
 Instagram
Instagram
IUD coils explained
.png?v=1666085903642)

Related products
What’s covered?
The IUD coils are an excellent alternative contraception method.
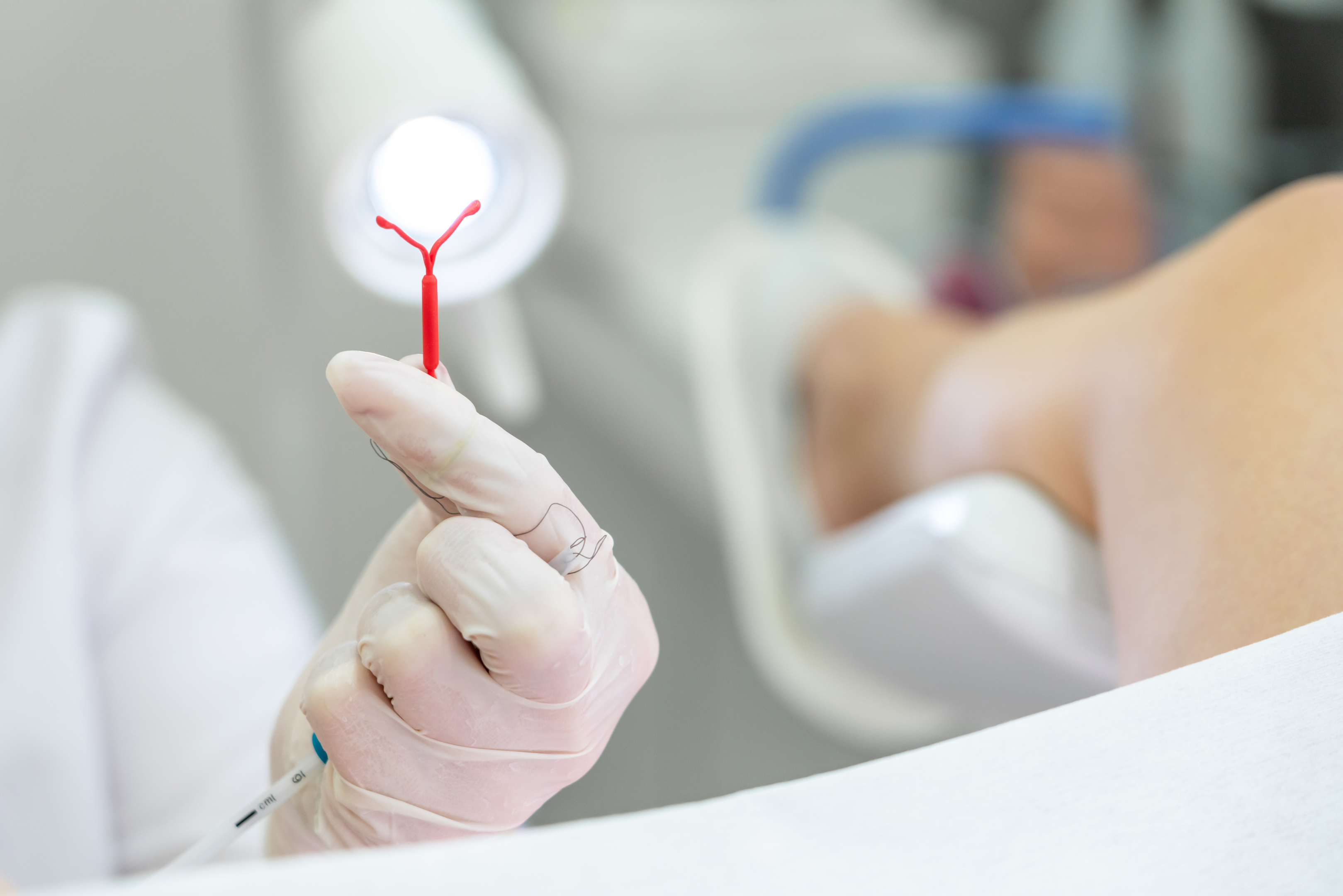
An intrauterine device, called the 'copper coil', 'copper IUD' or 'the coil', is a pregnancy prevention device. After inserting it in your womb, you don't need to worry about pregnancy for a very long time (5-10 years). Despite its effectiveness, this method may not be right for everyone as there are pros and cons to this method of contraception.
What is an IUD? How does it work? How effective is it? What are its advantages and disadvantages? Let's answer these questions in detail.
What is an IUD coil?
IUD is an intrauterine device that is designed to prevent pregnancy. It is a T-shaped plastic and copper device inserted into the uterus where it influences the uterus to prevent pregnancy. It has two threads that hang into the vagina from the womb.
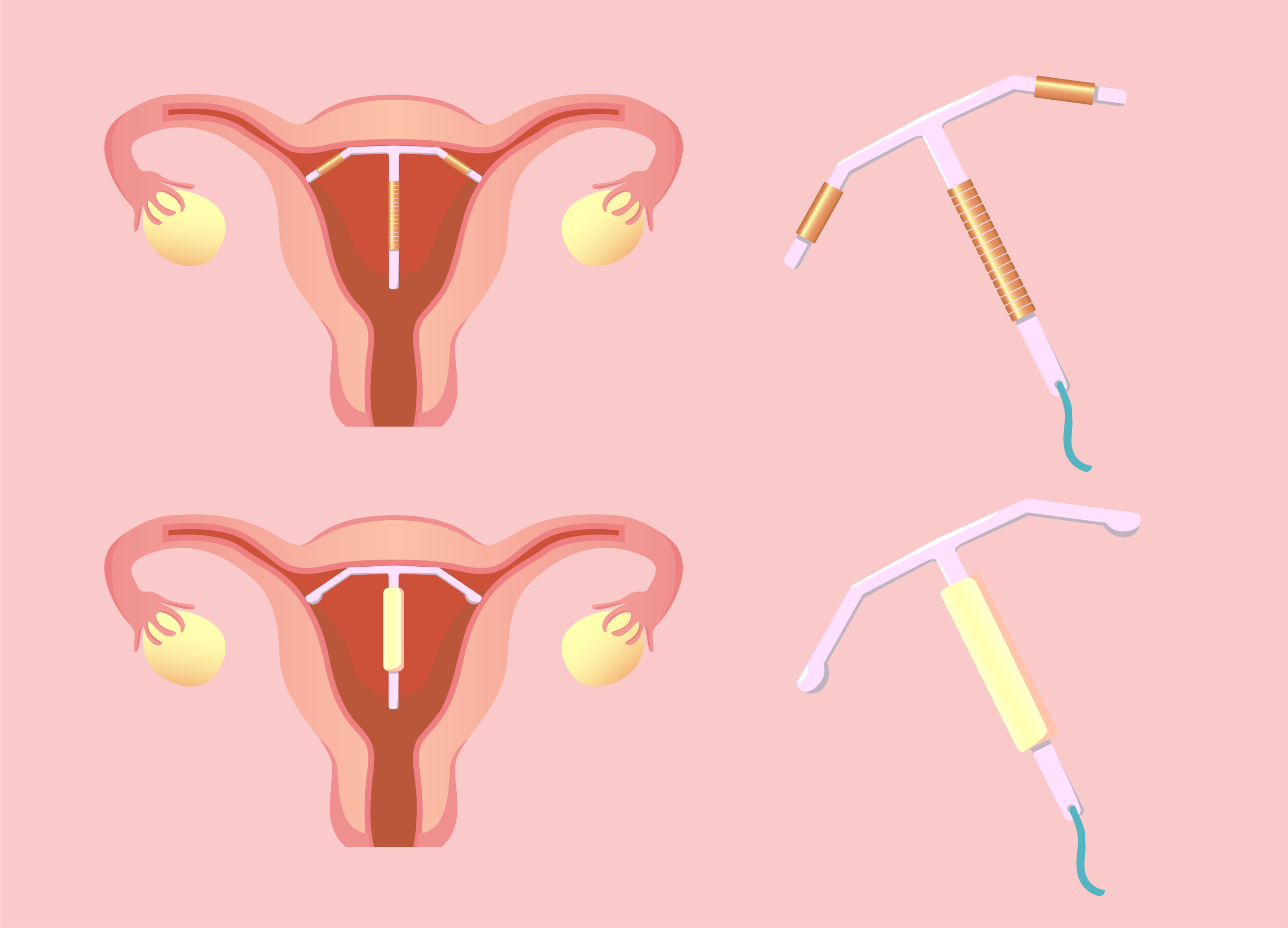
These devices could be hormonal or non-hormonal. The hormonal IUDs (e.g., Mirena®) slowly release progesterone, the synthetic analogue of progesterone. The non-hormonal IUDs (also known as copper IUDs, e.g., ParaGard®) have no hormones. These devices cause a slow release of copper into the uterus.
How does an IUD work?
The working depends upon the type of IUD used.
Hormonal IUD
These devices cause a slow release of progesterone. It causes the cervical mucus to become thick. So, the sperm cannot travel through it and reach its destination for fertilisation.
Non-hormonal IUD
This device causes a slow release of toxic copper ions in your sperm. The immune system will respond to these foreign bodies, and this immune response proves to be toxic for the sperm. It also disturbs the uterine lining, leaving it with very little capacity to receive the fertilised egg.
How an IUD is used?
This device can be introduced at any stage of the menstrual cycle. However, it would help if you were not pregnant to receive it. Before inserting it, the doctor or nurse will examine your womb to check its size and position of the womb. If your womb has any infections, it must be cleared before inserting it.
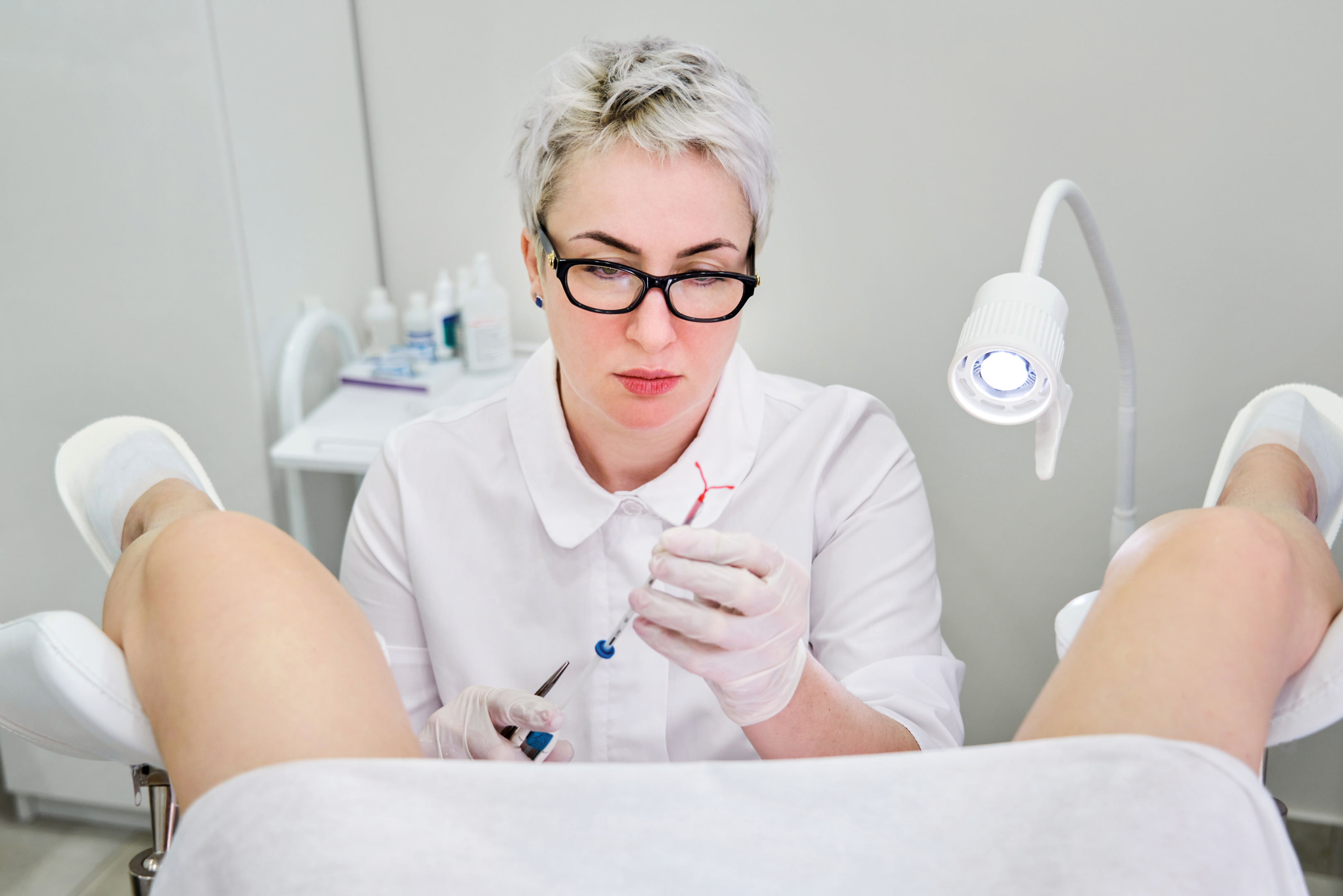
The implantation takes no more than 5 minutes to complete. , the vagina is opened, and the device is inserted and gently pressed through the cervix to the womb. Its threads will continue to hang in the vagina, and the doctor or nurse inserting it will tell you how to locate the threads to know if your device is still in place.
You may be advised to have a regular check-up every few weeks to ensure that you have no problem with the device. If you find any issues, e.g., cramps, pain, discharges, breast tenderness etc, you need to report them immediately to your physician.
What are the pros and cons of IUDs?
Although it is a good method, you should be aware of some of its pros and cons.Pros
-
It has a long duration of action, and some types can offer protection for up to 10 years. The duration of hormonal IUD is less; e.g., the Mirena is recommended for 5 years. The copper IUD can last for up to 10 years.
-
It is easy to place and remove, given that an experienced gynaecologist is doing the job.
-
The non-hormonal IUD is free of hormones; you are not likely to experience the side effects of hormonal contraceptives, e.g., headache, breast tenderness, acne etc. This fact also makes it safe to use during breastfeeding.
-
It doesn't interfere with your sex activities.
-
Its effects disappear quickly after removing the device, particularly for copper IUDs.
-
As the copper IUD is non-medicinal, you will not likely suffer from dangerous drug interactions.
-
The copper IUD doesn't increase the incidence of cervical, ovarian and uterine cancers, as with oral contraceptives.
-
A device may be more costly, but the added cost of pills for 5-10 years will be far more. So, it is pocket-friendly in the long run.
Cons
The users of IUDs can expect the following risks.
-
You can feel some issues at the beginning, e.g., painful and longer periods. But, these effects disappear over time.
-
Albeit the small risk, some people report the incidence of pain and unexplained bleeding through the vaginal. Sometimes, this pain could be so strong that they are forced to leave it.
-
It doesn't provide any protection against an untreated sexually transmitted infection. So, you still have to use barrier condoms and other protection mechanisms.
-
You can get infected if using an infected device.
-
There is a chance, albeit minimum, that it can be displaced or expelled by the womb due to internal pressure.
-
It can cause physical damage to the womb, although the risk is minimal if the physician is experienced in the job.
-
It also has a very small risk of causing thrush. It is a fungal infection which is caused by the notorious Candida albicans. If you experience thrush, consult your physician for treatment and shift to another contraceptive method.
-
It is associated with a risk of pelvic infection, particularly in the starting days. If you experience any sign of infection, e.g., pain, fever or abnormal discharge, you need to consult the physician immediately.
-
It has a higher risk of causing an ectopic pregnancy. A case report published in the Clinical Practice and Cases in Emergency Medicine in 2019 found that using this device can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.
How effective is the IUD?
The effectiveness depends on the purpose of use means you are using it for birth control or emergency contraception.

Fortunately, this intrauterine system provides excellent efficacy in both cases.
When used for birth control
It is one of the best contraceptive methods available and provides an efficacy of 99% or above. It means you have less than a 1% chance of getting pregnant while using it. Why is it so effective? It is so because once placed rightly, it can't rupture like a condom, or you can't miss it like a pill.
According to the data published by the National Library of Medicine, both types of IUDs are highly effective. The failure rate for copper IUD and hormonal IUD is 0.08% and 0.02%, respectively. So, you get 24/7 protection from unplanned pregnancy for up to 10 years. However, you need to keep a record of insertion and removal to ensure that it is not expired.
When used for emergency contraception
Sometimes, you need protection from pregnancy immediately after unprotected sex. It is called emergency contraception. You often need it in case of non-consensual sex, a ruptured male condom, or in case of a missed pill. We have detailed the information about emergency contraception in another article. Click here to read it.
Again, the copper coil is among the best methods available for emergency contraception, provided it is used within 3-5 days of unprotected sex. It promises an efficacy of up to 99.9%. A study published in the International Journal of Women's Health in 2019 found that the copper IUD is an extremely effective long-term and reversible emergency contraceptive, and it had a failure rate of just 0.1%, making it among the best choices for the purpose.
So what is the take-away?
A variety of contraceptive methods are available, including the IUD coils. These coils offer extremely good efficacy for very long periods but still have some issues e.g. no protection against sexually transmitted infections etc. You need to understand its pros and cons to avoid side effects fully.

You can choose an IUD after consulting your gynaecologist and discussing your problem. But don't forget to refer any issue back to the doctor.
At Welzo, we have more information about women's sexual health and contraception. Click here to view our contraception products or to take an online consultation to order your birth control.
Contraceptive pills & services
- Contraceptive treatment
- Buy rigevidon
- Buy Yasmin combined contraceptive
- Buy Cerazette
- Buy Mercilon
- Buy Cerelle
- Buy EllaOne emergency contraceptive
- Buy Triadene
- Buy Qlaira
- Buy Synphase
- Buy Sunya
- Buy Norgeston
- Buy Levonorgestrel
- Buy Ovranette
- Buy Femodette
- Buy Dretine
- Buy Levonelle
Contraception articles
- Is the morning after pill free?
- Can I get over the counter birth control pills?
- What are the benefits of the progesterone-only pill?
- What's The Difference Between The Combined Pill And The Mini Pill?
- When to take the morning-after pill?
- Natural Contraception Methods
- IUD Coils Explained
- Contraceptive vaginal rings explained
- What is a diaphragm contraceptive?
- What contraceptive is best for me?
- How does the contraceptive pill work?
- What is coil contraception?
- What are contraceptive injections?
- Is it safe to take contraceptives?
- What is the most effective form of contraception?
- Are contraceptive implants safe?
- Are birth control pills safe in the long run?


















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews