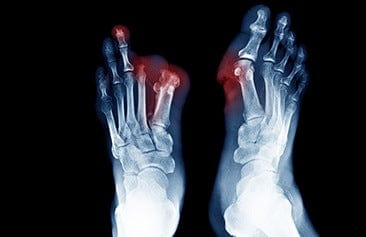
Bone Infection
Bone infections are difficult to identify because they frequently resemble other forms of diseases or injuries. Your doctor will most likely begin with a physical examination and questions about your medical history. They may also request tests like X-rays, MRIs, or blood tests. Antibiotics and surgery are frequently used to treat a bone infection. In order to better understand Bone Infection, Welzo users should read this article.

 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews