
 Instagram
Instagram
What are Hep C symptoms in a Female?
.png?v=1674477462696)

Related products
Hepatitis C is an infection of the liver with an inflammatory course of nature. Caused by the Hepatitis C virus, the infection can last for a short time in the form of mild illness or it may also have a chronic prognosis. Chronic hepatitis can be fatal, causing serious damage to the liver and other vital organs resulting in liver cirrhosis or liver cancer. Unlike Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B, there is currently no vaccine against hepatitis C. Therefore, Hepatitis C infection is a matter of grave health concern globally. Unfortunately, knowledge regarding the spread of the hepatitis C virus and its effect on the body is largely unknown. There is certainly an increased need for awareness about hepatitis C infection.
Read more: Who should get a Hepatitis B vaccine?
Symptoms of Hepatitis C in Females
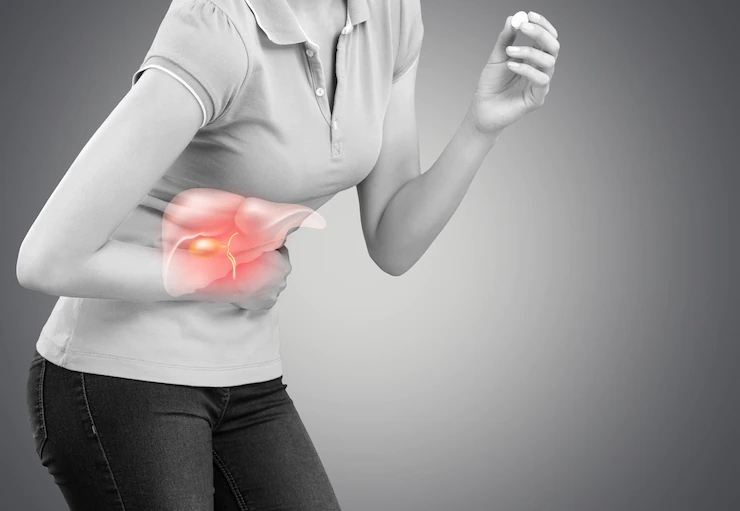
Common Symptoms
-
Fever
-
Vomiting
-
Nausea
-
Stomach pain
-
Swelling of the abdomen
-
Abnormally dark urine
-
Change in stool colour
-
Itchy skin
-
Jaundice
How does Hepatitis C infection Spread?
Blood to Blood contact
This is the major mode through which Hepatitis C infection may be passed. Hepatitis C infection can spread when an infected person's blood directly contacts another individual's blood. Sharing needles for injecting drugs, unhealthy hygiene practices in hospitals, healthcare workers being exposed to infected blood, and errors in the screening of blood transfusion are some of the risk factors for acquiring Hepatitis infection.
Sexual Contact
Though not very common, Hepatitis C infection can spread from an infected person via sexual activities like vaginal, oral, and anal sex in situations where blood contact has occurred in the case of small and minor cuts.
Mother to Foetus
In some cases, there is a rare chance of spreading a hepatitis C infection from a pregnant woman infected with hepatitis C to the foetus via the placenta.
Hepatitis C in Women vs Men
You may be surprised to know that hepatitis can sometimes affect women and men differently. The one good news for all women out there is that acute hepatitis C infection often heals much quicker in women than men.
Oestrogen is considered to be the hormone that's responsible for its protective function against hep C infection in women. In menstruating women with optimum oestrogen levels, liver damage progresses at a much slower rate as compared to men.
Women have higher chances of spreading hep C infection during menstruation through sexual contact. It is, therefore, best to avoid intercourse during menstruation if you have a Hep C infection.
Women on birth control pills may have to discuss with their doctor the consumption of the pill as the liver's ability to break down drugs is affected by hepatitis infection.
Post menopause, as the oestrogen levels drop low, women are more prone to be affected by the damage caused by Hep C infection.
Read more: The best diet for a healthy liver.
Diagnosis
If you are at risk of acquiring Hep C or are suffering from symptoms of Hepatitis C infection, your doctor would advise you to undergo a few blood tests to detect the Hepatitis C virus and its viral load in your bloodstream. These tests are specific for Hepatitis C and include the following:
-
A PCR blood test for measuring your Hepatitis C viral load
Your doctor may advise you to undergo additional blood tests to understand your liver health. These include blood tests measuring your bilirubin and albumin levels along with a measurement of your essential liver enzymes. You may consider doing a Welzo liver function test that would measure all the above-mentioned parameters and thereby assess your liver health and function.
A liver biopsy may also be required depending on the severity of your infection.























 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews