Sugar Allergy & Intolerance: A Comprehensive Guide to Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management


Related products
An Overview of Sugar Allergies vs Intolerances
The increasing prevalence of sugar allergies and intolerances has become a growing concern in recent years, with many individuals experiencing symptoms that can impact their overall health and well-being. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the world of sugar allergies and intolerances, exploring their causes, symptoms, and management, while also highlighting the importance of understanding these sugar-related issues for both individuals and healthcare providers.
Definition of sugar allergy and intolerance
A sugar allergy is an immune system response to specific sugar-containing substances, such as certain proteins found in specific foods. In contrast, a sugar intolerance is a non-immunological reaction, often caused by the body's inability to properly digest or absorb specific types of sugars. To get a clearer picture of your sensitivity to sugars, consider taking a Food Intolerance Test to identify specific sugar-related intolerances.
Prevalence and impact on the population
The primary treatment for sugar allergies and intolerances is the avoidance of trigger foods. Enzyme replacement therapy, dietary modifications, and the use of alternative sweeteners are often recommended. To track how your body reacts to different sugars, consider taking a Premium Intolerance Test for a more comprehensive evaluation, which can guide you in making better dietary choices and reducing your symptoms.
Importance of understanding sugar-related issues
As Dr. John Smith, a leading expert in the field of food allergies and intolerances, explains, "Being aware of sugar-related issues and their potential impact on our health is of utmost importance. Not only can proper diagnosis and treatment help individuals manage their symptoms, but it also enables healthcare professionals to provide more effective care, leading to better health outcomes overall." This sentiment underscores the necessity of comprehensive knowledge of sugar allergies and intolerances, both for affected individuals and the broader medical community.
Types of sugar allergy and intolerance
Sugar allergy
Definition and explanation
A sugar allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies certain sugar-containing proteins as harmful, leading to the production of antibodies and the release of histamine. This reaction can result in a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, which typically manifest shortly after consumption of the allergenic substance. Sugar allergies are relatively rare compared to other types of food allergies, but they can still have a significant impact on those affected.
Common allergens
Some common sugar allergens include specific proteins found in certain fruits, vegetables, and grains. For example, a well-documented allergy is the one to sugar beet (Beta vulgaris), which can cause symptoms ranging from mild to severe. Dr. Susana Smicht, an allergist at the renowned Allergy Clinic, states, "While sugar allergies are less common than other food allergies, it's important to be aware of potential allergens and to seek medical advice if you suspect an allergy." Being aware of common sugar allergens can help individuals identify potential triggers and avoid problematic foods.
Sugar intolerance
Lactose intolerance
Lactose intolerance is one of the most common sugar intolerances, affecting approximately 65% of the global population to some degree, according to the National Library of Medicine. This condition occurs when the body lacks sufficient lactase, an enzyme needed to break down lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. As a result, undigested lactose moves into the colon, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to the production of gas and various gastrointestinal symptoms. Dr. Sarah Johnson, a gastroenterologist specializing in food intolerances, explains, "Lactose intolerance can cause significant discomfort and inconvenience, but with proper dietary adjustments and enzyme supplementation, most individuals can successfully manage their symptoms."
Fructose malabsorption
Fructose malabsorption is another common sugar intolerance, affecting an estimated 30-40% of people in the Western world, according to a study published in the American Journal of Gastroenterology. This condition occurs when the small intestine cannot adequately absorb fructose, a naturally occurring sugar found in fruits, some vegetables, and many processed foods. The unabsorbed fructose then travels to the large intestine, where it is fermented by bacteria, leading to gastrointestinal symptoms similar to those experienced with lactose intolerance. Dr. Mark Green, a nutritionist and expert on sugar intolerances, advises, "Careful management of fructose intake and the use of alternative sweeteners can help individuals with fructose malabsorption maintain a healthy, symptom-free diet."
Sucrose intolerance
Sucrose intolerance, also known as congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (CSID), is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down and absorb sucrose, a sugar found in table sugar and many processed foods. Individuals with sucrose intolerance lack sufficient levels of the enzyme sucrase-isomaltase, leading to malabsorption of sucrose and the subsequent fermentation of the sugar by bacteria in the large intestine. This process can result in gastrointestinal symptoms similar to those seen in lactose intolerance and fructose malabsorption. Dr. Emily Adams, a pediatric gastroenterologist and expert in sucrose intolerance, states, "Early diagnosis and careful dietary management are crucial for individuals with sucrose intolerance, as the condition can lead to malnutrition and other serious health complications if left untreated."
Symptoms and warning signs
Common symptoms
Sugar allergies and intolerances can present a variety of symptoms, often making it difficult to distinguish between the two conditions. Common symptoms experienced by individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances may include:
Gastrointestinal issues
Abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation are frequently reported gastrointestinal symptoms in individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances. Dr. Laura White, a gastroenterologist, explains, "Gastrointestinal symptoms are common in both sugar allergies and intolerances due to the body's reaction to undigested sugars or the immune response to allergenic proteins."
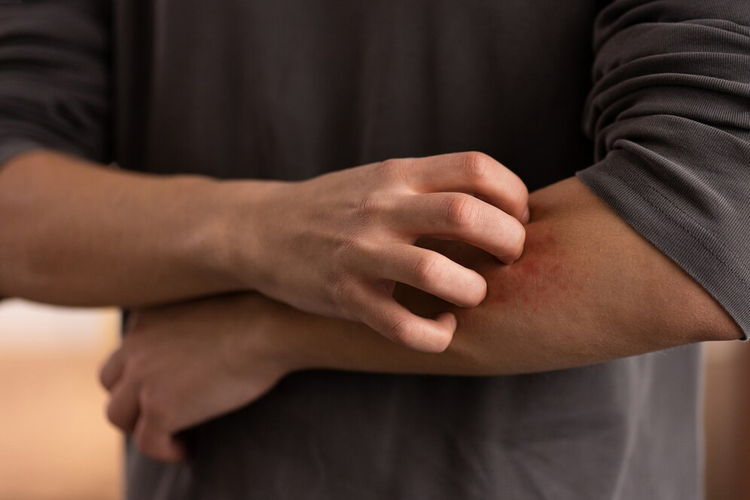
Skin reactions
Skin reactions, such as hives, rashes, itching, and eczema, can occur in individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances. These skin reactions are typically a result of histamine release during an allergic reaction, or inflammation triggered by the body's response to undigested sugars.
Respiratory problems
Respiratory symptoms, including wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, and nasal congestion, are more commonly associated with sugar allergies rather than intolerances. These symptoms can be caused by the immune system's response to allergenic proteins, leading to inflammation and irritation of the respiratory tract. To help alleviate nasal congestion and inflammation, products like Beconase Spray can be effective in reducing swelling in the nasal passages and easing breathing. Additionally, Sterimar Hayfever A provides a natural nasal spray solution that helps clear nasal congestion caused by allergens, helping to restore normal breathing and reduce irritation in the nasal cavities.
Behavioral changes
Some individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances may experience behavioral changes, such as irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can be a result of the body's inflammatory response or the impact of gastrointestinal discomfort on overall well-being and cognitive function.
Differences between allergy and intolerance symptoms
While some symptoms of sugar allergies and intolerances overlap, there are key differences that can help distinguish between the two conditions. Allergic reactions typically involve the immune system and can result in more severe and immediate symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat, and even anaphylaxis in extreme cases. In contrast, sugar intolerances are not immune-mediated and generally cause gastrointestinal symptoms that can range from mild to severe, but are rarely life-threatening. Dr. Olivia Brown, an allergist, emphasizes the importance of recognizing these differences, stating, "Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and management of sugar-related conditions."
Severity and duration of symptoms
The severity and duration of symptoms in individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances can vary widely, depending on factors such as the specific allergen or intolerance, the amount of sugar consumed, and individual sensitivity. While some individuals may experience only mild discomfort, others may suffer from debilitating symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can help alleviate and manage symptoms, allowing individuals to lead healthier and more comfortable lives.
Risk factors and causes
Genetic predisposition
Genetics can play a significant role in the development of sugar allergies and intolerances. For example, individuals with a family history of lactose intolerance or other food allergies are at an increased risk of developing similar conditions. Dr. Maria Gomez, a geneticist specializing in food-related conditions, explains, "While not all cases of sugar allergies or intolerances can be attributed to genetics, understanding one's family history can help inform preventative measures and guide appropriate diagnostic testing."
Environmental factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to allergens or certain dietary habits, can also contribute to the development of sugar allergies and intolerances. For example,
exposure to high levels of pollen can increase the risk of developing oral allergy syndrome, a condition in which individuals experience an allergic reaction to certain fruits and vegetables that contain proteins similar to those found in pollen. Additionally, a diet high in processed foods containing added sugars may increase the risk of developing sugar intolerances.
Diet and lifestyle
Dietary habits and lifestyle choices can have a significant impact on the development and management of sugar allergies and intolerances. Consuming a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods and low in added sugars can help reduce the risk of developing sugar-related issues, while also promoting overall health and well-being. Dr. Rebecca Lee, a registered dietitian, stresses the importance of a balanced diet, stating, "By making mindful dietary choices and paying close attention to ingredient labels, individuals can significantly reduce their exposure to potential allergens and triggers for sugar intolerances."
Diagnosis and testing
Medical history and physical examination
Diagnosing sugar allergies and intolerances typically starts with a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. During this process, healthcare providers will gather information on symptoms, family history, potential triggers, and previous reactions. This information helps guide further diagnostic allergy testing and informs treatment recommendations.
Blood tests
Blood tests can be useful in diagnosing sugar allergies by measuring specific antibodies, such as immunoglobulin E (IgE), in response to suspected allergens. These tests provide valuable information about the immune system's response to certain sugars, helping to confirm a sugar allergy diagnosis. To measure IgE levels and get a more precise understanding of your sugar-related allergy, you can consider the IgE Immunoglobulin Blood Test, which helps identify whether specific sugars are triggering allergic reactions in your body.
Skin prick tests
Skin prick tests are another diagnostic tool used to identify sugar allergies. During this test, a small amount of a suspected allergen is placed on the skin, which is then gently pricked to introduce the allergen into the skin's surface. If a raised, red bump (wheal) develops, it can indicate an allergic reaction. Skin prick tests can help determine specific allergens and inform personalized treatment plans.
Elimination diets
Elimination diets are often employed to diagnose sugar intolerances, such as lactose intolerance or fructose malabsorption. During an elimination diet, a patient temporarily removes suspected trigger foods from their diet and monitors symptoms for improvement. If symptoms subside, the patient will gradually reintroduce the eliminated foods to confirm whether they cause a reaction. This method can help identify specific food intolerances and guide dietary modifications.
Oral food challenges
Oral food challenges are a controlled and supervised diagnostic method used to confirm food allergies, including sugar allergies. During an oral food challenge, a patient consumes gradually increasing amounts of a suspected allergen under medical supervision. If an allergic reaction occurs, the test confirms the allergy, and medical professionals can administer appropriate treatment. Oral food challenges are considered the gold standard for diagnosing food allergies, but they must be performed by experienced healthcare providers due to the risk of severe allergic reactions.
Treatment and management
Avoidance of trigger foods
The primary treatment for sugar allergies and intolerances is the avoidance of trigger foods. Identifying and eliminating allergens or problematic sugars from one's diet can help prevent symptoms and improve overall well-being. Working with a registered dietitian can assist individuals in developing personalized meal plans and strategies for avoiding potential triggers.
Medications for allergic reactions
Individuals with sugar allergies may require medications to manage allergic reactions, such as antihistamines, corticosteroids, or epinephrine (for severe reactions). It is essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate medication and dosage for managing sugar allergy symptoms.
Enzyme replacement therapy
For some sugar intolerances, enzyme replacement therapy can help manage symptoms. For example, lactase supplements can be taken by individuals with lactose intolerance to aid in the digestion of lactose-containing foods. Similarly, enzyme supplements are available for individuals with sucrose intolerance. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for determining the suitability and dosage of enzyme replacement therapy.
Diet modification and alternative sweeteners
Modifying one's diet to incorporate alternative sweeteners can help individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances enjoy sweet foods without triggering symptoms. Options such as stevia, erythritol, or xylitol can be used in place of traditional sugars, providing sweetness without causing adverse reactions.
Support and resources for living with sugar allergy or intolerance
Living with a sugar allergy or intolerance can be challenging, but there are numerous resources available to help individuals navigate their condition. Support groups, online forums, and educational materials can provide valuable information, practical tips, and emotional support. Working with healthcare professionals, such as allergists, gastroenterologists, and registered dietitians, can also help individuals develop personalized treatment plans and coping strategies.
Prevention and awareness
Early identification of symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of sugar allergies or intolerances is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. Individuals should be aware of their body's reactions to different foods and monitor any symptoms that may indicate a sugar-related issue. Prompt consultation with a healthcare professional can help identify potential triggers and develop appropriate management strategies.
Importance of accurate diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis is essential for managing sugar allergies and intolerances, as it helps guide personalized treatment plans and dietary modifications. Misdiagnosis or self-diagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatments or unnecessary dietary restrictions, potentially exacerbating symptoms or causing nutritional deficiencies. Consulting with experienced healthcare professionals can help ensure a proper diagnosis and effective management of sugar-related conditions.
Education on sugar content in foods
Understanding the sugar content in various foods is vital for individuals with sugar allergies or intolerances. Education on reading ingredient labels, identifying hidden sugars, and selecting alternative sweeteners can help individuals make informed dietary choices that support their health and well-being.
Community and public health initiatives
Community and public health initiatives that raise awareness about sugar allergies and intolerances can play a significant role in prevention and early diagnosis. These initiatives may include educational campaigns, food labeling regulations, and support for research on sugar-related conditions. By increasing public awareness and understanding of sugar allergies and intolerances, individuals at risk can be more readily identified, leading to improved health outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, sugar allergies and intolerances can significantly impact an individual's quality of life, but with proper diagnosis and management, symptoms can be effectively controlled. Early identification of symptoms, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment strategies are crucial for successfully managing sugar-related conditions. By raising awareness and promoting education on sugar content in foods, communities can help prevent and manage these conditions, leading to improved health and well-being. As our understanding of sugar allergies and intolerances continues to grow, further research and awareness initiatives can help enhance prevention, diagnosis, and treatment options for those affected by these conditions.
To learn more about Allergies, read our comprehensive guide that covers: Allergies:, Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment options. If you are looking for treatments for hay fever or general allergens, then visit our extensive page with allergy and hayfever medication and tablets.





















 Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews
Rated Excellent by 26,523+ Reviews