Can chlamydia go away on its own?
.png?v=1675160210396)

Related products
An overview
First and most importantly, uncontrolled chlamydia rarely goes away. If untreated, it can become fairly unpleasant, so it's important to get medicine immediately. Fortunately, chlamydia is simple to diagnose and manage. The most typical chlamydia therapy is a course of antibiotics. Chlamydia frequently disappears in a few weeks with the help of an efficient prescription drug, and you'll be fully recovered.
Make sure to take the complete amount of medicines if your doctor recommends them. If you stop your medication too soon, the disease can come back. Additionally, you should abstain from having intercourse for at least 7 days after taking the last dose of the drug.
Medications can cure chlamydia, but they are unable to stop further infections or repair organ damage caused by the disease. If your spouse has chlamydia and is not being cured, or if you start dating someone who is affected by the infection, your risk of contracting it again increases.
Will it go away on its own?
Chlamydia will rarely disappear on its own without medical attention and it will usually take a long time. You could experience severe symptoms or consequences if you don't receive treatment and you are still capable of spreading it to others. You can prevent the worst side effects of chlamydia, like excruciating pain or miscarriage in women, by receiving quick antibiotic therapy.
What is chlamydia?
Chlamydia is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections found in both males and females. It is transmitted through vaginal, oral or anal sex from an infected person. It is also transmitted from pregnant mothers to their babies.
Your risk of acquiring chlamydia is increased if you are involved in sexual activity. If you indulge in unprotected sex and have several sexual partners for sex, your risk also increases.
Many individuals do not develop any symptoms and are unaware that they have chlamydia. However, Chlamydia can continue to spread even if you do not have any symptoms.
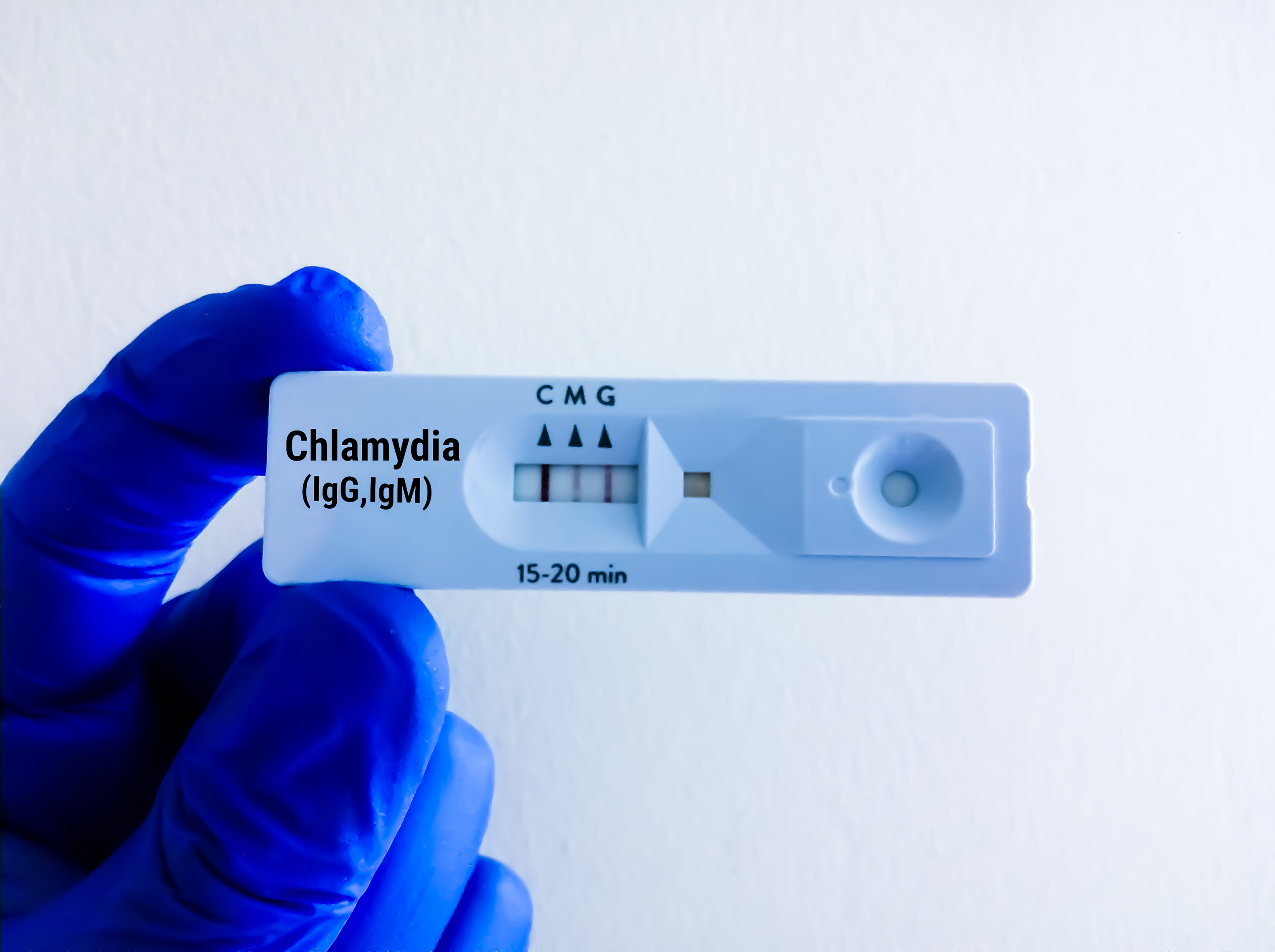
Testing is the only effective technique to determine whether you have chlamydia or not. A urine sample or a swab is used to get samples for chlamydia to diagnose.
Causes and risk factors of chlamydia
Chlamydia trachomatis bacteria are involved in bacterial infection. This bacteria affects the mucous membranes of your body.
Mucous membranes are present in the following areas.
-
Vagina and cervical areas in the women
-
Anus and rectum
-
Inside the eyelids
-
The inner side of the throat
Although the chlamydia-causing bacteria can enter the endometrium (the layer of tissue lining the uterus), the uterus itself is not affected by chlamydia because each month's menstruation will shed the infected cells and remove them from the uterus. However, because the fallopian tubes, which connect the ovaries and the uterus, do not frequently wash, they are susceptible to infection and long-lasting harm from the bacteria.
Any sexual relations might transmit chlamydia infection to the partner.
In addition, pregnant women can transmit chlamydia to a new-born baby during delivery, which leads to a vaginal or rectal infection in the child that could persist for a year or more. Chlamydia can also result in new-born pneumonia or catastrophic eye infections.
Chlamydia is particularly common among young individuals for various behavioural, societal, and biological causes.
Young individuals are involved in multiple sexual contact and unsafe sex. Which makes them highly susceptible to the infection.
Read more: What are the most common STIs?
Diagnose of chlamydia infections
There are several various kinds of chlamydia tests. The most recent kind is called nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs). This test can be carried out either on a vaginal swab or a urine sample. If you are conducting the test in women, then you should take vaginal swabs; however, in men, urine tests are used.
Women who are under 25 years of age and sexually active should undergo for taking the test. A pregnant mother should be tested during her third trimester for chlamydia infections to minimize the chances of transmitting the untreated infection to her baby.
Symptoms of chlamydia
Women may have one or more of the following chlamydia symptoms:
-
While urinating, there is pain or a burning sensation
-
Abnormal vaginal fluid leaking that may be creamy or watery
-
Unpleasant oozing or bleeding from the anus
-
Affecting eyelids
-
Pain during intercourse
-
Pain in the lower abdomen region
Chlamydia symptoms for men can include:
-
A discharge from the tip of the penis that looks white, cloudy or watery
-
A burning or itching from the urethra
-
Testicle pain
-
Pain when urinating
Duration of Chlamydia infection
The first signs of chlamydia infection may appear one to three weeks after the infection. However, there are frequently no symptoms in some patients who test positive for chlamydia, which make it difficult to determine how long the infection has lasted.
Read more: Can I get chlamydia in my eye?
Treatment of Chlamydia
Chlamydia is handled by taking a course of antibiotics. Depending on your particular specific treatment and other factors, your doctor will pick which medication to recommend and at what dosage.
To avoid passing chlamydia to a sexual partner, you must wait seven days after the commencement of your antibiotic therapy before engaging in sexual activity. The same advice is also applicable to your partner if they are receiving chlamydia treatment.
After beginning your therapy, if your symptoms last longer than a few days, you should see your physician regularly to have your condition reviewed.
Untreated chlamydia may result in ectopic pregnancy and pelvic inflammatory disease PID.
If you test positive for chlamydia, you should also get treatment for gonorrhoea because the two conditions have identical symptoms. This is because treating both infections at once is frequently quicker and more cost-effective than ordering a second gonorrhoea test following a positive chlamydia positive test.
For adult patients, the most common antibiotics are azithromycin and doxycycline. These antibiotics are used twice a day for seven days to cure the infection completely.
You can also get your treatment for chlamydia and other sexually transmitted diseases from the Welzo store.
Read more: Best chlamydia treatment
Prevention of Chlamydia
You can take a few actions to lessen or completely remove your chance of contracting chlamydia.
Avoiding vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse is the only sure-fire approach to prevent chlamydia. You can take a few actions to lessen or completely remove your chance of contracting chlamydia.
It is important to use a barrier method of contraception while involved in vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse.
Find the Welzo range of chlamydia treatments here.






















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews