
 Instagram
Instagram
What is LDL cholesterol?


Related products
What’s covered?
What is LDL cholesterol?
Know your bad cholesterol, its sources, levels in the blood and the best strategies to control it.
LDL cholesterol explained?
The LDL molecule is a protein that is found in the bloodstream. In higher amounts, this can cause heart problems. Low LDL cholesterol is essential cholesterol in your blood. LDL particles contain cholesterol. Although often called the "bad cholesterol", DLDL cholesterol is not necessarily unhealthy. LDL is required for cell protection and hormone production. HDL cholesterol is another type of cholesterol that is often known as "excellent" cholesterol. The liver contains HDL and LDL cholesterol.
Facts About LDL: The Bad Kind of Cholesterol
During digestion, blood cholesterol is created by the body. Cholesterol can help improve cellular health. These enzymes help regulate hormone production and digest fatty foods. During a healthy life, our bodies have a good amount of dietary cholesterol found in most food items including meat and fish. Cholesterol is transmitted to the blood via two different proteins known as lipoproteins. These lipopeptides consist of low-density lipoprotein LDL, often called "bad" cholesterol or HDL, commonly known as good cholesterol.
You might be familiar with cholesterol. It’s the fat flowing in your blood. Don’t worry, it is not so bad. Its extra level is bad. Natural cholesterol is used by the body for a variety of functions e.g., to maintain the integrity of cell membranes and for the production of steroid hormones e.g., reproductive hormones.
Cholesterol could be bad too
Wickedness is a part of nature. Every good thing will have a bad aspect too. Cholesterol is not an exception. Along with the useful cholesterol (so-called good cholesterol), there is also cholesterol called bad cholesterol. But what makes this cholesterol bad? It could settle in your blood vessels, particularly in the arteries that are involved in supplying fresh blood to your body. The settled cholesterol could accumulate in the form of plagues and could mechanically obstruct the blood supply. Can you imagine the consequences if the blood supply to your body (or body parts) is obstructed? It will increase the likelihood of heart disease. To find out more about this topic, read High Cholesterol - Symptoms, Causes & Levels.
Why bad cholesterol is called LDL?
Medical men don’t like the terms bad and good. They use chemical terms to distinguish the good and bad cholesterol. The good cholesterol molecules are high-density lipoproteins (HDL). They remain in the centre of the bloodstream and are not dangerous. They have another useful habit. The HDL cholesterol attaches to other cholesterol molecules and carries it to the liver which flushes them out of the body.
The bad cholesterol is low-density lipoproteins (LDL). In the moving blood, these cholesterol molecules settle towards the walls of the blood vessels and may attach to the walls forming plaques. These are dangerous and their prolonged levels increase the chances of cardiovascular diseases e.g., heart attack.
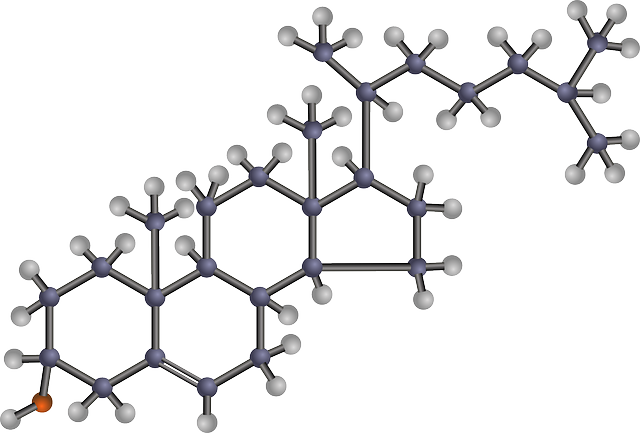
How LDL cholesterol is formed?
LDL cholesterol is formed normally inside your body. Whenever you eat fat, it is digested by your digestive system. The digestion produces very small fatty acids which are absorbed in your body and utilised. Besides the fatty acids, several products of variable density are produced. If you are taking an excess of low-quality fats, very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs) are formed in increasing quantity and enter your liver. These VLDLs are made up of lipids (triglycerides), cholesterol and proteins.
The liver breaks these VLDLs into smaller fragments. They become denser and smaller and are converted into low-density lipoproteins (LDLs) in which the triglycerides are lesser than VLDLs.
What is the normal value of LDL in the body?
Usually, LDL is not considered separately. Whenever you will approach your physician, he will ask you to undergo a complete lipid profile. The lipid profile is a comprehensive test used to quantify all fatty contents of your blood i.e., triglycerides (TGs), high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). HDL and LDL combine to give total cholesterol (TC). Although the doctor will take help from your overall body condition, for guidelines, the optimum total cholesterol is less than 200 mg/dL for healthy adults. The values in the range of 200-239 mg/dL are taken as moderately high while above this threshold is taken as very high.
In the total cholesterol, LDL forms a major portion. About 2/3rd of your total cholesterol is LDL. As a general role, the values up to 110-120 mg/dL are counted as normal, the values between 110-129 mg/dL are midline values and above 130 mg/dL will count as high LDL. Some sources consider the values up to 159 mg/dL to be in the borderline zone.
As LDL is bad cholesterol, its higher level is more dangerous than the lower level of HDL.
Why LDL levels could rise in the body?
Not a single factor could be held responsible. The accumulation of bad cholesterol in your body could be due to several causes ranging from nutritional to lifestyle factors. In general, if you have a sedentary lifestyle and you are also taking foods containing low-quality fats e.g., red meats, full-fat dairy products e.g., full-fat yoghurt, butter, cheese, full cream milk and processed meat, baked and fried foods, eggs, sweets and salty foods etc., your LDL levels are more likely to be higher. Your favourite beef steaks processed in low-quality oils may be a handsome source of cholesterol for your body.
What does the body do with extra LDL
Your body is a two-way cavity. It can store and can also remove unwanted things. But, what does it do to your cholesterol? Some cholesterol may be excreted in your faeces. Your urine and faeces may have small amounts of cholesterol. In hypercholesteremia people, the body may excrete up to 200-499 mg/dL of cholesterol regularly throughout the body while the value of 150 mg/dL or below is counted as normal for total cholesterol in the urine.
Due to the low density of LDL and high pressure of blood in the arteries, it is forced towards the walls of blood vessels. As few molecules find some space of attachment on the wall of the artery, it attracts more molecules until a large plague is formed (Figure).
What to do if your LDL is high
If you are diagnosed with high LDL, the following points may help you,

-
- The first and foremost thing for you is to change your lifestyle. Aim to burn all unnecessary calories before going to sleep. A morning walk and walk after dinner may help you. Then manage your nutrition. Decrease the proportion of cholesterol-rich foods in your regular diet. Add more fibre and vitamins to your food and reduce fats.
- If your LDL level remains persistently higher, consult your doctor who will recommend cholesterol-lowering medications e.g., statins. Include the complete lipid profile test in your regular health monitoring program. Reduce weight and try to maintain it.
- In serious cases of hypercholesterolemia e.g., when a huge plague in your blood vessels restricts the supply of blood to the heart, the doctors may opt for bypass surgery. This surgery will not disturb the fatty clot, it will provide an alternative path to the blood.
The ideal is to stay safe and stay healthy. Medical complications are not a good experience for many of you. So, care is always better than cure. Keep an eye on your lipid profile.
Tell me the meaning of LDL.
Often known as “bad” cholesterol, LDL accumulates in your blood vessels increasing the risk for heart disease and stroke. But cholesterol is not harmful. Your body must have nerve protection to keep the body functioning and to provide a good supply of nutrients to y body and its tissues. Cholesterol is found in food, and your liver produces it. The protein does not dissolve in blood so that it can be carried there. This carrier is known as a lipoprotein. LDLs is the small blob t contains lipoprotein and cholesterol. This product is named Lipoprotein low density.
Causes
Cholesterol passes in your vein, attaching to protein molecules. The mixture of protein and lipids is referred to as lipoproteins. Cholesterol is a protein depending on the amount the protein contains. It consists of the cholesterol levels in the blood and the cholesterol in triglycerides and other types. In addition, triglycerides increase your risk for cardiac disease. Factors t are controlled — inactivity or overweight or poor nutrition — are a contributor to a high blood glucose level. Factors t cannot be managed also play a part.
Risks of High LDL Cholesterol
High LDL cholesterol may lead to health issues including Guidelines aimed at reducing "bad" cholesterol at an appropriate number. Now you and my doctor could collaborate on lowering this percentage. This is calculated by the probability of having heart disease and strokes in your lifetime. Doctors use a calculator to estimate the chances that these problems will occur within 10 years. The calculator considers many factors, including This can impact your chances of heart problems. Other dangers include:
High LDL cholesterol diagnosis
Tests are done to assess LDL cholesterol. It also measures lipid levels in your body which stores energy in your diet. High cholesterol increases your risk of cardiovascular disease.
How to Lower High LDL Cholesterol?
Your doctor will prescribe you medication to reduce your cholesterol and your overall risk for heart problems. Depending on the situation, the plans may be:
For a full range of blood tests and medications, visit our Welzo Online Pharmacy Page. To find out more about Home Cholesterol Tests, click here.


























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews