
 Instagram
Instagram
How does DHT cause hair loss?


Related products
What’s covered?
How does DHT cause hair loss?
What is DHT?
One of the most prevalent causes of male pattern baldness, also known as androgenic alopecia, is ageing. Although it is far less prevalent, this form of hair loss can also occur in women. Approximately 30 million women and 50 million men in the US experience this sort of hair loss.
The most important underlying cause of male pattern hair loss is thought to be the male sex hormone in the body. Male pattern hair loss is thought to be most significantly caused by male sex hormone in the body.
An androgen is a dihydrotestosterone (DHT). A sex hormone known as androgen is responsible for the growth of what are seen as ‘masculine’ sex traits, such as body hair. However, it can also hasten and accelerate hair loss. By explicitly focusing on DHT, several treatments aim to delay the onset of male pattern baldness.
Let’s talk about how DHT functions, how it relates to testosterone and your healthy hair growth, and what you can do to prevent or at least delay male pattern hair fall.
What is DHT used for?
The source of DHT is testosterone. Both men and women have the hormone testosterone in their bodies. It and DHT are androgens, or hormones, that have a role in the development of male sex traits throughout puberty. Among these qualities are:
-
Deep voice
-
Increased facial hair and pubic hair
-
Changes in how fat is deposited all over your body
-
Sperm production begins with the expansion of the penis, scrotum, and testicles
-
Stimulate hair growth
The benefits of testosterone production and DHT to your body as you age are numerous, including increased muscle mass and fostering sexual health and fertility.
In general, testosterone levels in men are higher. In Adults, testosterone is converted into DHT.
DHT can link to receptors on hair follicles in your scalp once it has entered your bloodstream freely. This causes the hair follicles to contract and lose their capacity to support a healthy head of hair.
And DHT can affect more than just your hair. DHT, particularly extremely high amounts of it have been connected to:
-
Slow healing of the skin after an injury
-
Enlarged prostate
-
Prostate cancer
-
Coronary heart disease
-
Thinning hair follicles
DHT and hair loss
Follicles are cells beneath your scalp that create hair on every region of your body. They are essentially microscopic capsules that each carry one piece of hair.
A follicle’s hair normally experiences a growth cycle that lasts between two and six years. The identical hair will reappear in the follicle from the root of the hair that was previously housed within it, regardless of whether you shave it off or trim it.
The hair enters a phase known as resting at the end of this cycle before finally falling out a few months later. The cycle then again when the follicle grows new hair.
Increased estrogen levels, especially DHT, can reduce the process and reduce the number of hair follicles in your skin, causing your hair to grow out looking weaker and more fragile and fall out more rapidly.
DHT can also lengthen the time it takes for your follicles to produce new hair once an old hair has shed.
Depending on the polymorphisms in their androgen hormone receptor (AR) gene, certain persons are more prone to these effects of DHT on scalp hair. Proteins are called androgen receptors to allow hormones like DHT and testosterone to connect to them. Body hair growth and other regular hormonal activities are frequently the results of this binding action.
However, changes in the AR gene can make your scalp follicles more responsive to androgen, increasing your risk of developing male pattern hair loss.
Why different people are affected by DHT?
Your hereditary predisposition to hair loss means that it runs in your family. For example, If your father is a man and has male pattern baldness, There is a chance that you can experience the same.
The follicle-shrinking effects of DHT are typically more noticeable if you are predisposed to male pattern baldness.
How quickly DHT decreases your follicles may also depend on the size and shape of your head.
Effective treatments of DHT hair loss
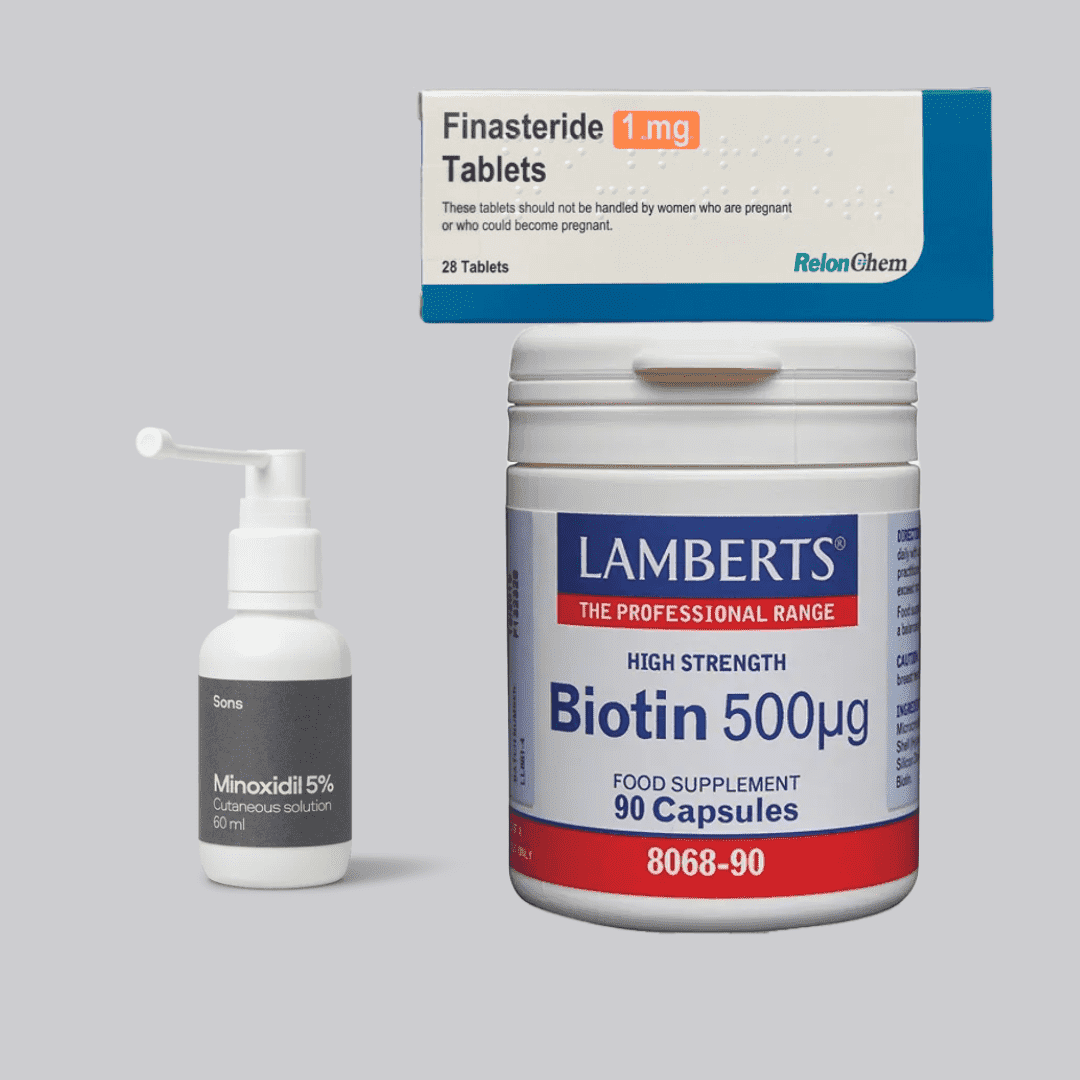
Buy Hair Loss products online here.
Numerous treatments for DHT-related hair loss are effective by particularly focusing on DHT synthesis and receptor binding. There are mostly two kinds:
DHT Blockers:
DHT blocker inhibits the ability of DHT to bind to 5-AR receptors, including those in your hair follicles that may otherwise allow DHT to cause follicular shrinkage.
Inhibitors:
These lessen the amount of DHT your body produces.
-
Finasteride
Oral finasteride (Proscar, Propecia) is a drug that is only available via prescription. In 2012 research on 3,177 males, Trusted Source found that it had a minimum success rate of 87 per cent and minor adverse effects.
To prevent DHT from interacting with 5-AR proteins, finasteride binds to them. As a result, the receptors on the hair follicles aren't able to bind to DHT and get smaller.
-
Topical Minoxidil
A peripheral vasodilator is known as minoxidil (Rogaine). This indicates that it aids in dilating and loosening blood arteries to allow for easier blood flow.
It is often taken to lower blood pressure. But when minoxidil is given topically to the scalp skin, it can also aid in hair regrowth.
-
Oral supplement
Varies oral supplements consist of naturally occurring products that help in new hair growth and widely use in hair loss treatment. This includes Vitamin B which converts foods and liquids into energy. Similarly, Keratine present in the supplement stimulates the hair growth cycle and produce new hair follicle.
There is conflicting evidence as to why biotin is crucial for maintaining your body’s keratin levels. However, a 2015 study contends that biotin can both promote hair growth and prevent the loss of hair.
At Welzo, we offer a Hair Loss Blood Test that can help you determine the underlying cause of your hair loss. To view or order your test, click here.
Or, to learn more about hair loss treatments, view our information page here.
Related Services
- Hair loss treatment
- Finasteride
- Female hair loss blood test
- Alpecin Shampoo
- Regaine
- Regaine for women
- Regain foam for men
Related articles
- What vitamins support hair growth?
- Cures for itchy scalp and hair loss
- Can stress cause hair loss?
- Can masturbation cause hair loss?
- Can creatine cause hair loss?
- Best female hair loss treatments?
- The most common causes of hair loss
- How to cope with postpartum hair loss?
- How does DHT cause hair loss?
- Cures for itchy scalp and hair loss
- What vitamin deficiency causes hair loss?
- Can wearing a hat cause hair loss?
- Dutasteride vs Finasteride: What's Best for Hair Loss?
- Relationship between diet and hair loss
- Top 7 Hair loss treatments
- What happens if you stop taking finasteride?
- Does stress cause hair loss?
- Why do men go bald?
- Guide to hair thinning
- Hair thinning at the front - what are the options?
- 11 Ways you may be damaging your hair
- What is non-surgical hair replacement?
- Hair growth explained
- Why does hair fall out in clumps?
- 5 Signs of hair thinning
- How many hairs should you lose per day?
- Do I have a receding hairline?
- How to spot a balding crown
- Early signs of balding and how to stop it
- Regaine vs rogaine - what's the difference?
- How long does minoxidil take to work?
- What are DHT blocking shampoos?
- How to get rid of split ends


















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews