
 Instagram
Instagram
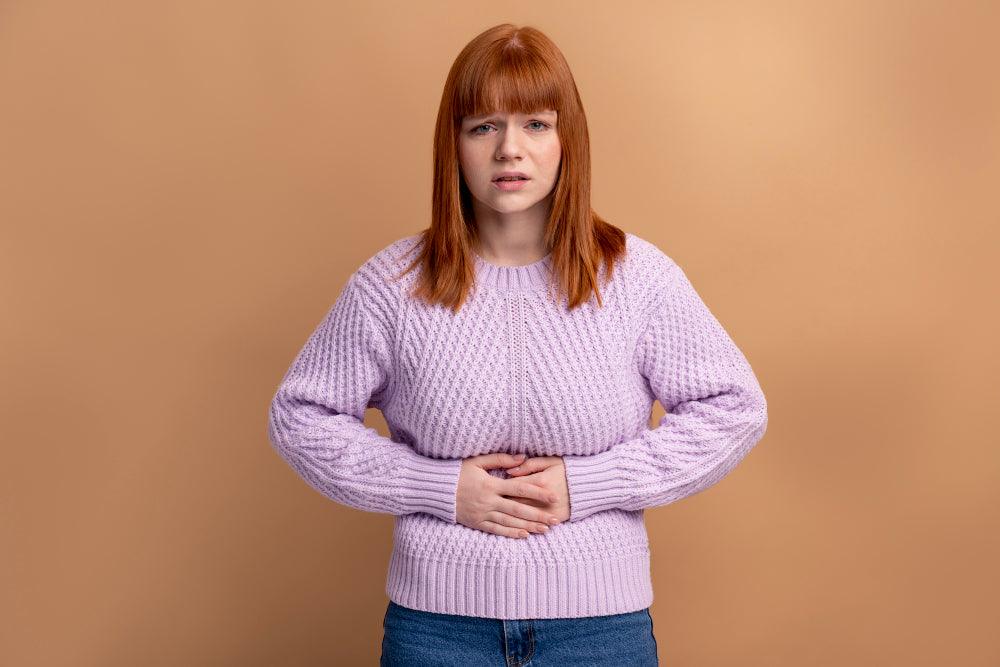
What is Bulimia Bloat?


Related products
Introduction
Bulimia nervosa, a complex psychological and physical eating disorder, is characterised by a cycle of binge eating followed by purging. It affects a multitude of individuals across various demographics and has far-reaching health implications. A less frequently discussed but significant aspect of this disorder is 'bulimia bloat', a term that encapsulates the gastrointestinal discomfort and swelling often experienced by individuals with bulimia. This phenomenon not only adds to the physical discomfort but also perpetuates the cycle of bulimia due to the distress and body image dissatisfaction it causes.
Dr. Emily Clarkson, a gastroenterologist specialising in eating disorders, explains, "Bulimia bloat is primarily the result of gastrointestinal disturbances caused by recurrent bingeing and purging behaviours. It is a condition that not only affects physical health but also impacts psychological well-being." The significance of understanding bulimia bloat lies not just in addressing the physical discomfort but also in comprehending its role in the continuation and severity of bulimia.
Understanding Bulimia
Bulimia nervosa is defined by the National Eating Disorders Association as an eating disorder marked by a cycle of binge eating and compensatory behaviours such as self-induced vomiting. The characteristics of bulimia include an excessive preoccupation with body image and weight, leading to severe eating patterns and an unhealthy relationship with food.
The psychological symptoms encompass feelings of shame, guilt, and lack of control during binge eating episodes, often followed by extreme measures to avoid weight gain. Physically, individuals may experience symptoms like sore throat, swollen salivary glands, and dental erosion, primarily due to the acidic nature of vomit.
Misconceptions about bulimia are widespread, including the false belief that it only affects young women or is merely a lifestyle choice. According to Dr. John Richards, a psychiatrist specialising in eating disorders, "Bulimia nervosa can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. It's a serious mental health condition that requires appropriate intervention and support."
What is Bulimia Bloat?
Bulimia bloat refers to the bloating and abdominal discomfort often experienced by individuals with bulimia nervosa. This condition is attributed to the physiological impact of irregular eating patterns and purging behaviours on the digestive system. Dr. Clarkson states, "The recurrent cycle of bingeing and purging in bulimia can lead to disturbances in the natural rhythm of digestion, resulting in gas, bloating, and discomfort."
This bloating differs from typical digestive bloating in its causes and persistence. While ordinary bloating might occur due to dietary factors or temporary digestive issues, bulimia bloat is directly linked to the behaviours associated with bulimia, such as purging, which can disrupt the balance of stomach acids and gut flora. Additionally, the psychological stress associated with bulimia can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms.
Statistics show that gastrointestinal complaints, including bulimia bloat, are common among individuals with bulimia. A study published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders revealed that over 70% of individuals with bulimia nervosa report gastrointestinal issues, including bloating. This underlines the importance of addressing not only the psychological aspects of bulimia but also its physical manifestations like bulimia bloat. Understanding and treating this aspect of bulimia is crucial for holistic management and recovery.
Causes of Bulimia Bloat
Bulimia bloat arises from several interconnected factors primarily linked to the behaviours characteristic of bulimia nervosa. The act of purging, often through self-induced vomiting, has a significant impact on the digestive system. Dr. Emily Clarkson notes, "Purging disrupts the natural function of the gastrointestinal tract, leading to issues like delayed gastric emptying, which can contribute to bloating." This disruption hinders the normal digestion and movement of food, causing bloating and discomfort.
Binge eating episodes further exacerbate these issues. The sudden intake of large amounts of food stretches the stomach and intestines, contributing to bloating and pain. "The gastrointestinal tract is overwhelmed during binge eating, which results in acute gastric dilation and contributes to chronic bloating," explains Dr. Clarkson.
Additionally, dehydration and electrolyte imbalance, often side effects of purging, play a role in bulimia bloat. These conditions affect the body's ability to regulate fluids, leading to disturbances in the digestive system. Electrolyte imbalances, particularly a deficiency in potassium, can disrupt muscle function in the gastrointestinal tract, further contributing to bloating and discomfort.
Health Implications
The health implications of bulimia bloat are both immediate and long-term. In the short term, individuals may experience significant abdominal discomfort, pain, and distension. These symptoms can lead to further distress and may perpetuate the cycle of bulimia as individuals seek relief through continued purging.
Long-term, the chronic irritation and stress on the digestive system can lead to more serious gastrointestinal issues, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). "Repeated purging can cause lasting damage to the gastrointestinal tract, increasing the risk of chronic disorders," states Dr. Clarkson.
The psychological effects of bulimia bloat are equally significant. The distress and self-consciousness caused by bloating can exacerbate body image issues and feelings of shame, potentially reinforcing the cycle of bulimia. The interplay between physical discomfort and psychological distress is a critical aspect of the disorder that must be addressed in treatment.
Management and Treatment
Effective management of bulimia bloat involves a combination of dietary changes, medical treatment, and psychological therapy. Dietary strategies focus on regularising eating patterns and including foods that are less likely to cause bloating. "Incorporating a balanced diet with adequate fibre and hydration can help alleviate symptoms of bulimia bloat," suggests Dr. Clarkson.
Medical treatments may include medications to regulate digestion and reduce bloating. Prokinetic agents, which improve gastrointestinal motility, can be beneficial in managing delayed gastric emptying. Treatment of any underlying electrolyte imbalances is also crucial to restore normal digestive function.
However, the cornerstone of managing bulimia bloat is addressing the underlying psychological issues. Cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) is widely recognised as an effective treatment for bulimia nervosa. It helps individuals understand and change their thought patterns and behaviours related to their eating disorder. "CBT can be instrumental in breaking the cycle of bingeing and purging, thereby alleviating the physical symptoms of bulimia bloat," concludes Dr. Clarkson. Comprehensive treatment that integrates dietary management, medical intervention, and psychological therapy is essential for effective management and long-term recovery from bulimia and its associated symptoms like bulimia bloat.
Prevention and Awareness
Preventing bulimia and its associated symptoms like bulimia bloat involves a multifaceted approach, focusing on early intervention, education, and awareness. Promoting healthy eating habits and a balanced approach to food from an early age can be instrumental in reducing the risk of developing eating disorders. Encouraging a positive body image and self-esteem, irrespective of body shape or size, is also crucial.
Education plays a pivotal role in reducing the stigma associated with bulimia. Dr. Emily Clarkson emphasises, "Educational programs in schools, communities, and through media can help dispel myths about eating disorders and encourage those affected to seek help." Awareness campaigns should also focus on the signs and symptoms of bulimia, including lesser-known aspects like bulimia bloat, so that early intervention can be sought.
Resources for help and support are vital. This includes access to mental health professionals, nutritionists, and support groups. Websites, helplines, and community centres can provide valuable information and support to those struggling with bulimia.
Personal Stories and Case Studies
Personal narratives and case studies offer invaluable insights into the realities of living with bulimia bloat. For instance, a case study published in the International Journal of Eating Disorders detailed the experience of Anna, a 25-year-old who struggled with bulimia for several years. Her story highlighted not only the physical discomfort of bloating but also the emotional distress and shame associated with it. Such accounts can help others feel less isolated and more understood in their experiences.
Medical professionals and therapists also share insights from their clinical practice. Dr. John Richards, a psychiatrist, notes, "Every individual's experience with bulimia is unique, but common threads include the struggle with body image and the physical discomfort of symptoms like bloating. Understanding these experiences is key to effective treatment."
Conclusion
Bulimia nervosa is a complex eating disorder with significant psychological and physical ramifications, including bulimia bloat. This condition, characterised by abdominal discomfort and swelling, not only affects physical health but also exacerbates the psychological distress associated with bulimia.
It is imperative for individuals experiencing symptoms of bulimia or bulimia bloat to seek professional help. The combination of medical treatment, dietary management, and psychological therapy offers the best approach to managing and overcoming bulimia.
The importance of understanding and addressing bulimia bloat cannot be overstated. It is a condition that sheds light on the intricate interplay between physical and psychological health in eating disorders. As Dr. Clarkson aptly puts it, "Treating bulimia bloat is not just about alleviating physical symptoms; it's about breaking a cycle of psychological distress and physical discomfort. It's a step towards holistic healing and recovery." Therefore, continued efforts in awareness, education, and comprehensive treatment are crucial in the battle against bulimia and its associated symptoms.














 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews