Prostate cancer screening: Should you get a PSA test?
Related products
Understanding PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) Testing
A. Brief overview of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting men, with the American Cancer Society estimating that 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer during their lifetime 1.
B. Importance of early detection
Early detection plays a crucial role in improving treatment outcomes and reducing mortality rates. According to Dr. Anthony D'Amico, a leading prostate cancer specialist, early intervention can increase the 5-year survival rate to nearly 100% 2.
C. Introduction to the PSA test
One widely-used method for prostate cancer screening is the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. In this article, researched for Welzo, the medical website, we will explore the PSA test, its benefits, and the factors to consider before undergoing this screening test.
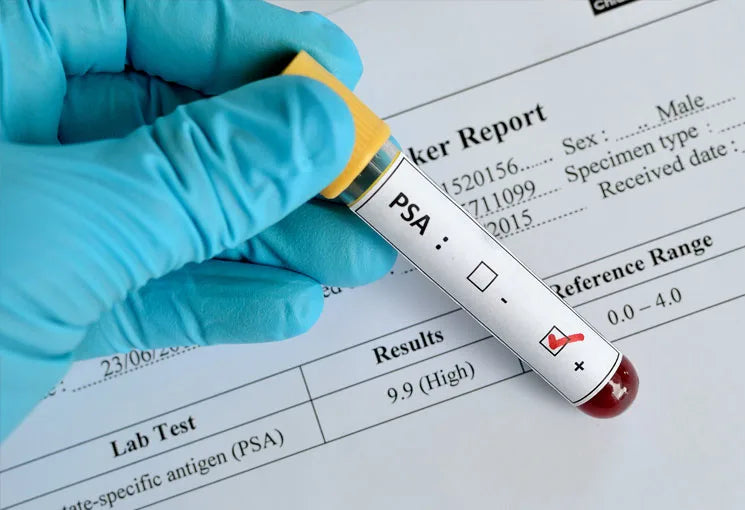
II. What is a PSA Test?
A. Definition of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
PSA is a protein produced by both cancerous and noncancerous cells in the prostate gland 3. Elevated levels of PSA in the blood can be indicative of prostate cancer or other prostate-related conditions.
B. Explanation of the PSA test
The PSA test is a blood test that measures the level of PSA in the bloodstream 4. Doctors use the test to help detect prostate cancer and monitor its progression or recurrence.
C. How the test is performed
A healthcare professional will draw a small sample of blood from a vein in your arm. The blood is then sent to a laboratory, where the PSA levels are measured and reported to your doctor 5.
III. Benefits of PSA Testing
A. Early detection of prostate cancer
The PSA test can help identify prostate cancer in its early stages when it is more treatable. According to the National Cancer Institute, the widespread use of PSA testing has led to a significant increase in the early detection of prostate cancer 6.
B. Potential for better treatment outcomes Dr. Peter Scardino of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center highlights that early detection can lead to better treatment outcomes and improved chances of survival 7. When cancer is found early, less invasive treatments may be used, reducing side effects and complications.
C. Monitoring cancer recurrence
For patients who have undergone treatment for prostate cancer, regular PSA tests can help monitor for any signs of recurrence, allowing for prompt intervention if needed 8.
IV. Risks and Limitations of PSA Testing
A. False positives and increased anxiety
False positives occur when a PSA test indicates a high level of PSA, but no cancer is present. According to the National Cancer Institute, about 75% of men with elevated PSA levels do not have prostate cancer 9. False positives can lead to unnecessary anxiety and additional testing, such as biopsies, which carry their own risks.
B. False negatives and missed diagnosis
On the other hand, false negatives can occur when PSA levels are within the normal range, but cancer is present. This can result in a missed or delayed diagnosis, potentially leading to more advanced disease and worse outcomes 10.
C. Overdiagnosis and overtreatment
Some prostate cancers are slow-growing and may not require immediate treatment. However, the PSA test cannot differentiate between aggressive and indolent cancers, leading to overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which can cause unnecessary side effects and complications 11.
V. Factors to Consider Before Getting a PSA Test
A. Age and life expectancy
The American Cancer Society recommends discussing PSA testing with a healthcare provider starting at age 50 for men at average risk and at age 45 for those at higher risk 12. Your life expectancy should also be considered, as older men with a limited life expectancy may not benefit from screening.
B. Family history of prostate cancer
Men with a strong family history of prostate cancer should consider getting a PSA test, as they are at a higher risk of developing the disease 13.
C. Race and ethnicity
Certain racial and ethnic groups, such as African American men, have a higher risk of prostate cancer and should consider PSA testing 14.
D. Personal preferences and values
Ultimately, the decision to get a PSA test should be based on an individual's preferences, values, and a thorough discussion with their healthcare provider.
VI. Guidelines and Recommendations for PSA Testing
A. American Cancer Society 12 B. American Urological Association 15 C. U.S. Preventive Services Task Force 16 D. World Health Organization [17]
Different organizations have varying recommendations for PSA testing. It's essential to consult your healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your individual situation.
VII. Alternatives to PSA Testing
A. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
A DRE is a physical examination in which a healthcare provider inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to check for abnormalities in the prostate gland [18].
B. Multiparametric MRI
This imaging technique provides detailed information about the prostate, potentially helping to identify cancerous tissue without the need for a biopsy [19].
C. Biomarker tests
Newer biomarker tests, such as the Prostate Health Index (PHI) and 4Kscore, can help provide more accurate information on the likelihood of prostate cancer and guide further testing [20].
VIII. Making an Informed Decision about PSA Testing
A. Discussing your risk factors with your healthcare provider
Before deciding on PSA testing, it is crucial to have a thorough conversation with your healthcare provider. They can help assess your risk factors, such as age, family history, and race, and provide personalized guidance based on your medical history and current health status.
B. Weighing the benefits and risks
It is essential to consider both the benefits and risks of PSA testing before making a decision. The primary benefit of PSA testing is the early detection of prostate cancer, potentially leading to better treatment outcomes. However, risks such as false positives, false negatives, and overdiagnosis should also be taken into account.
C. Considering your personal values and preferences
Ultimately, the decision to undergo PSA testing should align with your personal values and preferences. Some individuals may prioritize early detection and are willing to accept the risks associated with testing, while others may prefer to avoid potential anxiety or overtreatment. Discussing these concerns with your healthcare provider can help you make an informed decision.
IX. Conclusion
A. Importance of personalized decision-making PSA testing is not a one-size-fits-all approach to prostate cancer screening. Each individual's unique risk factors, health status, and personal values should be considered when deciding whether to undergo testing. Personalized decision-making ensures that screening choices are tailored to each person's specific needs and preferences.
B. Encouraging open communication with healthcare providers Open communication with healthcare providers is essential in making informed decisions about PSA testing. Discussing your concerns, risk factors, and values with your healthcare provider can help you better understand the potential benefits and risks of testing and determine the best course of action for your situation.
C. The role of PSA testing in prostate cancer prevention and management While PSA testing has its limitations, it remains an essential tool in the early detection and management of prostate cancer. By making informed decisions about PSA testing and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can play an active role in their prostate health and overall well-being.






 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews