Explore Welzo’s Vitamin D collection, featuring high-strength Vitamin D3, plant-based Vitamin D2 and combined formulas designed to support immunity, bone strength, mood balance and overall wellbeing. Vitamin D is one of the most commonly recommended supplements in the UK, especially during autumn and winter when sunlight exposure is limited. Buy Vitamin D online at Welzo and discover options suitable for adults, children, vegans and individuals needing higher-dose support.
Our Vitamin D range pairs naturally with immunity supplements, bone & joint support, essential minerals, and calcium supplements, helping you create a complete daily routine for long-term health.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin essential for regulating calcium absorption, supporting immune responses, and maintaining healthy bones, teeth and muscles. The body naturally produces Vitamin D when skin is exposed to sunlight; however, due to the UK climate and indoor lifestyles, deficiency is extremely common.
Vitamin D supplements are available in two key forms:
-
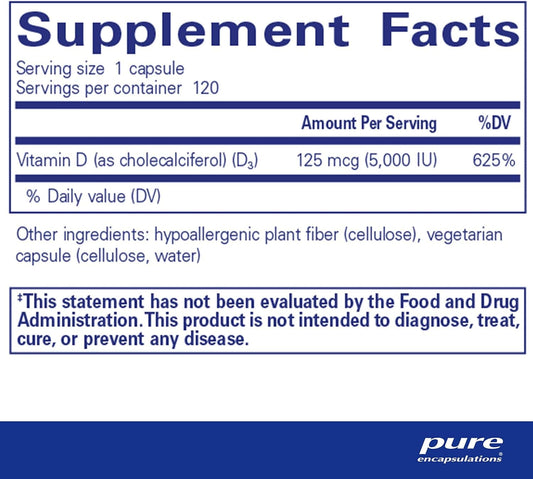
Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) – the most effective and well-absorbed form, usually derived from lanolin or lichen (vegan).
-
Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) – plant-derived and suitable for vegans.
Vitamin D is also included in many formulas across our multivitamin and pregnancy vitamins categories.
Benefits and Features of the Welzo Vitamin D Collection
Our range includes high-purity Vitamin D tablets, sprays, capsules and combined formulas designed to meet different needs. Key benefits include:
-
Supports immune function – Vitamin D contributes to the normal function of the immune system.
-
Essential for bone and muscle health – helps maintain normal bones and supports normal muscle function.
-
Mood & cognitive wellbeing – low Vitamin D levels are commonly associated with tiredness and low mood.
-
Suitable for all ages – children's liquid drops, adult capsules, sprays and high-dose options available.
-
Vegan and allergen-friendly choices – including lichen-based D3 and combined formulas with magnesium or K2.
Vitamin D works well alongside magnesium supplements, Vitamin K2, and omega-3 supplements for a more complete nutritional approach.
Why is Vitamin D Important?
Vitamin D plays a central role in:
-
Immune resilience throughout the year, especially winter.
-
Bone mineralisation and maintaining healthy calcium levels.
-
Muscle strength and reducing risk of deficiency-related fatigue.
-
Mood stability and cognitive wellbeing.
Public health guidance in the UK recommends daily Vitamin D supplementation during autumn and winter. Many people benefit from year-round support, particularly those who spend limited time outdoors, cover their skin, or follow vegan diets.
How to Use Vitamin D Supplements?
Usage instructions may vary depending on strength and format, but general guidance includes:
-
Take Vitamin D3 with a meal containing healthy fats to support absorption.
-
Sprays may be absorbed through the soft tissues in the mouth and can be taken without food.
-
High-dose Vitamin D should only be taken as advised by a healthcare professional.
-
Children should follow age-appropriate doses as indicated on product labels.
If combining Vitamin D with calcium, magnesium or K2, check serving sizes across all products to avoid duplicating nutrients unnecessarily. Pair it with our magnesium range for optimal absorption and muscle support.
What are the Different Types of Vitamin D Supplements Available?
Our curated Vitamin D collection includes multiple forms suitable for different preferences:
-
Vitamin D3 capsules – the most common and effective format.
-
Vegan Vitamin D3 – sourced from lichen.
-
Vitamin D2 – plant-based and suitable for vegans.
-
Vitamin D sprays – easy absorption and ideal for those who dislike tablets.
-
Vitamin D + K2 formulas – support calcium utilisation and bone health.
-
Children’s Vitamin D drops – gentle, easy-use format for infants and toddlers.
You can also explore related categories such as immune health, bone & joint support, and popular supplement brands.
What Are the Most Popular Vitamin D Supplements Available?
Customer favourites frequently include:
- High-strength Vitamin D3 1000 IU – 4000 IU capsules
- Vegan Vitamin D3 sourced from lichen
- Vitamin D oral sprays for quick delivery and convenience
- Vitamin D3 + K2 bone health formulations
- Children’s Vitamin D drops compliant with UK guidelines
These products are often purchased alongside calcium supplements and multivitamins for a complete nutritional foundation.
Statistics, Research, Expert Information & Quotes on Vitamin D
Research consistently highlights the widespread prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in northern climates like the UK. Studies indicate potential associations between low Vitamin D and reduced immune function, impaired bone metabolism, poor muscle performance, and low mood—though supplements should not be viewed as treatment for medical conditions unless guided by a clinician.
Vitamin D supplementation is particularly recommended for adults with limited sunlight exposure, older adults, individuals with darker skin tones, and those who wear full-coverage clothing.
For a deeper look into related immune-support nutrients, read our expert guide Can Vitamin C Prevent a Cold? which offers insight into how Vitamin C and Vitamin D may work together to support everyday immune health.
How We Select Our Vitamin D Collection on Welzo
Welzo’s Vitamin D collection is carefully chosen based on:
-
Purity – products free from unnecessary fillers and artificial additives.
-
Evidence-based formulation – strengths aligned with UK and EU nutritional guidance.
-
Bioavailability – vitamin forms that are well-absorbed, such as D3 and D3+K2.
-
Brand trust – only manufacturers with strong testing, safety and compliance protocols.
-
User suitability – options for children, adults, vegans and individuals requiring higher strength support.
We ensure that every listed product aligns with the same high standards applied across our vitamins & supplements portfolio.
Trusted by Experts and Verified Vitamin D Quality on Welzo
Welzo partners with clinicians, pharmacists and nutrition experts to curate our supplement catalogue. We provide transparent information so customers can make informed decisions. Learn more about our team and quality standards below:
Vitamin D Supplement Reviews
Customer reviews highlight improved energy, better mood stability, and seasonal wellness support when using Vitamin D consistently. Many customers appreciate the convenience of sprays and the strong absorption of D3+K2 combinations. You can explore experiences and feedback on our Welzo reviews page.
Vitamin D FAQs
How much Vitamin D should I take daily?
Public Health England recommends 10 micrograms (400 IU) of Vitamin D daily for most adults. Some individuals may require higher doses under medical supervision.
Is Vitamin D deficiency common in the UK?
Yes. Due to limited sunlight, especially in autumn and winter, Vitamin D deficiency is widespread across the UK population.
Can I take Vitamin D all year round?
Yes. Many people benefit from year-round supplementation, particularly those with darker skin tones or limited sunlight exposure.
What is the difference between Vitamin D2 and D3?
D3 is generally better absorbed and more effective at raising blood Vitamin D levels, while D2 is a vegan alternative.
Can Vitamin D improve mood?
Low Vitamin D levels are associated with low mood, though supplements should not replace clinical treatment for mental health conditions.
Can children take Vitamin D?
Yes. Specific doses exist for infants, children and adolescents. Always follow the dosing instructions on child-specific products.
Should I take Vitamin D with Vitamin K2?
Many people combine D3 with K2 to support calcium utilisation and bone health, though this is optional unless clinically recommended.
Can I take too much Vitamin D?
High doses taken for long periods may cause toxicity. Only take high-dose Vitamin D under medical supervision.






























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews