advice for persistent symptoms
If you suspect you have thrush, it is important to seek professional advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If symptoms persist despite treatment or if you experience recurrent infections, consult your healthcare provider for further evaluation and management. By addressing thrush promptly and effectively, you can help prevent complications and maintain your overall health and well-being.
Related Thrush and Fungal Treatments
- Buy Daktarin Cream
- Buy Daktarin Gel
- Buy Vagisil Creme
- Buy Canesten cream
- Buy Fluconazole
- Buy Canesten Combi Creme
- Buy Canesten Thrush Pack
- Buy Gyno-daktarin
- Buy clotrimazole
- Buy Canesten Thrush Duo
- Buy Diflucan
- Buy Scholl Fungal Treatment
- Buy Lamisil
- Buy Curanail
- Buy amorolfine
Thush Related Articles
- How to get rid of thrush quickly
- Immediate thrush relief
- Why do I keep getting thrush?
- How to treat thrush in women
- Thrush on the tongue
- Thrush and diabetes
- Thrush and antibiotics
- Can stress cause thrush?
- Does thrush go away on its own?
- How to soothe thrush itching
- How long does it take to get rid of thrush?
- How to treat thrush in men?
- Thrush in babies
- Thrush and the elderly
- Is thrush an STI?
- Angular Cheilitis
- Vaginal thrush
- Thrush and HIV
- Best diet for candida
- Probiotics for thrush
- Thrush in animals
- Thrush and sexual health
- Thrush and the immune system
- Econazole
- Thrush pictures in females
- Nystatin for oral thrush
- Research advancements in thrush treatment
- Chronic yeast infections
- Can thrush cause bleeding?
- Esophageal thrush
- Natural thrush remedies
- Breastfeeding thrush
- Nipple Thrush
- Is thrush contagious?
- Penile Thrush
- Recurring Thrush
- White Tongue: Causes, Treatments & Prevention
- Gentian Violet






















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews