Why does progesterone increase after ovulation?
.png?v=1673004262075)

Related products
Progesterone is a steroid hormone released by the adrenal glands and also secreted by the corpus luteum in the ovary. It is important in regulating the menstrual cycle and maintaining the early stages of pregnancy. Progesterone is necessary for developing the endometrium, the lining of the uterus that nourishes and supports the embryo. Additionally, it helps the body to prepare for childbirth by softening the cervix and stimulating milk production in the breasts.
Progesterone also helps balance the effects of oestrogen, another hormone critical for reproductive health.
This article will discuss why progesterone increases after ovulation, its role in the reproductive cycle, the effects of increased progesterone on the body, and its importance in preparing the body for pregnancy.
Hormones regulating the menstrual cycle
Every month during the menstrual cycle, hormones fluctuate and are responsible for many physical changes a woman experiences. One of the primary hormones that changes are progesterone, which increases after ovulation.
A woman's menstrual cycle is a process of her uterus preparing for a potential pregnancy. It typically begins when she starts her period and ends when the next menstruation occurs.
The bleeding is a result of uterine wall shedding. The progesterone levels change depending on which phases of the cycle a woman is in.

The average menstrual period is expected to last between 21 and 35 days, with an average of 28 days. Women typically bleed for 3 to 7 days, although this number may vary from one woman to another.
Hormones mainly regulate this cycle by acting on the uterus, and the main ones are
-
Oestrogen
-
Progesterone
-
Luteinizing hormone (LH), and
-
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
The Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
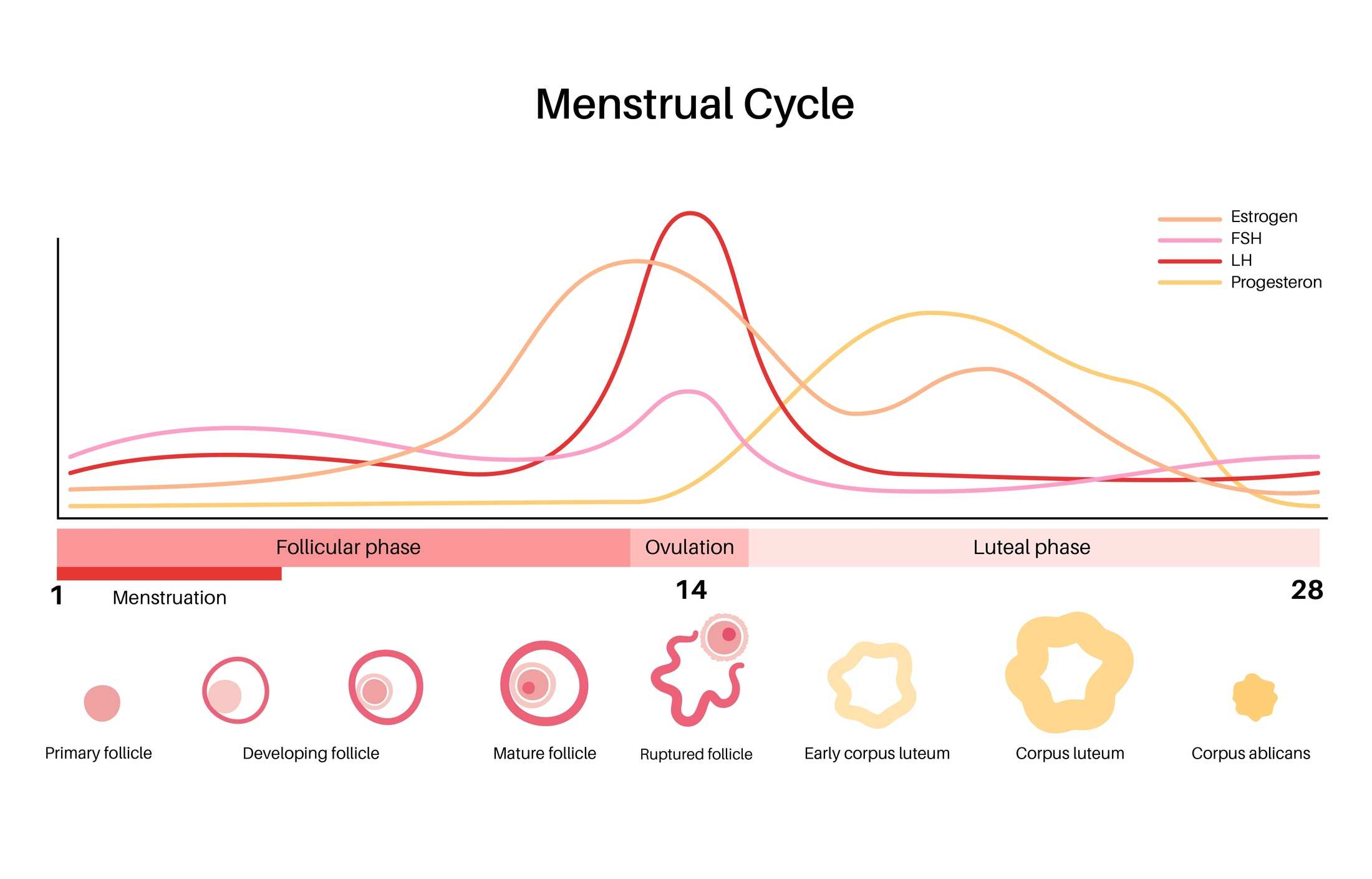
-
The menstrual phase is when a woman bleeds for 3-7 days, and the lining of the uterus is swept away, leaving it with a thin wall.
-
The follicular phase: As your period ends, your uterus starts to rebuild its lining starting from the last day of menses. Oestrogen helps with this process, making the wall thicker and more robust. Simultaneously, FSH will act on the ovarian follicles, helping them grow and develop and getting them ready to release.
-
Ovulation: After around 14 days, ovulation occurs, and the eggs are ready to be released from the ovaries with the help of LH, which reaches its peak levels.
-
The luteal phase: Once the mature egg is released, It's time to travel through the fallopian tube and make its way to the uterus. Here is where progesterone comes into play. There are high levels of progesterone.
Why does progesterone increase after ovulation?
The primary role of progesterone is to encourage the development of glands and new blood vessels in the uterus since the uterine wall is where implantation takes place.
If a woman has intercourse near her ovulation period, there's an increased chance of pregnancy. If she did have intercourse and there is a fertilized egg, then implantation would occur on the uterine wall, which is specifically prepared for this purpose.
However, if no fertilization takes place, the progesterone level will drop, the thick wall that was built will break down, and the woman will begin to bleed, which will be her next cycle. It's all part of the natural process!
What are the normal progesterone levels?
The progesterone test can determine the woman's progesterone levels at any phase. The progesterone levels fluctuate throughout the cycle.
- Follicular phase: <0.616
- Ovulation phase: 0.175 - 13.2
- Luteal phase: 13.1 - 46.3
- Post-menopause <0.401
Progesterone >30 nmol/L: Ovulation may have occurred.
Progesterone <5 nmol/L: Ovulation unlikely to have occurred.
There are multiple tests available for testing progesterone levels. You would have your blood drawn for these tests, from which the serum progesterone levels would be investigated. The test results will be easy to interpret. Here is an available ovulation progesterone blood test. Click Here.

































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews