Why Are Veins Blue?
.png?v=1674480138787)

Related products
Have you ever wondered why veins appear blue when filled with red-coloured blood? The colour of veins often confuses people - why are veins blue? Find out why your veins appear blue and why people tend to have different colours in their veins. Learn about the factors that can cause veins to look blue or green and the medical conditions that can cause abnormal vein colours.
Why do Veins appear Blue?
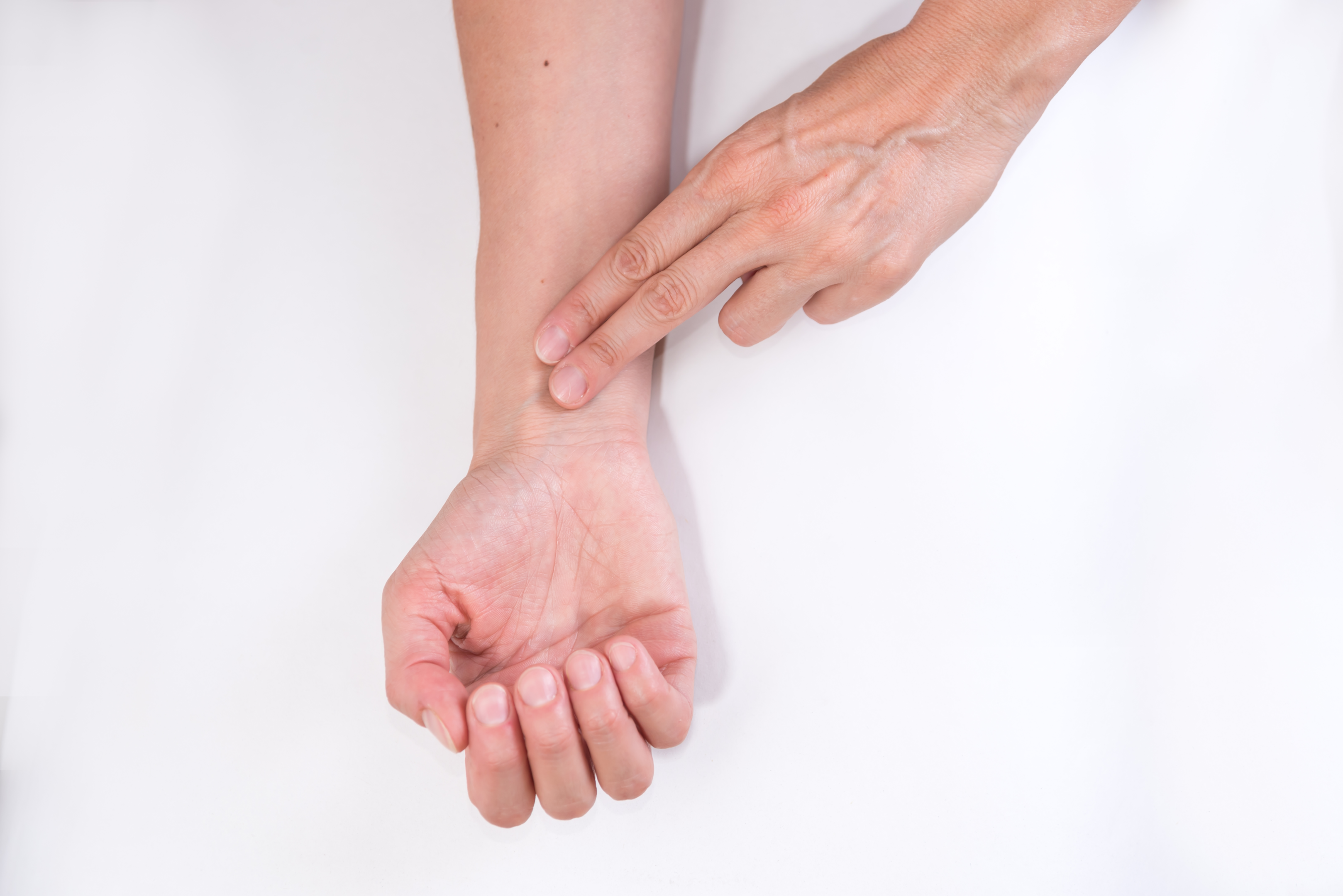
Veins are an essential part of the human body, providing a network of pathways for bringing oxygen-deprived blood from the body back to the lungs and heart. Blood is always red and veins don’t actually carry blue blood. There isn’t such a thing! If you see a vein that has been dissected from the body, you would realize that it is actually a colourless tube instead of blue. So, why do veins appear blue?
To begin, it is essential to understand how colours are formed. Colours are formed by the way our eyes perceive different wavelengths of light. When light hits an object, there are basically three ways how the object interacts with the different wavelengths of the light. It either absorbs it, the light gets scattered in different directions or reflects back. It's all about which wavelengths of light are absorbed and which are reflected. For example, a banana appears yellow to our eyes because it reflects yellow light and absorbs all other colours of light. And red light reflected in red objects.
Read more: Why does my arm hurt after a blood test?

Similarly, based on this concept, the colour of our veins is determined by how light interacts with the skin and the blood vessels underneath. When light hits the skin, it penetrates through the layers of the skin and underlying tissues before it reaches the veins. Blue light is absorbed the least and does not deeply penetrate our bodies. So the blue light is bounced back through the skin and seen by the observer, giving the impression that veins appear blue.
Overall, the vein's blue colour is simply an optical illusion. Veins appear blue because blue light shining on the skin is not absorbed by the tissue and the blood vessels underneath and is reflected back. As a result, when the blue light reflects back to our eyes, the veins appear blue.
What are the other vein colours?
It's important to note that veins do not contain pigment; they appear to be different colours due to how light interacts with them. Several factors determine the colour of a vein as the light that hits our skin and traverses through our body. This includes the depth of the vein beneath the skin's surface, the thickness of the skin, and the amount of fat tissue present. The veins appear blue and more prominent if the skin is thin or has less fat tissue. On the other hand, if the skin is thicker or there is more fat tissue present, the veins may appear less prominent and less blue.
Veins can appear in various colours, including blue, purple, green, and red.
-
Veins appear purple when they are typically deeper beneath the skin's surface.
-
Green veins are less common and are caused by the reflection of green light off of the skin.
-
Red veins are usually a sign of inflammation or irritation in the veins
Other factors can affect the appearance of veins, such as age, skin tone, race, and overall health. If you are concerned about the appearance of your veins, it is always best to consult a medical professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Read more: Skin Diseases.
Should I be worried if my vein does not appear blue?
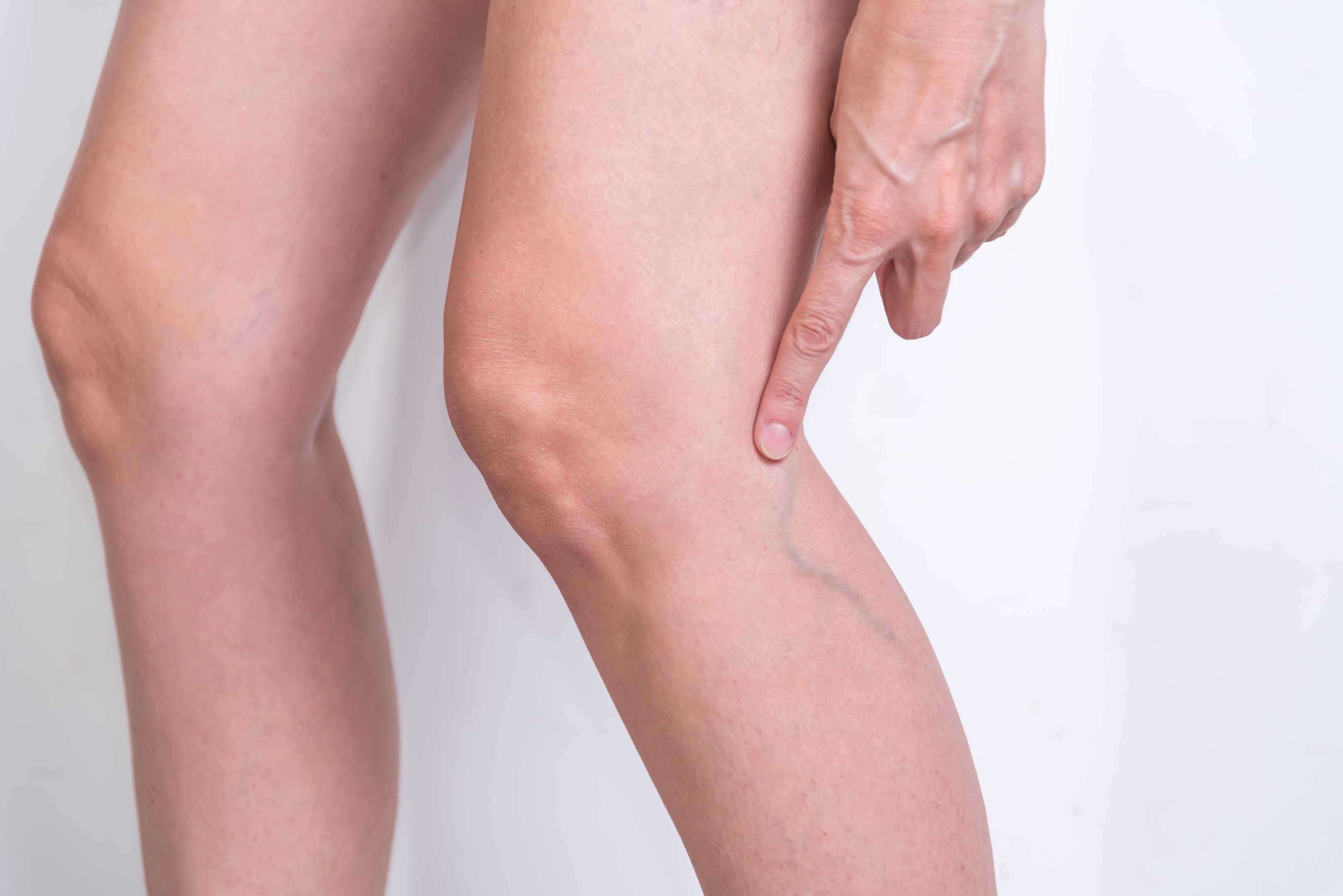
The colour of a vein is not necessarily an indicator of vein health or function, nor do colour changes usually indicate any specific health issues. However, changes in vein colour can be a sign of a medical condition affecting the circulatory system and the oxygen levels in the blood. It is important to speak with a healthcare professional if you notice any changes in your skin colour. Some of these conditions include the following medical conditions-
-
Cyanosis is a condition due to a lack of oxygen in the blood. Cyanosis can manifest an underlying lung disease, heart defects, and blood disorders. It is typically characterized by blue skin and lips.
-
Raynaud's disease: This condition causes the blood vessels in the fingers and toes to narrow, reducing blood flow and oxygen to the affected areas. Very narrow veins can lead to basically blue skin and body tissues, particularly in response to cold temperatures or stress.
-
Venous insufficiency: This is a condition in which the veins have difficulty pumping blood back to the heart, leading to a build-up of blood and a bluish skin discolouration.
-
Anaemia is when your body does not have enough red blood cells to transport oxygen to the body's tissues. Anaemia makes the skin pale or blue, particularly on the fingertips and lips.
-
Jaundice is a condition in which the skin and whites of the eyes turn yellow due to a build-up of bilirubin in the body. It can be caused by liver disease, gallstones, or other conditions that affect the liver's ability to process bilirubin.
-
Blood clots: Blood clots can form in veins for various reasons, including injury, surgery, or prolonged periods of inactivity. Clots may cause the vein to appear red, purple or dark depending on the duration of impeded blood flow.
What tests can be done for abnormal vein colour?
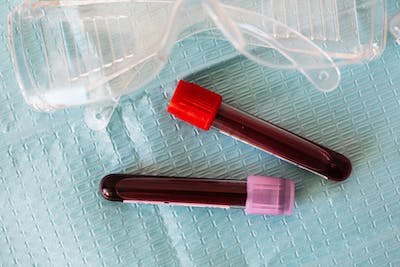
Several tests can be performed to evaluate abnormal discolouration of veins. These tests may not be necessary if the odd vein colour is not causing any symptoms or problems. These tests include:
-
Complete blood count (CBC) - This test measures the number and types of cells in your blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
-
Coagulation panel - This test measures the time it takes for your blood to clot and the levels of clotting factors in your blood. It can help detect bleeding disorders or evaluate your risk of developing a blood clot.
-
Blood smear - This test involves examining a thin layer of blood under a microscope to look for abnormal cells or other abnormalities. It may be used to diagnose conditions such as anaemia.
-
Venography: This test involves injecting a contrast dye into the veins and taking X-rays to visualize the outline of the veins and evaluate their shape and size.
-
Doppler ultrasonography: This test helps the detailed image of the veins and blood flow through them. It can help identify any issues with blood flow, such as clots or narrowed veins.
Learn more about your skin at the Welzo Health Hub. Click here to browse.

















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews