
 Instagram
Instagram
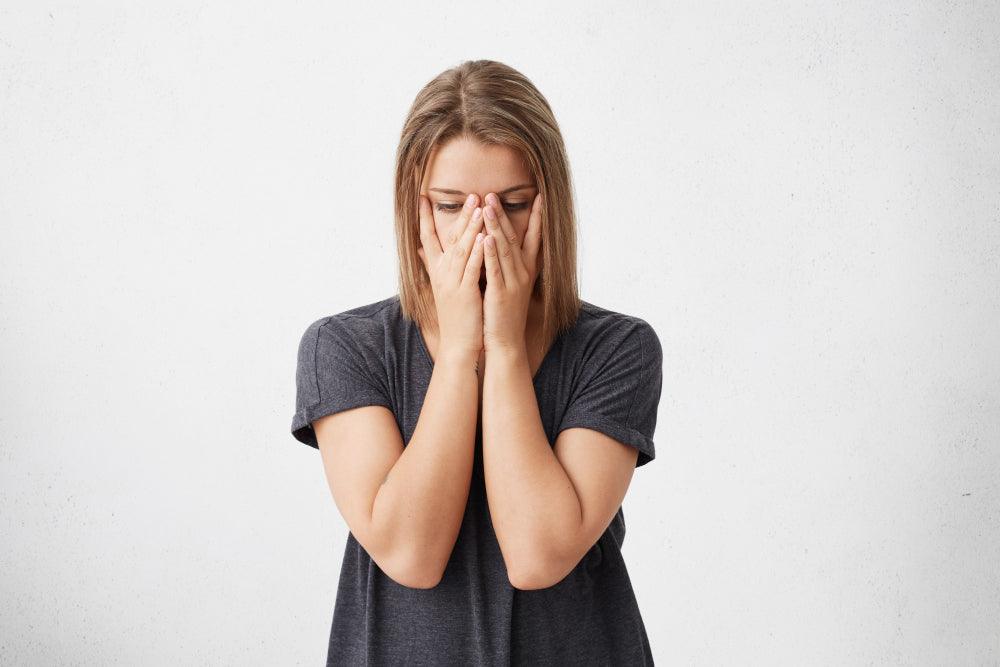
What is stress?


Related products
What’s covered?
What is stress?
What happens within the body during stress?
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for controlling your breathing, heart rate, and other physical processes. The "fight-or-flight response," the body's response to stress, allows it to cope with stressful situations.
Long-term (chronic) stress results in ongoing activation of the stress hormones, which break down the body over time. Symptoms emerge that are behavioural, emotional signs, and physical symptoms.
Types of stress;
Not every form of stress is detrimental or even negative. You could endure a variety of stressors, some of which include;
1. Acute stress;
Acute stress is the kind of stress we experience most frequently in day-to-day living. It is a relatively short-term sort of stress that can either be helpful or more upsetting.
2. Chronic stress;
Stress that feels unending and inescapable, such as the stress of an unhappy marriage or a difficult profession, is known as chronic stress. Traumatic events and early childhood trauma can also cause chronic stress.
3. Episodic stress;
A continuing state of anguish is caused by episodic acute stress, which is acute stress that appears to be a prevalent way of life.
Among the physical signs of stress are:
Following are some negative impacts of a stressful event
-
Ill health
-
Chest discomfort or deep breathing
-
Fatigue or trouble sleeping.
-
Emotional exhaustion
-
High blood pressure due to stress and anxiety.
-
Jaw clenching or tightness in the muscles.
-
Issues with the stomach or digestion.
-
Difficulty having sex.
-
Weak immune system.
-
Digestive problems
-
Difficulty concentrating
How the stress can be identified?
Stress cannot be evaluated with testing. Its presence and intensity are only discernible to the individual who is experiencing them. A healthcare professional may use questionnaires to learn more about your stress and how it affects your life.
Your healthcare professional can also assess stress-related symptoms if you have chronic stress. For instance, it is possible to diagnose and treat high blood pressure.
Causes of stress;
There are numerous factors in life that might lead to stress. Work, finances, relationships, children, and everyday annoyances are a few major stressors. The fight-or-flight response, which is the body's reaction to a perceived threat or danger, can be triggered by stress. Adrenaline and cortisol, among other hormones, are released during this reaction. This boosts the body's autonomic nervous system activity, increases heart rate, delays digestion, diverts blood flow to major muscle areas, and alters several other autonomic neurological activities.
Systems are built to function normally once the apparent threat has passed, thanks to the relaxation reaction. But when there is ongoing stress, the relaxation reaction doesn't happen frequently enough, and the body can become damaged by being in a near-constant fight-or-flight state.
Additionally, stress can cause bad habits that are detrimental to your health. For instance, many people turn to overeating or smoking as a coping mechanism for stress. These bad behaviours harm the body over time and lead to more serious issues.
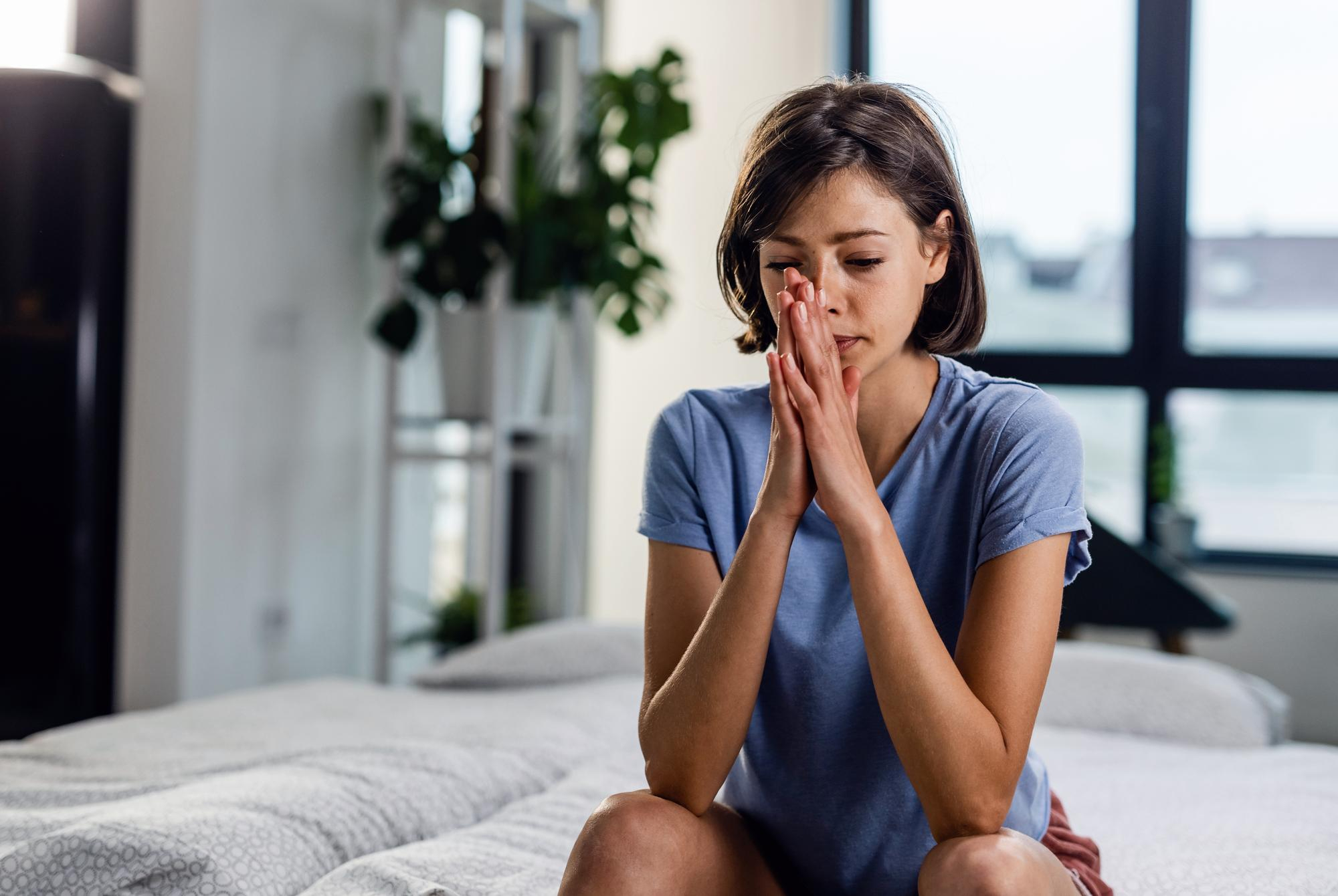
What are some strategies for reducing acute stress?
Numerous everyday techniques can assist you in reducing stress:
-
Try relaxing exercises like yoga, tai chi, breathing exercises, and muscular relaxation. Programs can be found in numerous gyms and community centres, on mobile apps, and online.
-
Take good care of your body. Your body handles stress considerably better when you eat well, exercise, and get adequate sleep.
-
Stay happy and express thanks for the positive aspects of your day or life.
-
Recognize that there are things you cannot control. Try to find strategies to stop worrying about things you can't alter.
-
Learn to say "no" when you are too busy or under pressure to accept new obligations.
-
Keep in touch with those that uplift you, make you smile, provide you emotional support, and assist you with daily tasks. To prevent stress from becoming too much, a friend, relative, or neighbour might share tasks or act as a good listener.
Stress management techniques
-
Complementary and alternative medicine
Therapies like mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and meditation effectively treat stress and anxiety.
Meditation is an age-old technique that promotes relaxation by emphasizing breathing and present-moment body awareness.
Evidence suggests that mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques like meditation are particularly effective at treating too much stress, and professionals strongly advise them.
-
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy
Talk therapy with an emphasis on identifying and challenging unfavourable, frequently incorrect attitudes that might contribute to behavioural and mental health issues, such as anxiety, is known as cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT).
According to research, those who receive CBT experience a higher decrease in physical and mental health symptoms than those who only utilize medicine.
Strong evidence supports the efficacy of MBSR, CBT, and meditation in managing stress.
These methods are all risk-free and have no negative side effects. Anyone motivated can practice them independently. Discussing your symptoms with your doctor is vital since integrative medicine may complement traditional care, but it does not serve as a substitute.
-
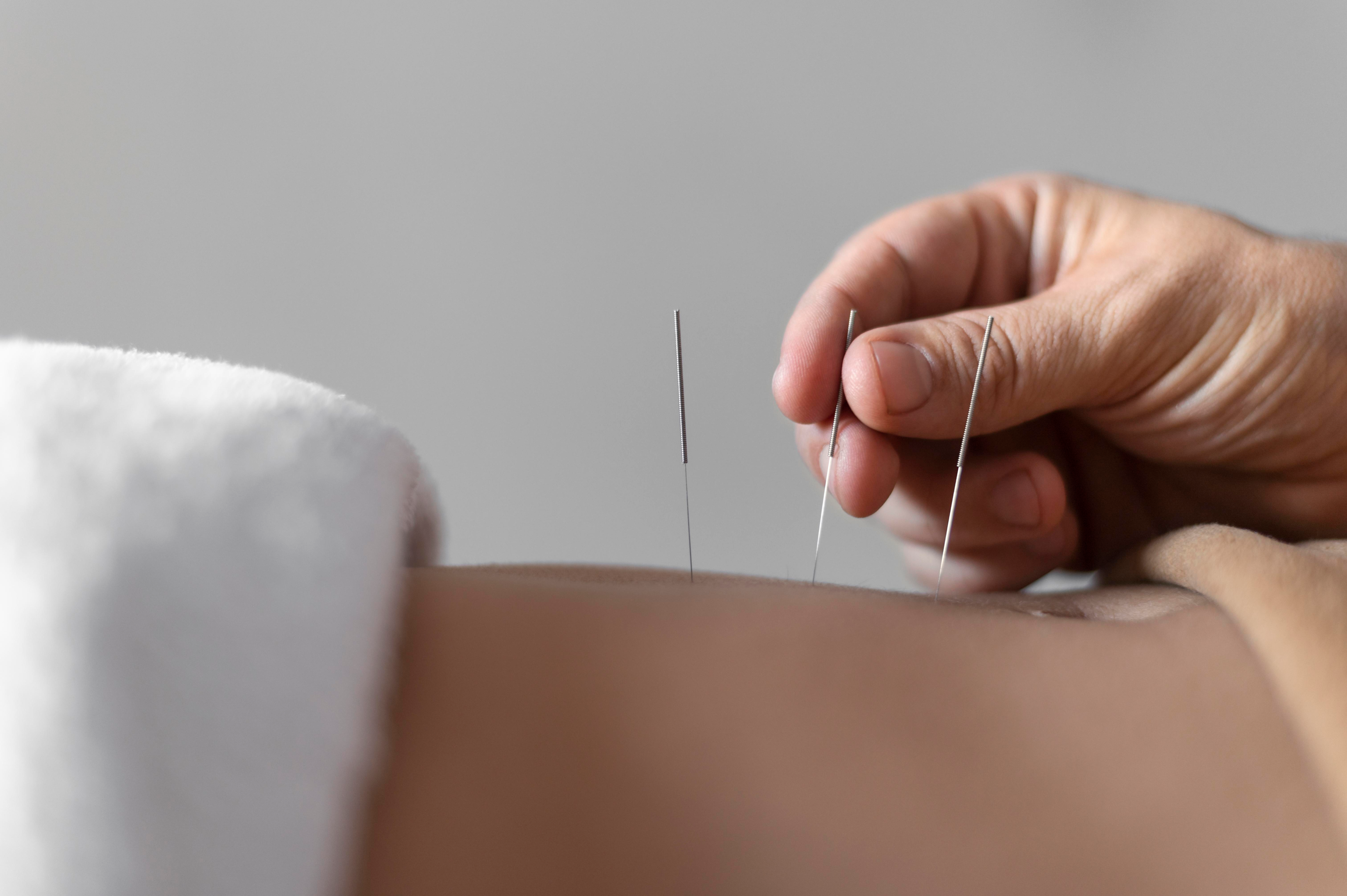
Acupuncture
Tiny needles are used in the traditional Chinese medical procedure known as acupuncture to activate the neurological and immunological systems. A certified acupuncturist places hair-thin needles under the skin at predetermined sites on the body throughout the process. Research demonstrates that painless acupuncture supports conventional treatment for various issues, including stress, chronic pain, and digestive problems. Experts point out that it might work especially well for insomnia.
Stress response can be a very frustrating emotion to feel. Here at Welzo, we offer tests that can help you understand if there are underlying issues that may be impacting your stress, including a Cortisol Test and Health and Lifestyle Test.
Relaxation techniques for stress relief:
-
Autogenic relaxation.
Autogenic refers to something that originates within of you. You can lower tension by using this relaxation technique, which combines body awareness with visual images.
You mentally repeat phrases or ideas that can ease tension in your muscles and promote relaxation. For instance, picture a calm environment. Following that, your attention can be directed toward relaxing your breathing, lowering your heart rate, or experiencing other bodily sensations, such as relaxing each arm or leg one at a time.
-
Progressive muscle relaxation techniques
You concentrate on gradually tensing and then releasing each muscle group when using this relaxation technique.
Your ability to distinguish between muscle tension and relaxation will be aided by this. Physical experiences can help you become more conscious.
One technique for progressive muscle relaxation involves starting with your toes and gradually working your way up to your neck and head. The ideal setting for doing this is a peaceful, distraction-free environment. Alternately, you might start at your head and neck and work your way down to your toes. Repeat by making your muscles tense for five seconds, then relax for thirty.
To learn more about your health and underlying concerns that may be causing you additional stress, check out our Cortisol Blood Test by clicking here.
Additionally, read through our mental health information pages by clicking here.
































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews