Reactive Airway Disease: Is it asthma?
Related products
Reactive airway disease (RAD) is a term often used to describe a set of symptoms that may indicate the presence of a lung condition, such as asthma. However, the term is not universally accepted among healthcare professionals and may cause confusion when discussing respiratory issues. This article aims to clarify the concept of reactive airway disease, its relation to asthma, and the importance of accurate diagnosis and management, with insights from expert physicians in the field of respiratory medicine.
What is Reactive Airway Disease?
Reactive airway disease (RAD) is a term used by some healthcare providers to describe symptoms suggestive of asthma or other respiratory conditions in individuals who have not yet been formally diagnosed. These symptoms may include wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness, which can be triggered by factors such as allergens, infections, or environmental irritants.
Dr. James T. Good, a pulmonologist at National Jewish Health, explains that the term "reactive airway disease" is often used when a patient's symptoms are suggestive of asthma, but diagnostic testing has not yet been performed or is inconclusive (Good, 2019). However, this term is not universally accepted among medical professionals, as it lacks specificity and can lead to confusion regarding the underlying respiratory condition.
Asthma: A Common Reactive Airway Disease
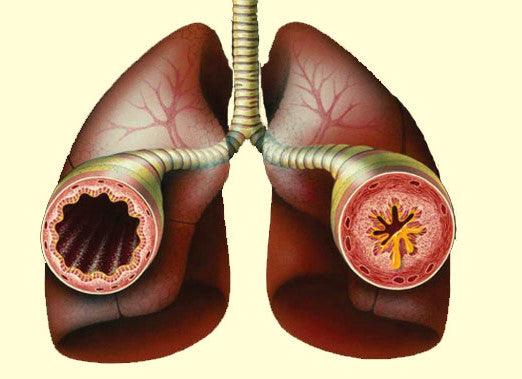
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways characterized by episodes of wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), over 25 million people in the United States have asthma, making it one of the most common chronic respiratory conditions (CDC, 2021). For more details on Asthma, check out our article that covers asthma diagnosis and symptoms.
Dr. Sally Wenzel, a pulmonologist at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, emphasizes the importance of early and accurate diagnosis of asthma to ensure appropriate treatment and management (Wenzel, 2015). When symptoms suggestive of reactive airway disease are present, healthcare providers should conduct a thorough evaluation to determine if asthma or another respiratory condition is the underlying cause.
Diagnosing Asthma: Moving Beyond Reactive Airway Disease
In order to accurately diagnose asthma and differentiate it from other respiratory conditions, healthcare providers should conduct a comprehensive evaluation that includes a detailed medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic testing. Some of the tests used to diagnose asthma include spirometry, peak flow measurements, and bronchial provocation tests.
Dr. Fernando D. Martinez, Director of the Asthma & Airway Disease Research Center at the University of Arizona, emphasizes the importance of using objective measures, such as spirometry, to assess lung function and confirm an asthma diagnosis (Martinez, 2017). Additionally, healthcare providers should consider potential asthma triggers, such as allergens, infections, and environmental factors, when evaluating a patient's symptoms.
The Role of Allergens and Environmental Factors in Reactive Airway Disease
Allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, animal dander, and mold, can trigger airway inflammation and contribute to the development of asthma or other respiratory conditions. Dr. Stanley J. Szefler, a pediatric allergist and asthma specialist at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, notes that identifying and managing allergen exposure is critical for individuals with reactive airway disease symptoms, particularly when asthma is suspected (Szefler, 2013).
Environmental factors, such as tobacco smoke, air pollution, and occupational exposures, can also play a role in the development and exacerbation of reactive airway disease symptoms. Dr. David A. Schwartz, a pulmonologist and environmental health expert at the University of Colorado, emphasizes the importance of addressing environmental factors in the management of respiratory conditions, including asthma (Schwartz, 2016). Patients and healthcare providers should work together to identify potential environmental triggers and implement strategies to minimize exposure and reduce symptom severity.
Treatment and Management of Asthma and Reactive Airway Disease
Once a proper diagnosis has been made, appropriate treatment and management strategies can be implemented to control symptoms and improve lung function. For individuals diagnosed with asthma, this typically involves a combination of pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions.
Dr. Monica Kraft, a pulmonologist at Duke University Medical Center, explains that inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are the cornerstone of asthma treatment, helping to reduce airway inflammation and prevent exacerbations (Kraft, 2020). In addition to ICS, other medications such as short-acting and long-acting bronchodilators may be prescribed to provide relief from asthma symptoms.
Non-pharmacological interventions, such as allergen avoidance, smoking cessation, and trigger management, are also essential components of asthma management. Dr. Jean Bousquet, an allergist and asthma expert at the University of Montpellier, stresses the importance of personalized treatment plans that consider each patient's unique triggers, symptoms, and response to therapy (Bousquet, 2018).
For patients with symptoms suggestive of reactive airway disease but without a definitive asthma diagnosis, healthcare providers may recommend a trial of asthma medications to determine if they provide relief. However, it is essential to closely monitor the patient's response to treatment and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure optimal symptom control and lung function.
Reactive airway disease is a term used by some healthcare providers to describe symptoms that may indicate the presence of a respiratory condition, such as asthma. However, it is crucial to move beyond this non-specific term and accurately diagnose the underlying condition to ensure appropriate treatment and management.
Healthcare providers should conduct a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic testing, to diagnose asthma or other respiratory conditions in patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of reactive airway disease. By accurately identifying the underlying cause and implementing personalized treatment strategies, patients can achieve better control of their symptoms and enjoy a higher quality of life.
Related Asthma Treatments
- Buy Asthma Inhalers & Treatment Online
- Buy Ventolin Accuhaler
- Buy Ventolin Evohaler
- Buy Salbutamol Inhaler
- Buy Clenil Modulite
- Buy Qvar Aerosol Inhaler
- Buy Salamol Inhaler
- Buy Able Spacer
- Buy Symbicort Turbohaler
- Buy Salamol Easi Breathe Inhaler
- Buy Sereflo
- Buy Child Aerochamber
- Buy Spiriva Respimat
- Buy Sirdupla
- Buy Duoresp
- Buy Qvar Inhaler
- Buy Pulmicort Turbohaler
- Buy Seretide Accuhaler
- Buy Montelukast
- Buy Serevent Evohaler
- Buy Kelhale Inhaler
- Buy Fostair Inhaler
- Buy Flutiform Inhaler
- Buy Flixotide Accuhaler
- Buy Bricanyl Inhaler
- Buy Atrovent Inhaler
- Buy Alvesco Inhaler
- Buy Airomir Inhaler
Related Asthma Articles and Information
- Asthma: Definition, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatments
- Living with Asthma
- Allergic Asthma
- Brittle Asthma
- Asthma Diagnosis and Testing
- Eosinophilic Asthma Guide
- BTS Asthma Guidelines
- Allergies & Asthma
- Reactive Airway Disease
- Do I have Asthma? (Quiz)
- Is Asthma a disability?
- NICE Guidelines on Asthma
- Asthma Control
- Difference Between Asthma and COPD
- Vocal Cord Dysfunction
- Asthma Attacks
- Exercise-Induced Asthma
- What does an Inhaler do to someone without an Inhaler?
- Can I claim PIP for Asthma?
- How to use an asthma inhaler
- How to use a peak flow meter
- Is Salbutamol a Steroid?
- Montelukast, Side Effects and Uses
- AERD




















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews