Photos of Warts on Different Body Parts
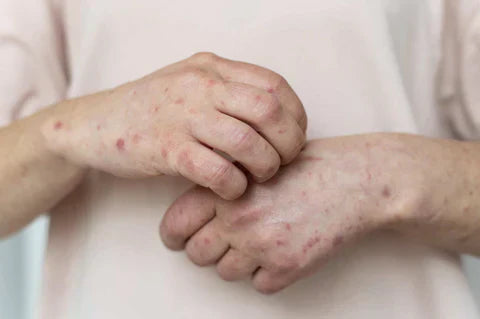

Warts are noncancerous growths caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), resulting in rough textured skin with raised nodules. They develop on different body parts, e.g., hands, knees, soles, palms, back, neck, face etc.
Warts are small, non-cancerous, fleshy growths that develop anywhere on the body. They are caused by more than 100 types of human papillomavirus (HPV) and are of various kinds, each with a distinct clinical picture. Most warts are painless except the plantar warts that appear on the sole of feet and cause pain while standing and walking.
Most untreated warts recover automatically. However, topical medications help facilitate the recovery process. In some cases, non-invasive surgical procedures, e.g., cryotherapy, electrosurgery, laser therapy and photodynamic therapy, are used to remove them. Before seeking medical help, it is essential to identify various types of warts and what they look like.
Various types of warts and their clinical picture are given below.
These are the standard types of warts that appear on different body parts like the skin of toes, knees and fingers. They have rough and pebble-textured raised surfaces. They are ubiquitous in children and teenagers. The most common sites are the finger ends close to the nails, the back side of the hands, face, knees and elbows, anal and genital areas, face etc. Sometimes, they become covered with tiny blood clots, giving the appearance of black seeds; that's why the term "seed warts" is sometimes used.

Figure 1: Appearance of common warts on knees.

Figure 2: Common warts on arm.
These warts are smooth, smaller, and slightly raised. They are Brownish-yellow or skin coloured. They mostly appear as clusters. They develop anywhere on the body, the most common sites being the face in children, the beard area in males and the legs in females. They are painless but are a cosmetic blemish and difficult to treat. For additional skin care products, visit the skin care collection.
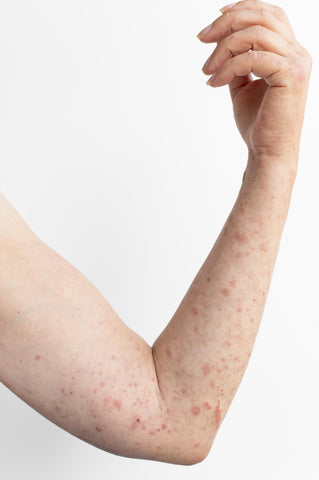
Figure 3: Flat warts on arm.
They develop on the sole of the feet. Their rough surface resembles corn or calluses rather than the common warts. They are tender, causing pain and discomfort during standing and walking. They are of two types; Mosaic plantar warts and Myrmecia type of plantar warts. Plantar warts can be persistent and difficult to treat, but using products like Wartie Cool Wart Verruca Remover can help target the root of the wart and provide a cooling, soothing treatment. They are of two types;
Such warts grow in the form of clusters. They are caused by human papillomavirus type 1. Occasionally, they develop on the palms of one or both hands and are known as palmar warts. Such types of warts are difficult to treat.
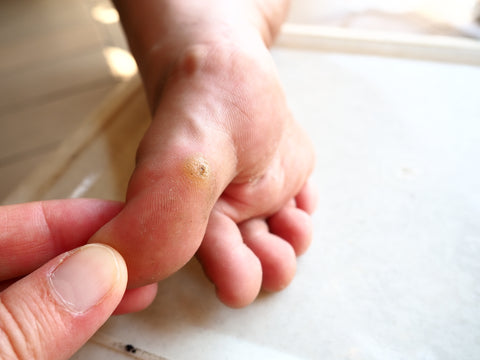
Figure 4: Close-up of a plantar wart.
Such warts are due to human papillomavirus type 2 and are tender and deep warts that grow inwards and cause problems when walking and standing. They cause pain when direct pressure is applied, as a person feels like walking on the pebbles. Sometimes, black dots develop and cause calluses like yellow skin (Cornell University).
Genital warts on the penis appear like small bumps. They can be of variable size, flat or raised, and sometimes appear like cauliflower. The most common sites of genital warts in males are the scrotum, shaft and top of the penis and anus. They are sexually transmitted during oral sex with an infected person and develop in the mouth and throat of the partner. Most of the time, they are painless, but sometimes, they cause a variable degree of itching.

Figure 5: Warts on penis cause significant distress.
Genital warts in the females develop close to the opening of the vulva and are slightly raised, soft and pink. They vary in size and occasionally develop in clusters. The common symptoms are tenderness, itching and burning. The strains responsible for genital warts differ from those responsible for the common warts. They are among the most common sexually transmitted infections in the UK and worldwide with thousands of new cases diagnosed each year.

Figure 6: Vaginal warts cause itching and uneasiness.
In rare cases, the warts give rise to a slowly growing cancer called verrucous carcinoma. Such warts sometimes grow large but don't undergo metastasis and never spread to the other body tissues. They are removed surgically. Periungual warts: Such types develop around toenails and fingernails and cause rough surfaces and peeling. The most common site of cancerous warts (verrucous warts) is the oral cavity, although they sometimes develop on the skin (Nejc Kristofelc, MD).

Figure 7: Some untreated warts become cancerous.
These warts develop under the nail plate or around the edges of the nails. They are either white or flesh-colored and have raised and rough surfaces. Due to their location, they cause pain and itching. These warts change the shape of the nail by resulting in partial detachment or by pushing it on the side or upwards. In such cases, they interfere with nail growth and cause pain. If you experience warts around the nail area, products like Bazuka Gel can be applied directly to help treat the affected area.

Figure 8: Warts in and around the nails.
Such types are unusual in shape and are in the form of thin, long columns of flesh that protrude from the skin. They mostly appear on the face, particularly around the lips, nose and eyes. They are harmless and don't appear in clusters. They mostly heal automatically without any treatment.

Figure 9: A filiform wart close to the eye.
The warts look like rough bumps on the skin. They are oval or round and have a diameter of less than one centimetre. Occasionally, they grow larger or join together.
The pain depends upon the location of the warts. Warts on most body parts are painless- however, those on soles and other surfaces that face pressure cause discomfort and pain.
No, touching the warts is not permissible. Human papillomavirus (HPV) is highly contagious and spreads from one person to the other through contact. Caution is essential for infected warts.
Warts are sometimes confused with other skin conditions, e.g., seborrheic keratosis, callus or corn, skin tags, molluscum contagiosum and syringoma.
Warts are benign fleshy growths that develop on the skin and are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are of different types, and these types develop on various body parts. Given their extremely contagious nature, they are passed from one person to the other during contact. They mostly heal automatically; however, if a wart persists and is causing pain and irritation, it is necessary to consult the healthcare provider. If you're struggling with warts, consider using effective treatments such as Salactol Wart Paint or Wartner Cryo Freeze for non-invasive removal options.
Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.