What is the best dieting for PCOS?
Related products
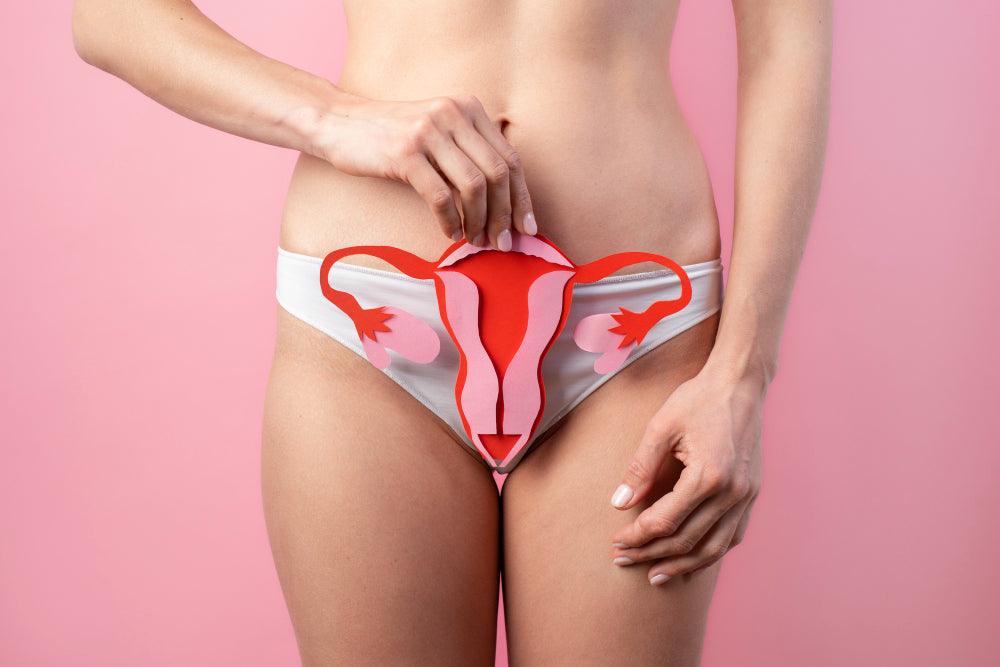
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) refers to cyst formation on the ovaries due to the overproduction of androgen hormones. It is a common health problem that affects one in every ten women worldwide.
PCOS can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular problems, diabetes, endometrial cancer, obesity, and depression. Women suffering from PCOS can experience the following symptoms:
- Excessive hairiness (hirsutism)
- Male pattern baldness
- Acne
- Menstrual Cramps
- Irregular or absent periods
If you suspect PCOS symptoms in yourself then taking a test with the help of our PCOS Blood Test kit would achieve the results for you. This kit will assess your blood hormone levels which are almost always abnormal in overweight and obese women with PCOS.
PCOS And Insulin Resistance:
PCOS patients have abnormally high insulin levels. Insulin hormone has a role in turning circulating sugar levels into energy. Overproduction of insulin results in insulin resistance, in which body cells stop responding to insulin. This leads to more insulin production, which triggers ovaries to produce androgens like testosterone.
Insulin resistance and higher body mass index (BMI) makes it challenging to regulate metabolism and body weight. Fortunately, one can control the symptoms through dietary interventions.
Diet and Its Role in PCOS Management:
Since there is no effective treatment, dietary interventions are the best and most effective in managing polycystic ovary syndrome. Research shows healthy eating habits and physical activities.
Eat a Balanced Diet

The best diet plan for PCOS is that which helps lower the cardiovascular and diabetes symptoms. The diet should generally be high in fibre, low in saturated fats, and balanced in other ingredients. Consuming a balanced diet helps keep the body in the homeostatic phase. Eating a balanced diet maintain glucose level and controls insulin production.
Low Glycemic Index (GI) Diets:
The Glycemic index is a worldwide ranking system that refers to how quickly your blood sugar level rises after eating a diet. Prefer low GI foods which gradually raise the sugar levels and keep it at the optimum level. Eating low-GI foods stops the unnecessary surge of insulin and helps combat insulin resistance.
Many carbohydrates and whole grains have a low GI, which decreases the insulin level and keeps it in the normal range, which in turn helps improve the cell's ability to respond to insulin.
Prefer Healthy Fats:
A diet rich in saturated and trans fat leads to high blood pressure and high circulating cholesterol levels in the blood. Replace saturated fatty acids with an unsaturated fatty acid of plant origin. Vegetable oils like canola, avocado, olive oil, and nuts benefit cardiovascular health.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
PCOS patients are advised to take omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory effects. Inflammation is commonly associated with PCOS. Many plant-based sources like flaxseed, seaweed, chia, and walnuts contain omega-3 fatty acids.
Oily fish is also an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids. 1-2 portions of fish per week provide sufficient omega-3 to the body.
High Fiber Diet:
Unsaturated fats combined with high-fibre diets make the best combination for diabetic or cardiovascular patients. High fibre not only checks cholesterol levels in the blood but is gentle on the digestive tract. High-fibre diets make you feel full, and being a less energy-dense diet, it helps maintain optimum body weight. You can try these foods:
Fruits: The best options are berries, figs, pears, kiwis, and oranges.
Vegetables: Go for spinach, peas, broccoli, and squash.
Legumes: We recommend chickpeas, lentils, kidney beans, and soybeans.
Whole grains: It is best to stick to oats, quinoa, whole wheat, brown rice, buckwheat, and barley.
Cereals: The advised diet includes cereals made with psyllium, wheat bran, or whole-grain oats.
Seeds and Nuts: Some beneficial seeds and nuts include flax, almonds, and sunflower seeds.
Protein diets:
Protein-source diets are mandatory at every meal. It is recommended to prefer plant-based proteins over animal-based proteins. Plant-based protein contains lower saturated fats and more fibre.
The healthiest sources of proteins include lentils, beans, nuts, peas, tofu, and seeds. Moreover, one can enjoy limited amounts of lean meats, poultry, fish, and eggs.
Foods to avoid
It is best to stick to natural healthy diets and avoid unhealthy eating habits. Avoid any diet that may raise blood sugar levels and disturb the metabolism.
Simple Carbohydrates:
Foods rich in like refined grains and white bread should be limited because they can spile blood sugar. Specific gluten diets have inflammatory properties, which may aggravate symptoms in susceptible patients. It is best to check carbs for better management of PCOS.
Sugary Foods:
All the raw and baked sugary food results in peaked glucose levels and higher insulin production. It is recommended to avoid cakes, pastries, cookies, candies, and beverages that contain excessive sugar content.
Processed Foods:
Commercially available fried foods are usually cooked with poor-quality oils. Such oils and fast foods may trigger inflammatory reactions in the body. It is advised to prefer natural or freshly baked foods.
Alcohol:
Alcohol causes inflammation and disrupts the body's balance, which may cause insomnia, impact food choices, and affect gut health.
Meat:
Limit red meat consumption, i.e., pork, steaks, and hamburgers. Processed meat like hot dogs, luncheon meats, and sausages consumption should also be limited.
Solid Fats:
Say no to solid fats! Margarine, lard, and shortening should be avoided to avoid elevated cholesterol levels.
Supplementation:
Sometimes it takes work to find the perfect combination of foods that provide all the essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. Dieticians recommend supplementing vitamin D, probiotics, and omega-3 if your diet is not balanced.
Tips For Better Management of PCOD Through Diet:
· Aim for balanced, healthy, and natural foods.
· Avoid over-eating; instead, take smaller meals more frequently.
· Balance your diet by including protein, unsaturated fats, and carb sources perfectly.
· Include a variety of vegetables and foods.
· Avoid intermittent fasting; sudden large meals cause hyperinsulinemia.
· Regular exercise and physical activity help manage weight.
· Don't compromise on sleep, stay stress-free and try to lose weight.
· Go for supplementation if your diet is deficient in essential nutrients.
· If you cannot manage the diet plan, consult a dietician for a healthy diet plan for PCOS.
Bottom Line:
Polycystic ovary syndrome(PCOS) is common in women worldwide, yet no exclusive measures are taken to control it. Since no treatment is available, dietary management can be crucial in lessening the symptoms. Avoid saturated fat and high-sugar food. Instead, prefer natural foods low GI diet for better management of polycystic ovary syndrome.
To find out more any other health concerns such as hormone levels, contracpetion or sexual health, browse through our Women's Health Hub at Welzo.
































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews