What are the signs and symptoms of vitamin C deficiency?


Vitamin C, also called ascorbic acid, is the key nutritional component in our human body. Vitamin C can not be stored in human bodies and therefore is a necessary component of all our food products. It is recommended that people need 40 mg of vitamin C every day. Taking vitamin supplements can help with the absorption of vitamin C.
Vitamin C is a vitamin that must be consumed regularly to avoid malnutrition. Even though this deficiency is uncommon in developed countries due to the abundance of fresh produce and the inclusion of vitamin C in specific diets, it is still a prevailing deficiency in today's society.
Poor nourishment, alcoholism, bulimia, severe mental disorders, and smoking are the most prevalent risk factors for vitamin C deficiency. While severe deficiency symptoms might take months to manifest, there are some subtle signals that you can look for. The most usual signs of a vitamin C deficiency are outlined below.
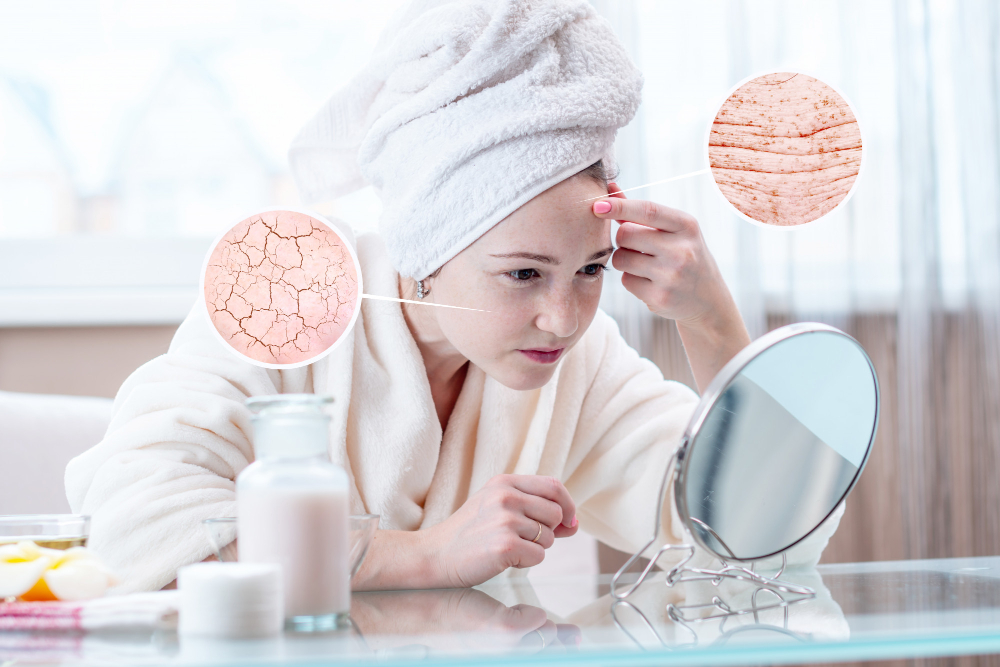

Vitamin C is essential for creating collagen in the body, a protein found in connective tissues such as skin, joints, hair, blood vessels, and bones. Keratosis pilaris is a skin disorder that can develop when vitamin C levels are insufficient. An accumulation of keratin protein within the pores causes rough "chicken skin" on the backs of the upper arms, thighs, and buttocks.
Moreover, deficiency causes problems such as keratosis pilaris, which usually emerges after three to five months of insufficient intake and disappears with supplementation. However, because keratosis pilaris can be caused by various factors, its existence alone is not enough to rule out a deficiency.
Hair follicles contain several tiny blood arteries that feed the area with blood and nutrients on the skin's surface. These microscopic blood vessels become ruptured and weak when the body lacks vitamin C, causing small, vivid red patches to form around hair follicles.
Perifollicular bleeding is a well-recognised symptom of severe vitamin C insufficiency. Hence, taking vitamin C tablets for two weeks usually improves this condition.
When blood vessels beneath the skin break, blood leaks into the surrounding areas, inducing bruising. Because insufficient collagen formation promotes weak blood vessels, easy bruising is a common indication of vitamin C insufficiency.
Bruises caused by this deficiency might cover vast sections of the body or look like little purple patches beneath the skin. One of the first apparent indicators of a deficit is easy bruising, which should prompt additional inquiry into vitamin C levels.
A vitamin C deficiency can weaken joints since they have much collagen-rich connective tissue. Numerous cases of joint discomfort linked to vitamin C shortage have been described, which is often severe enough to induce limping or cause trouble walking.
In persons lacking in vitamin C, bleeding within the joints can produce swelling and increased pain. However, both of these symptoms are treatable with supplements and usually go away within a week.
Gums that are red, swollen, and bleeding indicate a vitamin C shortage. Gum tissue becomes weaker and inflammatory without enough vitamin C, and blood vessels bleed more easily. Furthermore, during the mature stage of vitamin C shortage, gums may appear purple and rotten. Teeth can start falling out if the gums and the dentin, the calcified inner layer of the tooth, is weak.
According to studies, Vitamin C develops inside several types of immune cells to aid in the fight against infection and the destruction of disease-causing bacteria. Furthermore, this deficiency is linked to weakened immunity and an increased risk of infections like pneumonia.
Lack of vitamin C and iron frequently coexist. Paleness, weariness, difficulty breathing during exertion, dry skin and hair, headache, and spoon-shaped fingernails are all symptoms of iron deficiency (anaemia). This can be caused by a reduction in iron absorption from plant-based diets, as well as a disruption in iron metabolism.
Excessive bleeding, which can lead to anaemia, is also a risk of vitamin C deficiency. So, if you have had an iron deficiency for a long time with no apparent explanation, you should have your vitamin C levels checked.
Vitamin C may effectively safeguard you against obesity by controlling fat cell release, lowering stress hormones, and minimising inflammation. However, studies have associated low vitamin C intake with extra body fat, although it is unclear whether this is a cause-and-effect relationship.
Even in people with a healthy weight, low blood levels of vitamin C have been related to a considerable amount of belly fat. Excess body fat is not enough to suggest a vitamin C deficiency, but it is worth looking into once all other potential causes have been ruled out.

Vitamin C has a recommended daily intake (RDI) of 90 mg for men and 75 mg for women. Tobacco lowers vitamin C absorption and raises the body's nutrient consumption; therefore, smokers should consume an extra 35 mg of vitamin C per day.
Vitamin C can be found in many foods, including the following:
Guava
Cherry
Kiwi
Lemon
Strawberry
Orange
Sweet red pepper
Broccoli
Parsley
Papaya
When exposed to heat, vitamin C is rapidly degraded. Therefore, raw fruits and vegetables are a better source to eat than cooked ones. Because the body does not store massive amounts of vitamin C, eating fresh fruits and vegetables every day is recommended.
Vitamin C supplements are not harmful, but taking more than 2,000 mg per day might cause abdominal cramps, nausea, and diarrhoea. Overdosing on vitamin C could also increase the risk of oxalate kidney stones in men. Furthermore, doses greater than 250 mg per day may interfere with tests that detect blood in the stool or stomach and should be stopped two weeks before the test.
Only a tiny amount of vitamin C is required to avoid scurvy. It is enough to take 10 milligrams each day, about the same as one tablespoon of fresh bell pepper or the juice of half a lemon.
Scurvy describes vitamin C deficiencies in the human population. The disease can cause nausea, low moods, joint pains or bleeding gums. Usually, this happens if a person has been unable to consume enough Vitamin C. Fortunately, scurvy can usually be treated quickly after being diagnosed. Your doctor may advise adding vitamin C foods or dietary supplements until your health improves. When an underlying problem appears to be responsible for your symptoms, it may be necessary for medical treatment.
Because humans cannot produce or retain vitamin C in substantial quantities, it must be ingested on a regular basis to avoid deficiency, preferably through fresh fruits and vegetables. Supplements are also available for those who prefer that option.
There are numerous signs and symptoms of deficiency, which are caused by abnormalities in collagen formation or a lack of antioxidants in the diet. Fatigue, easy bruising, gum issues, joint pain, bleeding, and rough, wrinkled skin are some of the first indicators of deficiency.
Other warning indicators include inflammation, anaemia, and unexpected weight gain. Fortunately, once vitamin C levels are restored, deficient symptoms usually disappear.
To find out more about other deficiency tests, please click here.








Plus get the inside scoop on our latest content and updates in our monthly newsletter.