Related products
What’s covered?
Pros and Cons of HRT

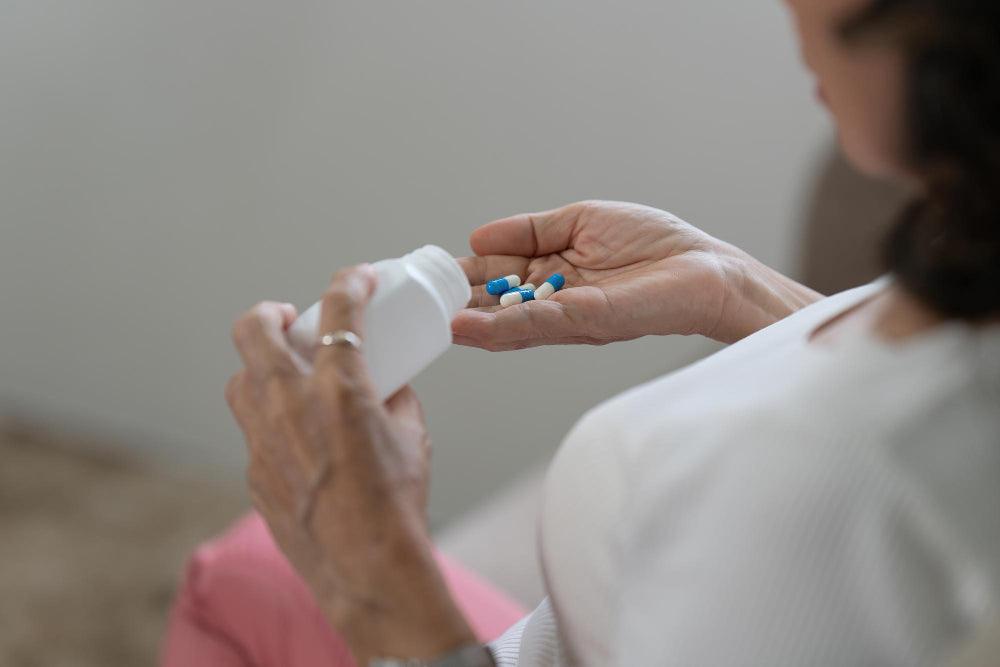
Every woman goes through menopause, a stage in her life where she no longer menstruates as her reproductive hormones naturally decline. Menopause comes with undesirable and uncomfortable symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, insomnia, altered libido, mood swings, irritation, dryness and itching in the skin or mouth, urinal urgency, and vaginal dryness or atrophy. In the 1940s, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was first introduced as a treatment to relieve these menopausal symptoms by replacing the hormones that are at a lower level.
So what is HRT treatment? Is it effective? Is it safe? Are there dangerous side effects associated? Read on to find out possible answers to these questions.
Types of hormone replacement therapy
There are two main types of HRT which are based on what hormone is being administered to a woman's body.
-
Oestrogen therapy. Women who have undergone hysterectomy (the uterus is surgically removed) do not need progesterone; thus, Oestrogen is taken alone in this therapy. A low dose of Oestrogen is typically prescribed for daily intake. Oestrogen may be prescribed as a pill (Cenestin, Estinyl, Estrace, Menest, Ogen, Premarin, Femtrace), patch (Alora, Climara, Minivelle, Estraderm, Vivelle, Vivelle-Dot, Menostar), cream (Estrace, Ogen, Premarin), vaginal ring (Estring, Femring), gel or spray (Evamist). It would be best if you took the lowest dose of oestrogen necessary to relieve menopause symptoms and/or to prevent osteoporosis.
-
Combination hormone therapy. It is the combination of oestrogen and progesterone hormones recommended to women who have not surgically removed their uterus. The progesterone in this therapy helps reduce your risk of endometrial (uterine) cancer. Available brands for this therapy are Activella, FemHRT, Premphase, Prempro, Angeliq, and Bijuva (for pills), and CombiPatch and Climara-Pro (for patches).
What are oestrogen and progesterone?
Oestrogen and progesterone are hormones that a woman's ovaries produce.
On the other hand, the roles of progesterone include:
-
Improving mood and sleep.
-
Preparing your uterus for the implantation of a fertilized egg and maintaining your pregnancy.
-
Regulating blood pressure.
How are the hormones administered to the body?
Hormone replacement therapy can be given to women either systemically or locally.
-
Systemic hormone therapy is mainly administered in a pill, injection, or patch. It functions by releasing hormones into the bloodstream and reaching the organs and tissues that require them. This administration type can address systemic symptoms like hot flashes, vaginal dryness, and mood changes.
-
Local hormone therapy is a cream, ring, or suppository employed on a localized area. It does not get into the bloodstream and is mainly used to relieve vaginal dryness due to the loss of oestrogen by rebuilding the vaginal lining and promoting lubrication. Fewer risks are associated with localized hormone therapy, but it does not alleviate systemic symptoms like hot flashes.

Benefits of hormone replacement therapy
HRT can be very beneficial and vital in managing menopause symptoms during the menopause transition.
-
HRT mainly alleviate menopausal symptoms such as vaginal dryness, hot flashes, and night sweats.
-
HRT helps you sleep better.
-
HRT relieves vaginal dryness, making sex less painful and elevating the reduced sex drive.
-
For some women, HRT can help with mood swings as oestrogen introduced to the body affect the levels of the happy hormones serotonin and endorphin in the brain.
-
HRT reduces the chances of osteoporosis and the loss of teeth.
-
HRT makes joint pains less painful.
-
HRT decreases the risk of diabetes, dementia, heart disease, and colon cancer, as studies claim.
Health risks of Hormone Replacement Therapy
Hormone therapy is a viable option for relatively young and healthy women. But, with significant advantages come several risks. And here are some of the identified risks associated with HRT:
-
Alzheimer's disease or dementia, for those who start HRT after midlife.
-
Blood clots in the legs and lungs (similar to the risks associated with hormonal birth control) could result in a stroke.
-
Deep vein thrombosis
-
Gall bladder or gallstone diseases, for those who undergo therapy in the form of pills.
-
Potential risks for endometrial cancer (womb cancer) for most women with an intact uterus and who are taking oestrogen-only replacement therapy.
-
Risk of breast cancer for those who take the combination therapy for over five years.
Side-effects of hormone replacement therapy
-
Bloating
-
Headaches
-
Nausea
-
Spotting or bleeding in the vagina that stops spotting around six months after treatment
-
Swelling or tenderness of the breasts
Should I go for hormone replacement therapy?
Many women are concerned about the safety of taking HRT. This article has provided you with the pros and cons of having this therapy. Start hormone replacement therapy by taking the hormones in minimal doses; it's up to you to decide whether the benefits outweigh the disadvantages or if it is the other way around. Consult your doctor for better guidance, have an annual assessment on your therapy, and avail of mammograms and pelvic exams regularly.
Under certain circumstances, the idea is not suitable for those who:
-
are pregnant or suspect pregnancy
-
have breast or endometrial cancer
-
have liver disease
-
have a history of heart attack or stroke
-
notice the appearance of blood clots
-
notice unexplained vaginal bleeding
Are there alternatives to HRT?
Several lifestyle changes can help you manage and relieve menopausal symptoms:
-
Balance your diet to maintain a healthy weight and ensure your bones stay healthy.
-
Develop a healthy bedtime routine and sleep schedule
-
Exercise regularly to improve sleep and reduce hot flashes. Physical activity improves your mental health and can boost your mood, too.
-
Limit intake of certain foods such as alcohol, spicy food and caffeine. They are known to trigger hot flashes.
-
Manage stress through relaxation and meditation
-
Quit smoking as it also triggers hot flushes and gives you an increased risk of developing heart disease or cancer.
Final words
Changing your lifestyle will greatly relieve menopausal symptoms. However, if HRT is a necessity, you should consult your doctor first to determine the right one for you.
To view our range of HRT medicines, click here.
If you would like to learn more about women's health click here.





























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews