Nail Psoriasis vs Fungus: Causes, Treatment and Differences

Maintaining nail health is not just about aesthetics, it's a significant marker of overall physical wellness. Nails serve crucial roles such as safeguarding the tender tips of our fingers and toes and enhancing fine touch sensitiveness. However, several individuals face issues related to various nail disorders that affect their well-being along with self-confidence.
Nail Psoriasis and fungal infections are two prevalent irregularities impacting quite a large number globally causing both visual disruptions alongside bodily distress. Psoriasis stands as an autoimmune disorder recurring and chronically affecting around 2-3% population worldwide.
Although psoriasis majorly impacts skin conditions, nail abnormalities remain a critical concern associated with this ailment too.
Research highlights anywhere between 15% -79% of people diagnosed having psoriatic symptomology show signs linked specifically towards Nail Psoriasis at some point in time. Furthermore, lifetime projections for these symptoms appearing range from high probabilities reaching up to 80-90%.
Differentiating between these two conditions is crucial for appropriate treatment protocols because despite presenting similar symptoms such as discoloration or thickening of nails they stem from entirely divergent causes: auto-immune response incites Nail psoriasis whereas fungi invasion results in Onychomycosis.
Dr. John Davis III, Rheumatologist at Mayo Clinic points out "Misdiagnosis often occurs due to symptom similarities; however, treatments widely vary". Therefore medical professionals need to employ specific methods like KOH exams or biopsies which aid in achieving accurate diagnosis.

Nail Psoriasis is a specific type of psoriatic disease influencing nail health. Manifesting as an autoimmune disorder, the body's immune response mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells leading to changes in the appearance and texture of nails.
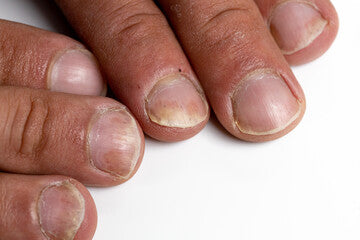
Current medical literature classifies Nail Psoriasis under chronic diseases- it continues for prolonged durations or recurs frequently over time. It primarily involves irregularities such as pitting (small dents or depressions on the surface), abnormal colorations – yellow-red discolouration often likened to oil drops - or separation of the affected nail from underlying bed commonly called Onycholysis with potential developments into more severe conditions like 'nail crumbling' if left untreated.
Characteristically inherent within those diagnosed with other forms of psoriasis, nearly 50% of people dealing with skin-based symptomology further exhibit signs of Nail Psoriasis and may manifest as nail pitting (indentation in the nails), onycholysis (separation of the nail plate from the nail bed), oil spots (discoloration of the nail bed), dystrophy and subungual hyperkeratosis.

The exact cause of Nail Psoriasis remains undefined in medical literature; however, an overactive immune response seems to play a critical role. Immune cells incorrectly target healthy skin and nail cells leading to accelerated cell turnover that further results in the characteristic pitted or thickened appearance seen with this condition.
Several risk factors have been implicated in the onset and progression of Nail Psoriasis:
Certain triggers exacerbate symptom severity like stress, injury to the nails due to environmental factors (in cold weather), and excessively hot showers/baths weakening the natural moisture barrier thus inviting fungal infections that mimic & aggravate existing issues related to Nail Psoriasis etcetera.
Nail Psoriasis manifests via several observable changes in the nails. These alterations span both appearance and structure, thus affecting not just aesthetics but overall nail health as well.

Onychomycosis, commonly known as nail fungus, is a prevalent condition characterised by the invasion of microscopic organisms—fungi—in nails. These fungi thrive in warm and moist environments making human feet prime targets owing to their usual housing inside shoes - an ideal breeding ground ensuring continued fungal propagation.
The infection begins as a white or yellow spot under the tip of your fingernail or toenail gradually deepening leading to considerable nail damage if untreated for extended periods.
NHS UK reports indicate approximately 2.7% population is affected annually with Onychomycosis cases outnumbering Nail Psoriasis incidences significantly maintaining its status among top-ranking common conditions impacting overall global health quality consistently
Fundamentally affecting structural integrity alongside visual degradation – discoloration, thickening etcetera form part symptoms seen chiefly during initial stages later progressing into painful physical manifestations such as discomfort while walking due to extreme swelling around infected areas besides potential spread risks associated with unchecked disease progression.

Onychomycosis occurs due to the invasion of fungi into nails; these organisms typically include dermatophytes, yeasts, or non-dermatophyte moulds. Environmental exposure often marks the initial contact point with such elements which gradually move under nail beds initiating their destructive cycle geared towards steady degradation.
Several risk factors significantly increase the chances of Onychomycosis development:
Onychomycosis or nail fungus presents with several observable changes :
Nail Psoriasis and Nail Fungus, albeit sharing some similar manifestations, are fundamentally different conditions each bearing unique characteristics that aid their clear differentiation:
On appearance & symptoms comparison: Both disorders might showcase discoloration or thickening of nails; however nail psoriasis often includes 'oil drop' discolorations while onychomycosis leans towards white to yellow-brown hues initially rising gradually deeper tones over time. Furthermore in contrast to crumbling edges commonly seen by Onychomycosis, pitting (small depressions) frequently signify the presence of nail psoriasis.
Nail fungus far exceeds numbers relative to those afflicted with Nail Psoriasis. An estimated 3 million people suffer from Onychomycosis annually within the UK as compared to roughly 12000 –24000 cases recorded for the latter condition according to NHS data trends.
Possessing a genetic predisposition along with existing skin-based symptomology extensively influences the likelihood of development-related aspects involved with Nail Psoriasis. In stark contrast advancing age, and compromised immune systems resulting in pre-existing health maladies like Diabetes besides environmental exposure form primary risk factors attributed to the onset progression associated with fungal infections.
An accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining whether an individual has Nail Psoriasis or Onychomycosis since the treatments differ significantly.
Clinical Examination: The first step in diagnosing either of these conditions involves a thorough visual inspection by experienced healthcare professionals to identify characteristic signs such as discoloration, pitting, or thickening.
Laboratory Tests: Further identification often requires laboratory examinations where direct microscopy using potassium hydroxide mounts helps visualise fungal elements attributed towards onychomycosis cases primarily.
Nail Clippings & Skin Scrapings: Samples obtained from suspect areas are cultured under lab settings to identify fungi responsible for causing infections. As per the British Association of Dermatologists, it takes approximately 3 weeks time before confirming negative results post-initial test conduct.
Biopsy: In complex cases, doctors resort to nail biopsies involving the removal of small sections of affected nails studying them microscopically aiding confirmation of suspected diagnoses conclusively.

The treatment for Nail Psoriasis employs a multi-faceted approach varying according to symptoms severity and overall health profile of patients.

Addressing Onychomycosis entails a comprehensive approach integrating medicinal interventions alongside vital lifestyle changes targeted towards fostering an inhospitable environment against fungal growth:
Keeping a vigilant eye on changes in nail health forms an important aspect of overall well-being. If any alteration - discoloration, thickening, or separation from the underlying bed is noted, seeking professional advice remains the most prudent course of action.
Particularly for individuals with pre-existing health conditions like diabetes or autoimmune diseases that weaken immune response capabilities thereby escalating the likelihood towards susceptibility against such disorders, regular check-ups remain a highly recommended approach ensuring early diagnosis and consequent treatment application.
Signs pointing to physical discomfort including pain while walking due to increasing swelling around infected areas indicate urgent medical intervention without delays. Additionally persistent symptoms not responding to self-care measures implemented at home require prompt consultation with healthcare professionals as it might signal complex scenarios requiring more aggressive therapeutic involvements.
Mitigating risks associated with Nail Psoriasis and Onychomycosis largely circles specific preventive measures designed toward maintaining optimal nail health.
To prevent flare-ups related to Nail Psoriasis:
Thus instilling these recommended practices within routine lifestyles aids in creating an environment less conducive for such conditions to prosper, hence promoting healthier outcomes over long-term perspectives.
Nail Psoriasis and Onychomycosis are prevalent nail disorders with different roots - the former is an autoimmune disorder while the latter relates to fungal invasion. Despite their similar symptoms, accurate diagnosis via clinical inspections or lab tests is vital as treatments differ widely. Treatment involves topical applications, and oral medications paired with diligent hygiene practices aimed at preventing further progression and ensuring recovery. Regular moisturization habits, protective wear usage, and maintaining good hygiene routines form part of prevention strategies in both conditions.
Differentiating between nail psoriasis and a fungal infection involves observing the unique characteristics of each condition. Nail Psoriasis often includes 'oil drop' discolorations and pitting, whereas onychomycosis leans towards white to yellow-brown hues with crumbling edges.
Treating nail fungus usually employs antifungal creams or medications like Ciclopirox & Efinaconazole while oral drugs terbinafine and itraconazole are common choices in stubborn cases. For nail psoriasis management, primarily topical treatments that contain corticosteroids or retinoids alongside Vitamin D analogs form part of therapeutic protocols frequently recommended by physicians.
Detecting whether it's psoriasis or fungus requires healthcare professional consultation because symptoms share similarities, yet underlying causes differ significantly. Clinical inspections along with laboratory examinations aid in distinguishing one from another effectively.
The best treatment for nail psoriasis varies based upon symptom severity; however, combination approaches including medicated ointments, UV light therapy besides injectable biologics have shown promising outcomes, and most individuals are affected extensively.
Causes behind Nail Psoriasis onset remain largely unknown but research indicates overactive immune response as a primary contributing factor. Genetic predisposition unruly stress levels even physical trauma nails seem to enhance susceptibility chances considerably.









