Causes of high prolactin in men
.png?v=1673453982062)

Related products
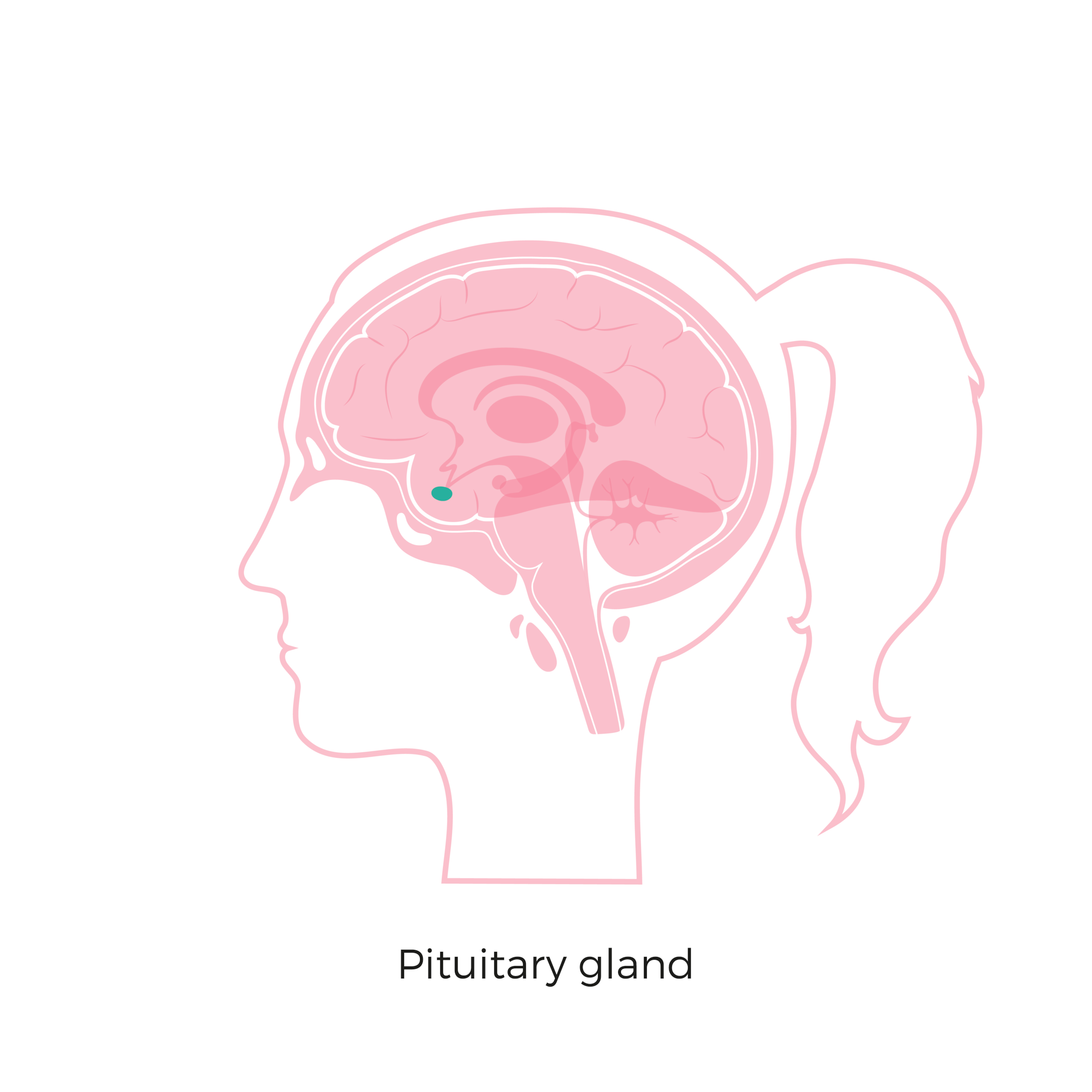
Prolactin is a hormone that plays a significant role in reproductive and metabolic functions in both men and women. While commonly associated with lactation and maternal behaviours in women, prolactin is also present and active in the male body. Produced by the pituitary gland, which is located at the base of the brain, prolactin helps regulate levels of other important hormones, such as testosterone and oestrogen. In men, elevated prolactin levels, a condition known as hyperprolactinemia, can lead to a variety of symptoms and health complications. Despite being less frequently discussed in men, high prolactin levels can seriously affect sexual function, fertility, energy levels, and even bone health.
Hyperprolactinemia is more commonly studied in women, especially those of reproductive age experiencing menstrual irregularities. However, in men, the condition is often underdiagnosed or misattributed to other health problems until symptoms become more pronounced. Prolactin levels in the blood are typically evaluated using a serum prolactin (PRL) test, which helps identify if the levels are above the normal range. It is essential to understand the implications of high prolactin in men, as it often signals underlying issues with the pituitary gland or side effects from medications.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the causes, effects, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of high prolactin levels in men. We will explore the functions of prolactin, detail the condition of hyperprolactinemia, explain why it occurs, and outline the possible interventions. We’ll also add new sections covering the effects on male fertility, links to mental health, lifestyle considerations, and hormone balance strategies. Whether you are dealing with symptoms or are a healthcare enthusiast, this resource aims to provide valuable, evidence-based insights.
What is Hyperprolactinemia?
Hyperprolactinemia refers to abnormally elevated levels of prolactin in the bloodstream. In men and nonpregnant women, this condition can disrupt normal hormone balance and cause a wide array of symptoms. While it is more frequently diagnosed in women, especially those with irregular menstrual cycles, men with hyperprolactinemia often remain undiagnosed until noticeable symptoms such as erectile dysfunction or decreased libido emerge.
The pituitary gland is responsible for prolactin production. Normally, prolactin levels in men should remain low. However, when the gland overproduces this hormone—often due to a benign tumour called a prolactinoma or as a result of medication side effects—hyperprolactinemia develops. Elevated prolactin levels interfere with the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, which regulates testosterone production. In men, this hormonal disruption can result in low testosterone, poor sperm production, and decreased sexual performance.
Hyperprolactinemia may also occur secondary to other health conditions such as hypothyroidism, chronic kidney disease, or liver dysfunction. In rare cases, no identifiable cause is found, a condition termed idiopathic hyperprolactinemia.
Proper diagnosis often involves a combination of blood tests, imaging studies, and patient history to pinpoint the underlying cause. Once identified, treatment aims to normalise prolactin levels and resolve the symptoms, often leading to significant improvements in quality of life and overall health.
Functions of Prolactin
Prolactin is a multifunctional hormone best known for its role in promoting lactation in females. However, its physiological impact extends far beyond milk production. In men, prolactin interacts with other hormonal systems to support various metabolic and reproductive functions. Though not fully understood, the biological actions of prolactin include regulation of immune response, behaviour, metabolism, and reproductive health.
Key functions of prolactin in men include:
-
Modulating testosterone levels and influencing testicular function.
-
Supporting spermatogenesis, particularly in synergy with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
-
Regulating mood and behavioural responses, with emerging research linking prolactin levels to mental health.
-
Influencing lipid metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
At physiological levels, prolactin may act as a mild gonadotropin. However, at elevated levels, it inhibits gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) secretion, leading to decreased luteinising hormone (LH) and FSH levels. This hormonal imbalance can suppress testosterone production and impair fertility.
Emerging evidence also suggests prolactin may influence inflammatory markers in the body. Chronic low-grade inflammation, often linked to endocrine disorders, can compound symptoms in hyperprolactinemic patients. If inflammation is suspected alongside hormonal irregularities, the CRP Blood Test available on Welzo can help detect systemic inflammation early and guide treatment decisions effectively.
Causes of High Prolactin in Men
High prolactin levels in men can result from a variety of causes, some physiological and others pathological. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for targeted treatment.
-
Pituitary tumours (Prolactinomas)
-
These benign tumours lead to the overproduction of prolactin. Larger tumours (macroadenomas) may compress adjacent structures, causing headaches and vision changes.
-
-
Medications
-
Many medications can increase prolactin as a side effect:
-
Antipsychotics (e.g., risperidone, haloperidol)
-
Tricyclic antidepressants
-
Antihypertensives (e.g., methyldopa, calcium channel blockers)
-
Gastrointestinal medications (e.g., metoclopramide)
-
-
-
Hypothyroidism
-
Low thyroid hormone levels can lead to increased thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates prolactin secretion.
-
-
Chronic illnesses
-
Kidney and liver diseases can reduce the clearance of prolactin, causing elevated levels.
-
-
Stress and lifestyle factors
-
Physical and emotional stress, as well as poor sleep, can transiently raise prolactin levels.
-
Additionally, abnormal lipid profiles and metabolic changes are not uncommon in men with high prolactin, especially when testosterone is suppressed. To evaluate cardiovascular health as part of a complete assessment, consider using the Cholesterol Blood Test which measures your lipid levels and supports better cardiovascular monitoring.
Symptoms of High Prolactin in Men
Symptoms of hyperprolactinemia in men typically stem from reduced testosterone production and pituitary gland dysfunction. These may include:
-
Sexual and reproductive issues:
-
Decreased libido
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Infertility
-
Reduced sperm count
-
-
Physical changes:
-
Breast enlargement (gynecomastia)
-
Breast tenderness
-
Muscle weakness
-
Weight gain
-
-
Neurological symptoms:
-
Headaches
-
Visual disturbances (from pituitary mass effect)
-
-
General symptoms:
-
Fatigue
-
Mood changes
-
Decreased bone density
-
The hormonal disruption can also lead to a cascade of related imbalances, particularly in the androgen pathway. For men experiencing reduced sex drive and fatigue, it is advisable to measure key markers with the Free Testosterone Blood Test. This helps assess bioavailable testosterone, which is often reduced in hyperprolactinemia.
Prolactin and Mental Health
Elevated prolactin is increasingly being studied for its effects on mental health. Prolactin interacts with various neurotransmitters and receptors in the brain, influencing mood, behaviour, and emotional well-being. Men with hyperprolactinemia may experience:
-
Depression
-
Anxiety
-
Low motivation or apathy
-
Irritability
Antipsychotic medications that raise prolactin levels often exacerbate these symptoms, creating a feedback loop of psychological and hormonal imbalance. Lowering prolactin levels in men has been associated with improvements in mood and cognitive clarity.
Beyond mood regulation, prolactin may also affect adrenal-related hormones that influence stress resilience. In men, adrenal health intersects with testosterone metabolism and energy levels. If adrenal fatigue is suspected, a DHEA Sulphate Blood Test can provide additional insight into adrenal function and chronic stress patterns.
Hormone Testing and Monitoring
Men experiencing symptoms of hormonal imbalance should consider comprehensive hormone testing. In addition to prolactin, assessing other hormones such as testosterone, LH, FSH, and thyroid hormones provides a complete picture.
Hyperprolactinemia can coexist with or even mask liver-related dysfunctions, which complicate hormonal balance further. A test such as the Bilirubin Blood Test may be useful if there’s any suspicion of hepatic involvement, particularly in patients with fatigue and unexplained hormone irregularities.
Whether you're addressing sexual health, fatigue, or general wellbeing, choosing the right diagnostics is essential. To explore a wide array of professional blood tests for different aspects of health and wellness, browse the All Health Tests Collection on Welzo, where options are grouped for convenience.
As part of a post-pandemic health screening or to rule out long-term systemic impacts that may interact with hormone levels, it's also worth checking out the COVID-19 Collection which offers tests designed to assess immunity and potential residual symptoms affecting overall wellbeing.
Conclusion
High prolactin levels in men, although less commonly discussed than in women, can have significant health consequences. From reproductive issues and mood disturbances to bone loss and neurological symptoms, hyperprolactinemia is a condition that requires timely recognition and appropriate intervention. The pituitary gland plays a central role in maintaining hormonal equilibrium, and any disruption—such as through a tumour, medication, or systemic illness—can lead to excess prolactin production.
Understanding the root causes, recognising symptoms early, and opting for comprehensive hormonal evaluation are vital steps in managing this condition effectively. Treatment options are generally successful and include both pharmacological and lifestyle-based approaches. Whether the goal is to restore fertility, improve sexual function, or simply achieve hormonal balance, addressing high prolactin levels can lead to marked improvements in quality of life.
Men are encouraged to monitor their hormonal health proactively, especially if they experience symptoms like low libido, fatigue, or unexplained weight changes. With accessible testing services such as those offered by Welzo Home Blood Tests, identifying and managing hormonal issues has never been easier. A proactive approach supported by medical guidance can empower men to take control of their reproductive and general health.































 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews